Volatile Organic Compounds
Ask the State and Holcim To Finally Give DFW “the Holy Grail” of Cement Pollution Control Technology
 Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
That's right. Holcim is asking the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) to OK a permit that will result in a "major modification" of its Midlothian plant and could produce significant amounts of new pollution before it even decides what the major modification is going to be. Anywhere else in the country this might be a bit odd, but hey, it's Texas, where Rick Perry's TCEQ has a rubber stamp standing by for anything industry requests.
Holcim's permit request is being prompted by a problem complying with new federal regulations limiting a kind of pollution called Total Hydrocarbons, or THCs. These are also sometimes referred to as "Volatile Organic Compounds." Think Benzene, and other kinds of hazardous flammable gases. In its permit application Holcim says it needs to add new controls to reduce THC to levels and come under the new federal standard. Fair enough. The company then says that it's still trying to decide between two different types of controls and will make up its mind after getting the permit and seeing how well its choice works out on one of its two separate giant kilns. That's the bogus part.
But wait, there's more! The two technologies Holcim is considering installing in Midlothian are: 1) A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, or RTO, which is a fancy way of saying setting them on fire and flaring them off, and, 2) A Selective Catalytic Reduction unit, or SCR, which is a tower of treated metal honeycombs that pick up pollution as the plant exhaust passes through them. RTOs are already installed on American cement plants, including TXI's huge Midlothian kiln just a few miles down Highway 67 from Holcim. On the other hand, up to now full-scale commercial SCR units have only been installed on European cement plants and in fact, the Portland Cement Association has lobbied long and hard to keep them out of the US for fear of raising the pollution control bar too high for all of the country's cement plants.
That's because SCR is more expensive to build and maintain than most cement plant control devices. But for the money, you get the Holy Grail of cement plant pollution control technology.
Most of the European cement plants that have SCR units install them to remove another type of pollution from their stacks – Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). If that sounds familiar, it's because NOx is a major smog-forming pollutant, and DFW has so much of it that the region has never been in compliance with the Clean Air Act standard for smog. And you'll never guess which facilities are the single largest sources of NOx pollution in North Texas. Or maybe you will: the Midlothian cement plants. That's why Downwinders at Risk has made it a point to campaign to require all three Midlothian cement plants – Holcim, TXI and Ash Grove – to install SCR….since all the way back in 2001, when the first European units were deemed a success at a German cement plant. SCR can remove 80 to more than 90% of all NOx coming out of a cement kiln. The 6500 tons of NOx a year that the Midlothian cement plants are permitted to release could be reduced to 650 tons with the application of SCR.
Now, as it turns out, SCR units are great not only at capturing large amounts of NOx pollution, but all kinds of other industrial pollution coming out of cement plants as well. Like THCs – up to 70% or so, but also Particulate Matter, Metals, Greenhouse Gases, Carbon Monoxide, and Dioxins. It's what's called a multi-pollutant control device because it does such a good job of eliminating a wide variety of nasty stuff from smoke stacks. This is what makes it the state-of-the-art technology for communities hosting kilns. In contrast, RTOs are single-purpose pollution devices aimed just at hydrocarbon removal and aren't designed to remove other kinds of emissions.
So even though Holcim is considering operating SCR because of its hydrocarbon problem, it would have a massive impact on the plant's air pollution across the board. And if Holcim were to set the precedent, the clock would begin ticking on bringing SCR to the other two Midlothian cement plants as well. It would only be a matter of time.
The public comment period for telling the state whether to accept or reject Holcim's permit application ends this Friday, July 11th at 5 pm. (If you're interested in jumping through the hoops to fill out the online form for official comments, you can go here and use Permit Number 8996)
Downwinders is submitting detailed comments praising Holcim for considering SCR, but urging the TCEQ to reject this permit because it's too vague and doesn't commit the company to any partciular technology, including SCR. We've also been collecting letters form local officials and stare legislators that urge Holcim to definitively choose SCR.
Now we're asking you to help us bombard both the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and Holcim's US headquarters in Dundee Michigan in the next 48 hours with the same message to show public support for the company to do the right thing while rejecting a placeholder permit that doesn't commit it to do that right thing.
We want a permit request from the company that says Holcim will definitely install SCR, becoming the first commercial application of this state-of-the-art technology in America.
Using our "Featured Citizen Action" link, you can send such a message to Austin and Michigan in a matter of seconds right now. All you have to do is click here and then send the e-mails. We guarantee there's no more important or easier thing you can do for clean air in North Texas this week than sending these e-mails to the TCEQ Commisisoners and Holcim Corporate leadership. Please help us get the cement plant pollution control technology DFW deserves. It will only take a matter of seconds for you to help us achieve a goal we've been working toward for 14 years. We can do this. But we need your help. Now. Thanks.
Highlights from Monday: How the State Hides Gas Industry Pollution
 Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
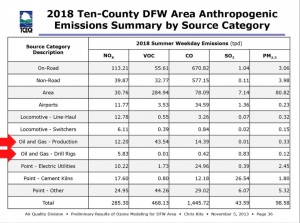
In the first you'll see how the state officially ranks all the "source categories" for human-made, or "Antrhopogenic," smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) pollution in North Texas (all the numbers are Tons Per Day):
Yes the pic is fuzzy, (we can land a person on the Moon but can't seem to get charts to show up with a jpeg format online) but if you squint really hard, you'll notice there are two categories for Oil and Gas pollution numbers among the more traditional "Point Sources," Off-Road, "On-Road", etc – "Oil and Gas Production" and "Oil and Gas – Drill Rigs." Looking at these two categories you might think that adding them together would produce total Oil and Gas pollution numbers. You'd be wrong.
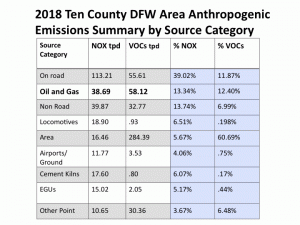
As it turns out, there are other Oil and Gas pollution numbers hidden away in other categories in this chart not labeled "Oil and Gas." For example, in both the "Area" and "Point-Other" categories are the numbers for NOx and VOCs pollution from gas compressors. But wait, you object, aren't gas compressors an integral part of any kind of "Oil and Gas Production?" Yes, yes they are. So why aren't they included in that category instead of being stuffed anonymously in these other categories? Great question. Perhaps it has something to do with the volume of pollution they release. Because when you finally wrestle the numbers from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (the TCEQ didn't voluntarily offer this information), compressor pollution turns out to double the amount of smog-forming NOx released from the Oil and Gas industry in the DFW 10-county "non-attainment area." And NOx pollution is what the TCEQ keeps saying is driving our chronic smog problem. Here's the way Schermbeck presented the same TCEQ "source categories" with the compressor numbers now teased out and added to the ones already identified as Oil and Gas: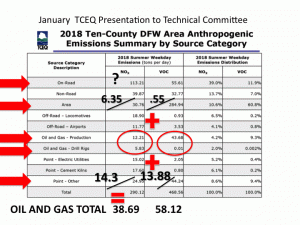
These additions raise the industry's polluter profile significantly. And that's what this next slide is doing. It's totaling all the Oil and Gas pollution and then re-ranking the categories based on these new numbers. Same totals, just different, and more honest, organization of the individual source figures. Instead of Oil and Gas emissions looking relatively small in relation to other sources like cement kilns and power plants and even locomotives, it escalates the Oil and Gas industry into one of the region's foremost industrial air polluters:
And even this much larger number is still underplaying the total amount of air pollution fracking adds to regional air quality because the state hasn't bothered to try to tease-out the "on-road" pollution that all those fracking waste and water trucks adds to the mix. State air modelers shrugged their shoulders and said they couldn't figure out how on earth to do that. Just by "Googling" the subject, Schermbeck found at least two previous studies that did that very thing – a 2005 Denton report and a 2013 Rand Corporation report that even estimated the amount of dust pollution raised by those trucks.
While those truck totals remain a mystery for now, using the TCEQ's own numbers, compressors make up at least 53% of the total NOx pollution released by the Oil and Gas industry in North Texas, and a full quarter of all VOC pollution released. According to Schermbeck, that's why they make such good targets for electrification, an air pollution control measure he was recommending as part of his larger presentation to the regional air planning committee on Monday.
This is just one example of the kind of duplicitous behavior the state of Texas is resorting to in trying to hide the true environmental and public health impact of the Oil and Gas industry. No slight of hand is too petty. Only by diligent digging by citizens is the truth coming out, ton by ton.
Schembeck's entire (unfuzzy) presentation is now online at the North Central Texas Council of Governments website as part of the June 16th agenda. It loses something without his accompanying narration but the jest of it is easily discerned for those who want to plod through it: TCEQ is doing anything but a sincere job of building a serious clean air plan for DFW. But then again, we bet you already knew that.
A Barnett Shale Manifesto…From Austin
 Sometimes it takes a perspective above the grind of trench warfare to give you a better sense of what the entire battlefield looks like. That's what UT Law Professor Rachel Rawlins has done for Barnett Shale activists with the recent publication of her article "Planning for Fracking on the Barnett Shale: Urban Air Pollution, Improving Health Based Regulation, and the Role of Local Governments" in the new Virginia Environmental Law Review.
Sometimes it takes a perspective above the grind of trench warfare to give you a better sense of what the entire battlefield looks like. That's what UT Law Professor Rachel Rawlins has done for Barnett Shale activists with the recent publication of her article "Planning for Fracking on the Barnett Shale: Urban Air Pollution, Improving Health Based Regulation, and the Role of Local Governments" in the new Virginia Environmental Law Review.
Don't let the academic title fool you. This is a call for a radically new approach to how communities in Texas regulate the risks of fracking, and every other type of heavy industry. We put the link up for the piece on our Facebook page on Saturday based on a quick reading of its commentary on the Flower Mound cancer cluster, but it's more, so much more than that. Among other things, it's a comprehensive rebuttal of every claim of safety and well-being ever issued by the industry or state authorities about the health of residents living in the Barnett Shale, of which the Flower Mound case is only one example. Rawlins has produced a one-stop catalog of each major air pollution health controversy in the Barnett since concerns began to grow in the last decade, with an almost 30-page review of why no industry or government-sponsored study of fracking pollution and its health effects is a satisfactory response to those concerns. Want to convince your local officials that fracking isn't as safe as it's touted? Here's the staggering blow-by-blow commentary to do it.
But all of that documentation is presented in service to making the point that current state and federal regulation of fracking is failing to protect public health, both in design and in practice. Professor Rawlins' solution to this problem is not to give the state and federal government more power to regulate the gas industry. No, it's to turn the current regulatory framework upside down and give more power to local governments to do the things that the state and federal government should be doing.
In making this recommendation, she echoes the strategy that's been driving Downwinders since it was founded – that the best way to regulate pollution problems is at the local level where the most harm is being done, and it should be directed by the people being harmed. This is what drove our Green Cement campaign that closed the last obsolete wet cement kiln in Texas. This is what fueled our campaign to close down the trailer park-come-lead smelter in Frisco. And it's what was behind the recent Dallas fights over drilling. In each case, it wasn't Austin or Washington DC that was the instrument of change – it was local governments, pressed by their constituents, flexing their regulatory powers. The same thing is driving activists in Denton who are organizing the ban fracking petition drive and vote.
This strategy avoids battles where industry is strongest – in the halls of the state capitol and in DC, where citizens are outspent millions to one. Instead, it takes the fight to neighborhoods where the harm is being done or proposed, where people have the most to lose, where the heat that can be applied to elected officials is more intense. Citizens will still get outspent, but the money doesn't seem to buy corporations as much influence among those actually breathing the fumes of the drilling site, or smokestack.
Particularly now, with corporate-friendly faux-Tea Party types in control of state government and the House of Representatives in DC, there is little room for grassroots campaigns to make a difference by passing new legislation. Even if by some miracle a few bills did pass, their enforcement would be up to the same state or federal agencies that are currently failing citizens. Local is more direct, and more accountable. Professor Rawlins agrees, and spends most of the rest of her 81-page journal article citing the ways in which local control of fracking in the Barnett Shale is hampered by the out-dated top-down approach to regulation, and what should be done to fix that.
Included in her recommendations are two long-term Downwinders projects: Allowing local governments to close the "off-sets" loophole for the gas industry that exempts them from having to compensate for their smog-forming pollution in already smoggy areas like DFW, and creating California-like local air pollution control districts that could set their own health based exposure standards and pollution control measures without having to go through Austin or DC.
If there's a single major fault in Rawlins's analysis, it's that she believes more local control of pollution risks is itself dependent on action by an unwilling state government. But Downwinders and others have shown that isn't true. Our most significant and far-reaching victories – from the closing of the Midlothian wet kilns to the new Dallas drilling ordinance – have all taken place while Rick Perry was Governor and the state legislature was in the hands of our opponents. We did these things despite Austin, not because we had its permission. Local zoning laws, local permitting rules, local nuisance acts, and other local powers are under-utilized by both residents and their elected officials when it comes to pollution hazards.
The same is true now of Downwinders' off-sets campaign aimed at the gas industry. We think we've found a way to avoid the "preemption" argument that would keep local governments from acting on smog pollution from gas sources by aiming the off-sets at Greenhouse gases – an area of regulation Texas is loathe to enter. By targeting GHG reduction, we also reduce a lot of toxic and smog-forming air pollution. It's a back door way, but it accomplishes the same goal. It's going to be up to Texas activists to sew similar small threads of change through an otherwise hostile political environment.
Even given that flaw, Professor Rawlins' introduction to her article is the most concise summary of the air pollution problems caused by gas mining and production in the Barnett, as well as the most credible call to action for a new way of doing business there. Here it is reprinted in full for your consideration:
In the last decade hydraulic fracturing for natural gas has exploded on the Barnett Shale in Texas. The region is now home to the most intensive hydraulic fracking and gas production activities ever undertaken in densely urbanized areas. Faced with minimal state and federal regulation, Texas cities are on the front line in the effort to figure out how best to balance industry, land use, and environmental concerns. Local governments in Texas, however, do not currently have the regulatory authority, capacity, or the information required to closet he regulatory gap. Using the community experience on the Barnett Shale as a case study, this article focuses on the legal and regulatory framework governing air emissions and proposes changes to the current regulatory structure.
Under both the state and federal programs, the regulation of hazardous air emissions from gas operations is based largely on questions of cost and available technology. There is no comprehensive cumulative risk assessment to consider the potential impact to public health in urban areas. Drilling operations are being conducted in residential areas. Residents living in close proximity to gas operations on the Barnett Shale have voiced serious concerns for their health, which have yet to be comprehensively evaluated. Given the complexityof the science, and the dearth of clear, transparent, and enforceable standards, inadequate studies and limited statistical analysis have been allowed to provide potentially false assurances. The politically expedient bottom line dominates with little attention paid to the quality of the science or the adequacy of the standards.
Determining and applying comprehensive health-based standards for hazardous air pollutants has been largely abandoned at the federal level given uncertainties in the science, difficulties of determining and
measuring “safe” levels of toxic pollutants, and the potential for economic disruption. Neither the state nor the federal government has set enforceable ambient standards for hazardous air pollutants.Identifying cumulative air pollution problems that may occur in urban areas, the State of California has called upon local governments to identify “hot spots” and to consider air quality issues in their planning and zoning actions. In Texas, however, preemption discussions dominate the analysis. Any local government regulation that might provide protection from toxic air emissions otherwise regulated by the State must be justified by some other public purpose.
Texas should consider authorizing and encouraging local level air quality planning for industrial activities, similar to what California has done. Care should be taken to separate these facilities from sensitive receptors and “hot spots” that may already be burdened with excessive hazardous air emissions. Given the difficulty of the task, there is also an important role for the state and federal governments in working to establish ambient standards for hazardous air pollutants, as well as standards for health based assessment and public communication. The uncertainty inherent in any of these standards should be made clear and accessible to local governments so that it may be considered in making appropriate and protective land use decisions. Texas should consider allowing local governments to have the power to establish ambient air quality standards, emissions limitations, monitoring, reporting, and offsets for hazardous air pollutants, following the model applied to conventional air pollutants pursuant to the federal program.
Professor Rawlins' article provides Barnett Shale activists with a new map to guide them toward more effective action. We'd all do well to study it and pick local battles that promise to contribute toward its realization.
New UNT Study-In-Progress Links Gas Pollution to Persistent DFW Smog
 This is why it's important for citizens to have real scientific horsepower.
This is why it's important for citizens to have real scientific horsepower.
DFW has a smog problem. It's not as bad as it used to be, but it's still at unsafe and illegal levels. And for the last four or five years, the air quality progress that should have been made has been stymied. Despite almost all large sources of smog-producing pollution being reduced in volume, our running average for ozone is actually a part per billion higher than it was in 2009.
Many local activists believe this lack of progress is due to the huge volumes of smog-producing air pollution being generated by the thousands of individual natural gas sites throughout the DFW region itself, as well as upwind gas and oil plays. In 2012, a Houston-based think tank released a report showing how a single gas flare or compressor could significantly impact downwind smog levels for up to 5 mile or more. Industry and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality say no, gas sources are not significant contributors to DFW smog. In fact, during this current round of planning, the state has gone out of its way to downplay the impact of gas pollution, including rolling back previous emission inventories and inventing new ways to estimates emissions from large facilities like compressor stations.
Into this debate steps a UNT graduate student offering a simple and eloquent scientific analysis that uses the state's own data on smog to indict the gas industry for its chronic persistence in DFW – especially in the western part of he Metromess, where Barnett Shale production is concentrated.
On Monday night Denton Record-Chronicle reporter Peggy Heinkel-Wolfe gave a summary of a presentation on local air quality she'd sat through that day at UNT:
"Graduate student Mahdi Ahmadi, working with his advisor, Dr. Kuruvilla John, downloaded the ozone air monitoring data from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality back to 1997, a total of more than 6.5 million data points, he said, and has been studying it for the past four months.
Ahmadi wanted to explore a basic question underlying a graphic frequently distributed by the TCEQ that shows gas wells going up in DFW as ozone goes down, which suggests in a not-very-scientific-at-all way, that the increasing number of gas wells is having no effect on the ozone.
Ahmadi adjusted for meteorological conditions to determine how much ozone DFW people are making and where. Such adjustments have been explored by others to understand better the parts of ozone-making we can control, because we can’t control the weather. He used an advanced statistical method on the data, called the Kolmogorov-Zurbenko filter, to separate the effects of atmospheric parameters from human activities.
According to the results, the air monitoring sites surrounded by oil and gas production activities, generally on the west side of DFW, show worse long-term trends in ozone reduction than those located farther from wells on the east side of DFW.
His spatial analysis of the data showed that ozone distribution has been disproportionally changed and appears linked to production activities, perhaps an explanation why residents on the western side of DFW are seeing more locally produced ozone, particularly since 2008.
Ahmadi's results are not definitive, and the paper he's writing is still a work-in-progress. But he's asking the right questions, and challenging the right unproven assumptions. He's at least put forth an hypothesis and is trying to prove or disprove it. He's using science. TCEQ's approach is all faith-based.
Anything that takes the focus off vehicle pollution is anathema to Austin and many local officials who want to pretend that industrial sources of air pollution don't impact the DFW region enough to make a difference so they don't have to regulate them. If there's a guiding principle to TCEQ's approach to this new clean air plan, due in July 2015, it's to avoid any excuse for new regulations while Rick Perry is running for President. The agency isn't interested in doing any kind of science that might challenge that perspective – no matter how persuasive. After all, you're talking about a group that doesn't believe smog is bad for you. TCEQ doesn't want to know the truth. It can't handle the truth. It's got an ideology and it's stickin' to it.
So it's up to young lowly graduate students from state universities armed only with a healthy sense of scientific curiosity to step up and start suggesting that the Emperor's computer model has no clothes, and offering up alternative scenarios to explain why DFW air quality is stuck in neutral. It turns out, just doing straight-up classroom science is enough to threaten the fragile House of Computer Cards with which the state's air plan is being built.
Perhaps equally as ominous for the success fo any new clean air plan is Ahmadi's discovery that ozone levels in DFW have been during the winter time, or "off-ozone-season." There could be a new normal, higher background level of smog affecting public health almost year round.
Mahdi Ahmadi's study is just one of the many that need to be done to construct an honest clean air plan for DFW, but it shows you what a curious mind and some computing power can do. Citizens can't trust the state to do the basic science necessary as long as the current cast of characters is running the show in Austin. EPA won't step in and stop the farce as long as TCEQ can make things work out on paper. If the scientific method is going to get used to build a better DFW clean air plan, it's going to have to be citizens who apply it.
Eagle Ford Expose Reveals Weakness in Gas Air Pollution Inventories and That’s Bad News For DFW
 By now, many of you have seen the massive eight-month act of journalism that the Center for Public Integrity committed in describing the situation in the Eagle Ford shale play in South Texas. It's probably the most comprehensive look at what it's like to live in Texas fracking hell that's been published, and it rightly got distributed far and wide.
By now, many of you have seen the massive eight-month act of journalism that the Center for Public Integrity committed in describing the situation in the Eagle Ford shale play in South Texas. It's probably the most comprehensive look at what it's like to live in Texas fracking hell that's been published, and it rightly got distributed far and wide.
Along with the now-familiar litany of acute human health effects from gas mining – nosebleeds, headaches, skin rashes, respiratory problems – the article also talked about the smog-forming pollution cause by the thousands of small, medium-sized and large gas facilities that invade a shale play. Together they represent a formidable air quality challenge.
Centering on the Buehring family of Karnes City, the piece lists the inventory of gas mining infrastructure surrounding their home. Besides the 50 wells within two and a half miles, they also host,
"….at least nine oil and gas production facilities. Little is known about six of the facilities, because they don't have to file their emissions data with the state. Air permits or the remaining three sites show they house 25 compressor engines, 10 heater treaters, 6 flares, 4 glycol dehydrators and 65 storage tanks for oil, wastewater and condensate. Combined, those sites have the state's permission to release 189 tons of volatile organic compounds, a class of toxic chemicals that includes benzene and formaldehyde, into the air each year. That's about 12 percent more than Valero's Houston Oil Refinery disgorged in 2012.
Those three facilities also are allowed to release 142 tons of nitrogen oxides, 95 tons of carbon monoxide, 19 tons of sulfur dioxide, 8 tons of particulate matter and 0.31 tons of hydrogen sulfide per year. Sometimes the emissions soar high into the sky and are carried by the wind until they drop to the ground miles away. Sometimes they blow straight toward the Buehrings' or their neighbors' homes.
That's 331 tons a year of smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides and Volatile Organic Compounds released from just a small number of square miles in the Eagle Ford. Just two more collections of facilities like that would equal all the smog pollution coming from the TXI cement plan tin Midlothian – North Texas' single largest smog polluter. It's no wonder then that a San Antonio Council of Governments air pollution model found that Eagle Ford smog pollution would make it impossible for the Alamo City to comply with the new 75 parts per million federal ozone standard.
Moreover, that 331 tons a year figure is just what can be discerned by reading Texas' archaic permitting records. The Center's reporters do a real public service in identifying the loopholes and gaps the system encourages that hide the true air pollution numbers,
Texas' regulatory efforts are also hamstrung by a law that allows thousands of oil and gas facilities—including wells, storage tanks and compressor stations—to operate on an honor system, without reporting their emissions to the state.
Operators can take advantage of this privilege—called a permit by rule, or PBR—if their facilities emit no more than 25 tons of VOCs per year and handle natural gas that is low in hydrogen sulfide. Two employees in the TCEQ's air permits office—Anne Inman and John Gott—estimate these PBRs could account for at least half of the hundreds of thousands of air permits the agency has issued for new or modified oil and gas facilities since the 1970s.
Operators with this type of permit aren't required to file paperwork backing up their self-determined status, so the TCEQ has no record of most of the facilities' locations or emissions. A chart generated in 2011 by the office of then-TCEQ executive director Zak Covar says the permits "Cannot be proven to be protective. Unclear requirements for records to demonstrate compliance with rules."
Big operators sometimes get a PBR for each component of a facility. Each might be under the 25-ton-per-year threshold that would require a more rigorous permit, but the facility as a whole could emit more than that.
The TCEQ refers to the practice as the "stacking of multiple authorizations," and the memo from Covar's office said its use "means that protectiveness and compliance with the rules cannot be demonstrated."
But of course that doesn't keep Rick Perry's TCEQ from saying everything is all right. As per usual, officials want to the results of stationary monitors in the region to assure residents that nothing unhealthy is being breathed-in.
"[M]onitoring data provides evidence that overall, shale-play activity does not significantly impact air quality or pose a threat to human health," agency spokeswoman Andrea Morrow wrote in an email."
But in this case, the region, covering a huge area from East Texas to the Rio Grande, has only five such monitors, "all positioned far from the most heavily drilled areas."
Moreover, that's just the holes in the permitting process itself. What about when a facility is a bad actor and has an "emission event' or "upset" where more than the permitted amount of pollution is released for hours or even days at a time?
"The number of emission events associated with oil and gas development doubled between fiscal years 2009 and 2013, from 1,012 to 2,023. The amount of air pollutants released into the Texas air during these events increased 39 percent."
A gas processing plant in McMullen County, in the southwestern portion of the Eagle Ford, reported 166 emission events last year, almost one every other day. From 2007 through 2011, the Tilden plant, owned by Regency Energy Partners of Dallas, discharged 1,348 tons of sulfur dioxide during such episodes. That's more than 30 times the amount it was legally allowed to release during "normal" operations.
Marathon waited three months to report a 2012 incident at its Sugarhorn plant near the Cernys and Buehrings. It released 26,000 pounds of VOCs in 12 hours, 1,000 times more than allowed under its air permit.
But what has this got to do with DFW smog? Everything. Besides the Barnett Shale play entering and enveloping the Metromess from the West, we also have the Eagle Ford and Haynesville shale plays to our South and East – upwind of DFW during our eight-month "ozone season." There are now as many wells in close proximity to DFW up wind as downwind.
Right now, as part of the new anti-smog plan for DFW being drafted by the TCEQ, the state is "re-calculating" oil and gas air pollution emissions and you'll never guess how that's working out – TCEQ is using industry advice to lower their estimates from last time around. At a January 31st meeting of what's left of the local air planning process, the state presented its new study that it's using to revise the considerable amount of air pollution coming from leaks and releases from condensate storage tanks in the Barnett and elsewhere. As of 2012, these releases are estimated by TCEQ to be only 25% of what they were in 2006. See how well that works out? And this number will be plugged into the computer model that then estimates how much of that air pollution turns into smog.
Instead of getting real world numbers for compressor stations, the TCEQ is now using a fomula based on local production and horsepower to estimate emissions, and guess which way this new technique is sending the numbers?
TCEQ is doing everything it can to make sure that the oil and gas air pollution numbers are as low for this new anti-smog plan as they can make them without breaking out laughing. Why? To prevent the call for new controls on these sources, even though everyone knows they're adding to the problem. Oil and gas emissions are the one air pollution category in DFW that's grown in volume since 2006, while others, like the Midlothian cement plants and East Texas coal plants, and even cars, have all gone down. Meanwhile, DFW ozone averages are higher then they were in 2009. Many of us don't think that's a coincidence. But the ideologically-driven TCEQ can't afford to admit the obvious – not while Rick Perry is running for President.
Compare the TCEQ strategy in DFW with the reality described in the Center for Public Integrity's reports from the Eagle Ford Shale and you have two completely different pictures of the amount of air pollution coming from the oil and gas industry. Which do your trust more – the official calculations coming out of Austin, or the secret memos and field reports uncovered by the reporters?
If what's happening in South Texas is also what's happening in the shale plays in and around DFW – and there's no reason to think it isn't – then the volumes the TCEQ is plugging into its anti-smog plan for the Metromess are off by large factors. That in turn could spell doom for the plan, due to be submitted to the EPA by July of 2015 – a little over a year from now.
This is why it's important for citizens to have their own computing power with their own modeling capabilities. It's the only way to call TCEQ's bluff that it's using all the right information to draft its new clean air plan to EPA. Without the technical know how to be able to look over TCEQ's shoulders and reveal its "GIGO"strategy, our lungs are hostages of Rick Perry's political ambitions.
The next North Texas appearance by TCEQ staff to explain how its estimating – or not – the air pollution from oil and gas industry sources as well as every other source – is scheduled for 10 am on Thursday, April 17th at the HQ of the North Central Texas Council of Governments located at 616 Six Flags Drive – right across the street from the Amusement Park. We need citizens to come out and ask pointed questions about the TCEQ effort to keep us from being taken on another ride to nowhere. Anyone can come and ask questions of the presenters – it's an open forum – and indeed it's the ONLY opportunity citizens have to actually quiz the TCEQ about the process. Please mark the date and try to be there. Meetings usually last until 12 noon or so. They think you're not paying attention. These numbers and quotes from the Public Integrity Center piece gives you lots of ammunition to prove otherwise.
Can a Council Whose Majority Voted for the Trinity East Permits Now be Expected to Defend the City’s Denial?
 As you might have heard by now, forlorn natural gas operator Trinity East has sued the City of Dallas for denying the three permits it was seeking to drill along the Trinity River in Northwest Dallas by the Irving border. Claiming breach of contract and even fraud, the company is saying it's owed millions of dollars above and beyond the $19 million it spent on leases for the three sites.
As you might have heard by now, forlorn natural gas operator Trinity East has sued the City of Dallas for denying the three permits it was seeking to drill along the Trinity River in Northwest Dallas by the Irving border. Claiming breach of contract and even fraud, the company is saying it's owed millions of dollars above and beyond the $19 million it spent on leases for the three sites.
Anyone who's seen the filing knows this is a lawsuit with no legs. Yes, Trinity East leased the land, but guarantees about permits being awarded were not part of the deal. Those can't be bought so blatantly. Even Mary Suhm's secret memo un-earthed last February by the Dallas Observer made it clear that her assistance was not a guarantee and "not a legally binding agreement." The leases were one thing. The permits another. Trinity East thought it had the permits in hand when Suhm signed her memo. So did Suhm.
That's why citizens were told in 2012 that Trinity East permits were a "done deal" by sources in City Hall, including Mayor Rawlings, who seems to have known about the Suhm memo before the public did. There was just no way those permits were going to be denied. Suhm and the Mayor were not going to let that happen. That's why they called for the hearing and permit vote two days before Christmas. They thought no one would show and they could wrap it up. So it was a big surprise when the City Plan Commission voted to deny the TE permits. Undeterred, there was suddenly a call for an unprecedented, second "reconsideration vote" by the Plan Commission by the Mayor's representative on the same permits. But Trinity East lost that fight too, by a wider margin, in January of 2013. This time without any public hearing.
When the CPC denial came to the City Council in August of 2013, charter rules demanded it must be overridden by a super majority of 12. The vote to overturn the CPC's denial was 9 to 6, leaving the denial in place, but showing a majority of the current council in favor of granting the permits.
Then the strategy turned to adapting the new drilling ordinance to fit the Trinity East permits. If they couldn't make it through the front door, they could go in the back way. And so City legal staff tried to manipulate the City Plan Commission into carving out exceptions in the new draft ordinance that would allow that. Instead of a 1500-foot setback, they urged 1000 feet with a variance back to 500 feet. That would allow all Trinity East sites. Then they tried to ease the rules on park drilling, and even succeeded to some extent, softening a ban on surface drilling in parks that was part of the old ordinance.
Only Dallas residents working overtime and applying more scrutiny saved the day and got Plan Commission support for a new ordinance that did finally shut the door on all three Trinity East permits. And of course, that's when Trinity East, aided by the entire gas industry, decided to sue.
So you now have the weird situation where the same City Hall that was trying so desperately to win those permits for Trinity East is now being sued by the company for not being conspiratorial enough to subvert the public process. Yesterday, the city issued an statement saying the company's lawsuit lacked merit and, "The city will vigorously defend its right to exercise its regulatory powers to protect public health and safety as well as the environment."
But here's the thing. Since a clear majority of current Dallas City Council members voted for the permits, how much will power is there among this same group to now defend a position they didn't take? And since it was often the Dallas City Attorney's office leading the charge to manipulate the system on Trinity East's behalf, how well do you trust that same crew to "vigorously defend" the outcome they tried so hard to prevent?
Three are some legal principles involving the city's right to control its own zoning decisions which could motivate the city and/or the Texas Municipal League into such a defense. But you have to wonder how much heart they really have for a fight, of which right up until the last vote, they were on the same side as the company now suing them.
To make sure the City doesn't settle with Trinity East, citizens are going to have to persuade the three council members who voted with them for the new ordinance, but against them on the Trinity East permits to change their minds – Jennifer Staubach-Gates, Dwaine Carrawy and Mayor Ralwings.
That won't be easy. Rawlings was making the "I told you so" rounds in the media yesterday. The first sign that they might be serious about defending themselves is whether they'll hire an outside law firm with municipal law experience to represent them. If they put the same people in the City Attorney's office who were working in concert with Trinity to win those permits in charge of this fight, we're doomed. If they hire a competent firm with a reputation for toughness, you'll know they think there might be some points of law worth going to court for.
Longer term, it once again puts a spotlight n the need to elect additional allies of the six council members who've been reliable allies to citizens on this issue. This coming Dallas municipal election cycle in 2015 will see almost half the council seats up for grabs as incumbents are term-limited out. Stay tuned.
Between Now and Friday: Tell Them What They Can Do With Their Smog
 Frustrated that Rick Perry's Texas Commission on Environmental Quality isn't doing enough to end DFW's chronic smog problem, the local "Council Of Governments" has issued a "Request for Information" asking for the public's help in suggesting ways to reduce ozone pollution in North Texas.
Frustrated that Rick Perry's Texas Commission on Environmental Quality isn't doing enough to end DFW's chronic smog problem, the local "Council Of Governments" has issued a "Request for Information" asking for the public's help in suggesting ways to reduce ozone pollution in North Texas.
Please use our Click N' Send E-mail form to make sure they get the message that the public wants:
1) State-of-the-Art pollution controls on huge "point sources" of pollution like the Midlothian cement kilns and East Texas power plants.
2) New pollution control equipment and strategies to reduce the air pollution from the thousands of natural gas facilities mining the Barnett Shale.
3) Inclusion of all trucks and off-road vehicles in the state's vehicle maintenance and inspection program.
You can also add strategies or ideas of your own as well. Just click here, fill out the e-mail and send it in to be counted.
It takes as little as 30 seconds.
BUT YOU ONLY HAVE UNTIL 5 pm FRIDAY, VALENTINE'S DAY.
______________________________________________________________
Rick Perry's TCEQ is so discredited on the matter of DFW smog, local officials usually working in concert with the state agency are now looking elsewhere for help.
Ever since DFW was required to write and submit new clean air plans, The North Central Texas Council of Governments has been the local vehicle used by the state to funnel information, concern, and ideas back and forth.
It was never easy to get Austin's attention or convince the Powers That Be of the need to take bigger clean air measures. It took a decade for Downwinders to get the State to admit that the Midlothian cement plants had a huge impact on local air quality before they were the targets of new controls.
But ever since Rick Perry began running for President in 2010, it's been impossible for Austin toget serious about any DFW clean air plan. For the past four years, TCEQ has claimed that it can reduce air pollution enough by doing nothing.
That strategy has been a dismal failure. New car buying in the middle of the worst economic downturn since the 1930's was the TCEQ clean air plan in 2011. Austin promised that if we just sat back, we'd have the lowest smog levels ever recorded. Instead we had worse air pollution levels than we did five years ago.
This time round, TCEQ is saying a new EPA-mandated low-sulfur gasoline mix in 2017 will be the region's savior for the new clean air plan that's supposed to be successful in reaching the new federal ozone standard of 75 parts per billion in 2018. We're at 87 ppm now – still in violation of the old 1997 standard.
Just watch this new fuel being added to cars and see the ozone numbers drop, TCEQ is saying. No need to put controls on gas facilities, or cement kilns, or power plants. Nothing that would give Rick Perry's opponents on the Right any opportunity to claim he was "anti-bidness."
Even the Council of Governments isn't buying it.
That's why, in their own bureaucratic fashion, this Request for Information that the COG has issued is it's own middle-of-the-road middle finger to TCEQ.
Usually, it would be the state facilitating a discussion of new air pollution control strategies, but since it's obviously not interested, the COG has decided to go its own way. That's how bad things have gotten in Austin – even their most reliable allies in DFW can no longer take them seriously.
It's not clear what will happen to the list of control measures that the Council of Governments is assembling. Some might receive some more official attention, but locals have no authority to write or override Austin's decisions. TCEQ is the only entity that's authorized to submit a new clean air plan to EPA by the June 2015 deadline.
But there are ways to use the useless clean air plans that Austin is submitting. Downwinders' own green cement campaign is a great example.
In 2007, we successfully inserted a voluntary air pollution control strategy into the TCEQ plan revolving around the purchasing of cement from newer cleaner "dry" kilns by local North Texas governments. We then took that "green cement" procurement option and went to Dallas to pass the nation's first green cement ordinance. Then Fort Worth passed it. Then Plano. Then Arlington. Then Denton. Then Dallas County. Then Tarrant County.
Within two years, we had established a de facto moratorium on dirtier "wet kiln" cement within at least a dozen municipal and counties. Combined with federal rule changes, we were able to get all Midlothian wet kilns closed. The last one is being be converted to a dry kiln this year. All while Rick Perry was governor.
The same thing could happen with a good "off-sets" policy for gas facilities if a local city of county could pass a template ordinance showing the way. Currently, most of the gas industry is exempt from being required to "off-set" their air pollution in smoggy "non-attainment" areas like other large industries in DFW. Take away this exemption and you'll see a swift decrease in gas industry air pollution.
It's these kinds of strategies that don't depend on action from Austin that offer the greatest potential for progress this time around.
TCEQ has never written a successful clean air plan for North Texas, and it's not going to start now. But citizens themselves can take their lungs' fate into their own hands and begin to build a system of local measures that can make breathing easier.
______________________________________________________________
CALENDAR AND STATUS REPORT OF DFW'S NEWEST CLEAN AIR PLAN
Reach a 3-year rolling average of no more than 75 ppm of ozone at all 18 DFW area air monitors.
Better Living Avoiding This Chemistry: An Industrial Toxic Primer
 Even though this EcoNews article is about air poisons that result from fossil fuel production, it applies to just about any combustion source, including cement plants, manufacturing plants, vehicles, and so on. It's a pretty good top ten list, although you wonder why Dioxins and Furans got left off, since they're toxic by the gram instead of pound. Also missing is Particulate Matter as a stand alone threat, although it gets a shout out as a by-product. Nevertheless, these are the among the most dangerous pollutants that have caused and are still causing a lot of problems in North Texas and elsewhere:
Even though this EcoNews article is about air poisons that result from fossil fuel production, it applies to just about any combustion source, including cement plants, manufacturing plants, vehicles, and so on. It's a pretty good top ten list, although you wonder why Dioxins and Furans got left off, since they're toxic by the gram instead of pound. Also missing is Particulate Matter as a stand alone threat, although it gets a shout out as a by-product. Nevertheless, these are the among the most dangerous pollutants that have caused and are still causing a lot of problems in North Texas and elsewhere:
1. Benzene
Benzene is a well-established carcinogen with specific links to leukemia as well as breast and urinary tract cancers. Exposure to benzene reduces red and white blood cell production in bone marrow; decreases auto-immune cell function (T-cell and B-cells); and has been linked to sperm-head abnormalities and generalized chromosome aberrations.
Benzene is one of the largest-volume petrochemical solvents used in the fossil fuel industry. It is a major component in all major fossil fuel production: oil, coal and gas. People are exposed to it from inhaling automobile exhaust and gasoline fumes, industrial burning such as oil and coal combustion, and exposure to fracking fluids.
There's a recent Emory University study concluding that risk for leukemia fell with every mile between a person's home and facilities that release benzene.
2. & 3. Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are two primary examples of particle-forming air pollutants (particulate matter). Particulate matter is known to contribute to serious health problems, including lung cancer and other cardiopulmonary mortality. SO2 and NOx are both highly toxic to human health, and contribute directly to thousands of hospitalizations, heart attacks and deaths annually.
SO2 is particularly dangerous for children. Studies correlate SO2 emissions from petroleum refineries—even in lower exposure levels over time —to higher rates of childhood asthma in children who live or attend school in proximity to those refineries. Similarly, small particles of NOx can penetrate deeply into sensitive lung tissue and damage it, causing premature death in extreme cases. Inhalation of such particles is associated with emphysema and bronchitis.
4. Petroleum Coke (Pet Coke)
Pet coke is a by-product of oil processing that's also used as a fuel. It's a heavy dust which resembles coal. It's burned in power plants and cement plants. It contains dozens of dangerous chemicals and heavy metals, including chromium, vanadium, sulfur and selenium. It's a huge contributor to particulate mater and NOx and SOx formation
5. Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is a carcinogen with known links to leukemia and rare nasopharyngeall cancers, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Formaldehyde is highly toxic regardless of method of intake. It is a potent allergen and genotoxin. Studies have linked spontaneous abortions, congenital malformations, low birth weights, infertility and endometriosis to formaldehyde exposure. Epidemiological studies link exposure to formaldehyde to DNA alteration. It is also contributes to ground-level ozone.
Independent studies, have detected dangerous levels of formaldehyde in both wastewater and ambient air emissions from fracking operations. One researcher, with the Houston Advanced Research Center, said reading from one test site in North Texas, “astoundingly high,” and, “I’ve never heard of ambient (formaldehyde) concentrations that high… except in Brazil.”
6. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)
In actuality, this is not a single listing—polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) is an entire class of toxic chemicals, linked together by their unique chemical structure and reactive properties.
Many PAHs are known human carcinogens and genetic mutagens. In addition, there are particular prenatal health risks: prenatal exposure to PAHs is linked to childhood asthma, low birth weight, adverse birth outcomes including heart malformations and DNA damage.
Additionally, recent studies link exposure to childhood behavior disorders; researchers from Columbia University, in a 2012 Columbia University study, found a strong link between prenatal PAH exposure and early childhood depression. Infants found to have elevated PAH levels in their umbilical cord blood were 46% more likely to eventually score highly on the anxiety/depression scale than those with low PAH levels in cord blood. The study was published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
7. Mercury
Mercury is a dangerous neurotoxin emitted from coal-fired power plants and any other combustion source using coal for fuel – like the Midlothian cement plants. It damages the brain and the nervous system either through inhalation, ingestion or contact with the skin. It is particularly dangerous to pregnant women and children. It is known to disrupt the development of the in-vitro brain. In low doses, mercury may affect a child’s development, delaying walking and talking, shortening attention span, and causing learning disabilities. High dose prenatal and infant exposures to mercury can cause mental retardation, cerebral palsy, deafness and blindness. In adults, mercury poisoning can adversely affect fertility and blood pressure regulation and can cause memory loss, tremors, vision loss and numbness of the fingers and toes.
One out of every six women of childbearing age in the U.S. have blood mercury levels that could be harmful to a fetus, according to EPA reports. The EPA estimates that 300,000 children are born each year at risk for significant development disorders due to mercury exposure.
8. Silica (Silicon Dust/Sand)
Crystalline silica (“frac sand”) is a known human carcinogen; breathing silica dust can lead to silicosis, a form of lung disease with no cure. This is a hazard in the cement industry and threat to those living downwind of cement plants, and now it appears to be one for natural gas roughnecks and adjacent homeowners as well.
Silica is commonly used, in huge amounts, during fracking operations. Each stage of the process requires hundreds of thousands of pounds of silica quartz–containing sand. Millions of pounds may be used for a single well.
The presence of silica in fracking operations, simply put, is a major safety risk with a high likelihood of dangerous exposure. Case in point: researchers from the National Institutes of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recently collected air samples at 11 fracking sites in five different “fracking states” (CO, ND, PA, TX and AR) to evaluate worker exposure to silica. Every single site had measures higher than the NIOSH threshold for safe exposure—so high, in fact, that about one-third of the samples collected were even above the safe threshold for wearing a safety respirator mask. This was reported in May 2013 in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene.
9. Radon
Radon is a colorless, odorless, tasteless radioactive gas which causes lung cancer. It is the second largest cause of lung cancer in the U.S. after cigarette smoking. About 20,000 people per year die from lung cancer attributed to radon exposure according to the National Cancer Institute. Further, there is no known threshold below which radon exposures carries no risk.
Radon exposure can come from a variety of natural sources. However, fracking (natural gas) represents a significant new and increased source of radon exposure to millions of citizens. Radon is released into local groundwater and air during fracking operations. It also travels through pipelines to the point of use—be it a power plant or a home kitchen.
The science behind radon release and exposure is complex but explained well here by Christopher Busby, the Scientific Secretary of the European Committee on Radiation Risk, who warns that radon dangers from fracking “have not been addressed properly (or at all) by the environmental impact statements published by the operators, or by the Environmental Protection Agency in the USA.”
10. Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) / Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is “one of the most dangerous acids known.” HF can immediately damage lungs, leading to chronic lung disease; contact on skin penetrates to deep tissue, including bone, where it alters cellular structure. HF can be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin.
The senior laboratory safety coordinator at the University of Tennessee said, “Hydrofluoric Acid is an acid like no other. It is so potent that contact with it may not even be noticed until long after serious damage has been done.”
Hydrofluoric Acid is a common ingredient used in oil and gas extraction.
Numerous studies, including recent ones conducted by both The Center for Public Integrity (CPI) and the United Steelworkers Union (USU) cite the oil industry’s abysmal safety record as a high risk factor for a major HF accident; over the past decade, more than 7,600 accidental chemical releases from refineries have been reported by the industry. In the past three years alone, a total of 131 “minor” accidents involved HF.
Something Wicked This Way Blows…..
 Events like the gas pipeline explosion in Milford are graphic reminders of just how vulnerable our North Texas air shed is to pollution sources from Ellis County. Proximity, predominant wind patterns, and potential for disaster combine to make our Southern neighbor a constant threat.
Events like the gas pipeline explosion in Milford are graphic reminders of just how vulnerable our North Texas air shed is to pollution sources from Ellis County. Proximity, predominant wind patterns, and potential for disaster combine to make our Southern neighbor a constant threat.
On Thursday, one could see the plume of smoke stretch out south to north across the entire Metromess. It's a safe bet that not too many of the 6 million plus residents of greater DFW knew there was a town called Milford near them at the beginning of the day, but a lot of them had inhaled Milford soot by evening.
That would be the same soot that reporters keep reminding us "the EPA" says is "non-toxic," based on measurements. Except there is no such thing as non-toxic smoke from a combustion source, which the Milford explosion and fire most certainly was. All combustion produces soot, or Particulate Matter. According to the latest evidence from research scientists, there is no safe level of exposure to PM Pollution. That is, any amount of PM pollution can do human health damage. Even short-term exposure can lead to asthma attacks, heart attacks and strokes. How do we know this – the EPA tell us so on their own website.
Only a couple of years ago, the Magnablend fire in Waxahachie poured its own plume of "non-toxic" smoke into DFW skies, despite the incineration of a large variety of chemicals used in the oil and gas industry. You might remember the water run-off from fighting that fire went into a creek and killed a lot of fish. But don't worry, that same stuff in your lungs is nothing to worry about. Perfectly natural to be able to see what your breathing.
Perhaps the most spectacular modern reminder of how close Ellis County is to us in air miles came back in 1995 when a Midlothian-based tire dump, called…wait for it…."Safe Tire Disposal Company" that was actually a collection site for the nearby cement plant tire-burning operation caught fire its own self.
There are fires, and then there are tire fires. They burn extremely hot, produce a lot of that "non-toxic" smoke, and can keep going for days. And that's exactly what happened in Midlothian. The predominant southerly winds carried all that dark dense smoke right into Downtown Dallas, where it surrounded and engulfed whole office buildings.
Timing is everything and so it was with the Safe Tire Fire. It happened at the exact moment when local citizens were engaged in very public debate with state and local officials over whether air pollution from the three large cement plants in Midlothian (two of which were burning tires) could impact air quality in DFW. You read that correctly. In 1995, citizens were still trying to make the case that millions of pounds of air pollution released just across the Dallas and Tarrant County lines could possibly have a negative impact on metropolitan smog levels. And it was an uphill fight. Officially, there was no confirmation of the impact of these facilities. The DFW air plan stopped at the County Line. Unofficially, you could see the cement plant smokestacks as you drove I-20 across Grand Prairie and Arlington.
When those tires went up in smoke, so did the arguments being used to downplay the impact of Ellis County pollution. It was like adding a dark black dye to the North Texas air flow, beginning in Midlothian, and watching it be carried downstream/downwind right into the heart of downtown Dallas. It was the most defiant demonstration of the citizen's arguments one could imagine. After that, it was a lot easier for everyone to understand Midlothian was only a breeze away from their lungs.
With yet another fire in Ellis County setting off yet another dark, thick plume of smoke that wafts into DFW, we get a reminder of how much closer together the air brings us. Only about half an hour or so away from Milford, a little bit further south, is a new belt of natural gas compressors churning out voluminous amounts of air pollution that's being blown in the same direction as the smoke from that gas pipeline explosion. Unlike that smoke, pollution from these facilities will keep being released 24/7 for the foreseeable future. Add up all this new compressor pollution and it could rival the impact of a new coal plant – just upwind of us. Just because you can't see it doesn't mean it's not having an impact.
Once again, the state's position is that this pollution is no big deal. Once again, citizens are disagreeing. Who would you put your money on?
2013 DFW Smog Report: Failure….Again
 (Dallas)— On the eve of constructing yet another DFW clean air plan, the 2013 Ozone Season ended on Thursday the same way the previous 16 have ended: with North Texas out of compliance with the 1997 federal clean air standard.
(Dallas)— On the eve of constructing yet another DFW clean air plan, the 2013 Ozone Season ended on Thursday the same way the previous 16 have ended: with North Texas out of compliance with the 1997 federal clean air standard.
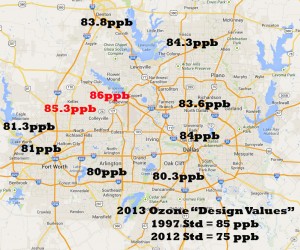
Even a mild summer with lower temperatures and more rain couldn't save the numbers from exceeding an illegal three-year running average of 85 parts per billion at monitors in Keller and Grapevine.
According to Jim Schermbeck with the clean air group Downwinders at Risk, what makes this year’s violation particularly troublesome is that the 1997 standard has been replaced with a more protective one that's 10 ppb lower. “For the next DFW air plan to succeed, it will have to reduce smog to levels that no DFW monitors have ever recorded. I don’t know anyone outside of Austin who thinks the state is up to that task.”
That new plan has its official kick-off event next Tuesday, November 5th, beginning at 9am in Arlington at the Council of Governments Headquarters. It's the first briefing from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality on the computer model it will be using to base the plan on. Everything about one of these plans is based on such a computer model, a model only the state can run. The plan must be submitted to EPA by June of 2015.
Even though extremely high ozone numbers were rarer this year, there were enough bad air days to cause the running averages of 10 out of 17 monitors, called "design values" to rise – not the kind of trend you want when you're next task is complying with a tougher standard.
Schermbeck was particularly concerned about a monitor near Mockingbird and I-35 in Central Dallas that’s seen its ozone average rise dramatically for three years in a row. “This is a monitor that had a "design value" of 67 parts per billion in 2010 – that is, it was in compliance with the new 75 ppb standard just three years ago. But now it’s up to 84 ppb and almost out of compliance with the 1997 standard. That's quite an increase in three years, and in a place where smog hasn’t been a problem for awhile.”
Every monitor inside the DFW metro area and even most "rural" monitors had a design value above the new standard of 75 ppb. Only Kaufman and Greenville made it under the wire, barely, with readings of 74 ppb.
As usual, the worst ozone levels were found in the northwest quadrant of the DFW area. This is a well-known historical pattern caused by the predominant southeast to northwest winds that blow pollution from the coast up through the coal and gas patches of East and Central Texas, over the Midlothian Industrial Complex and North Texas central urban cores into Northwest Tarrant Wise and Denton counties
This pattern has been the target of the last three state clean air plans, but has never been overcome. Schermbeck noted that last clean air plan to make a dent was the 2006 effort that produced lower numbers in steady fashion. Since 2008 however, air quality that was supposed to be getting better has gotten worse, or stagnated.
While cars have gotten cleaner during this time, and pollution from cement and coal plants has been reduced, there's one "source category" of pollution that's increased significantly since 2008: the gas industry.
In submitting the last DFW air plan to EPA in 2011, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality estimated there were more tons of smog-forming Volatile Organic Compounds being released by the gas industry in the official DFW "non-attainment area" than by all the cars and trucks on the road combined. That wasn't true in 2008.
Moreover, this is new air pollution in a smog non-attainment area that doesn't have to be off-set by reductions in pollution elsewhere in DFW. Unlike every other large industry, the gas industry is exempt from this offset requirement of the Clean Air Act.
Denton's Airport monitor's 4th highest reading of 85 ppb this summer, the one that officially counts toward its running average, was the highest such reading in the entire state, including Houston.
There's no doubt Denton is in the middle of the local gas patch, as are the Keller and Grapevine monitors that had the highest design values this year. Given the decreases in pollution from other categories, are gas patch emissions keeping these numbers from coming down they way they were supposed to? Austin keeps saying no, but the evidence is compelling.
Just last year there was a study out of Houston showing how a single flare or compressor station could significantly impact local ozone levels by as much as 5 or 10 ppbs. TCEQ itself just produced a study this last summer showing how Eagle Ford Shale gas pollution is increasing ozone levels in San Antonio.
Local Barnett Shale gas pollution might explain these Tarrant and Denton county monitors' problems, but they don't explain the rise in numbers of the Dallas monitors, since the wind during ozone season comes in from the south to southeast.
What new pollution is coming from that direction? Gas industry pollution from numerous compressor stations and processing plants stations in Freestone, Anderson, Limestone and other counties just about 90 to 100 miles south-southeast of Dallas. If one adds up all the emissions these facilities are allowed under their "standard permits." it exceeds the pollution from coal plants like Big Brown. That's a huge hit from sources that weren't there 10 years ago.
In effect, DFW is getting squeezed between gas pollution being produced in the middle of its urban areas, and gas pollution blowing in from the south.
“Officials with Rick Perry's TCEQ would rather drink lye than admit gas pollution is causing smog problems for DFW” says Schermbeck, “but such an admission might be the only way to bring DFW into compliance with the Clean Air Act.”
“This is why local DFW municipal and county governments serious about air quality must divorce themselves from Austin's politicized science and begin to seek their own solutions. Austin really isn't interested in solving DFWs chronic smog problems. Heck, the Commissioners who run TCEQ don't even believe smog IS a health problem.”