Posts Tagged ‘Holcim’
State Public Meeting Tonight on New Permit for Holcim’s Midlothian Cement Plant
 There's a public meeting hosted by TCEQ at 7pm tonight concerning the new permit for Holcim's Midlothian cement plant. It's taking place at the Midlothian Conference Center, at 1 community Center Road, right off Hwy 287. Here's a map if you need one.
There's a public meeting hosted by TCEQ at 7pm tonight concerning the new permit for Holcim's Midlothian cement plant. It's taking place at the Midlothian Conference Center, at 1 community Center Road, right off Hwy 287. Here's a map if you need one.
This is your only chance to ask questions and raise concerns about Holcim's new permit, or any other aspect of Holcim operations in a public forum in 2014.
Remember that Holcim's pollution contributes to higher smog levels as far north as Denton and Wise Counties. Along with TXI and Ash Grove, its plumes have been associated with higher childhood asthmarates in southeast Tarrant County.
Holcim is also still the only Midlothain cement plant still blasting for rock. The others use machinery to mine limestone, Holcim uses ammonium nitrate, the same explosives that caused the West, Texas catastrophe.
The good news is that Holcim has decided to install Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) pollution control on one of their two large cement kilns. That's what the new permit mostly is about. Although well-known for reducing smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) in the European cement industry, Holcim is using it to reduce Total Hydrocarbons – a category of pollutionthat includes toluene, benzene, and xylene.
You can read about how important a victory SCR is for all DFW breathers here. It's been a 15 year effort. Holcim's decision to install SCR should be celebrated.
But important questions remain about when the SCR unit will become operational and how reductions in airpollution like NOx will be tracked by the company.
SCR is only being installed on one of two Holcim kilns in Midlothian. The other kiln is getting a "Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer" – the equivalent of a flare on a gas well – to burn off its total Hydrocarbons.
Because they're combustion-based, RTOs increase NOx pollution. How much, and how Holcim can catch that increase before it goes up the stack is alsothe subject of the permit.
The public meeting on Monday is not a hearing. But it is the only public forum where citizens can thank Holcim for finally installing SCR, as well as express their concerns and ask questions about the permit.
We know it's a busy time of year, and it's the day before Election Day, but do your lungs a favor and attend a meeting about a permit that can affect them for good or bad.
After a 14-year Campaign, State-of-the-Art Pollution Control Finally Coming to Midlothian
 (Midlothian) After a 14-year effort by local citizens, Holcim US Inc. is applying for a permit to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to install a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit in their Midlothian facility. It's the first application for commercial use of SCR technology in any U.S. cement kiln.
(Midlothian) After a 14-year effort by local citizens, Holcim US Inc. is applying for a permit to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to install a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit in their Midlothian facility. It's the first application for commercial use of SCR technology in any U.S. cement kiln.
DFW-based clean air group Downwinders at Risk has been advocating the use of SCR in the three Midlothian cement plants located just south of I-20 since 2000, when a German cement kiln first operated the technology successfully.
Together, the TXI, Ash Grove, and Holcim plants represent the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the country and are a major contributor to DFW's historic smog problem.
"We need this pollution control technology in North Texas, and we're pleased to see Holcim's application," said Downwinders Director Jim Schermbeck. "But we wish residents could enjoy its results sooner than Holcim intends."
The SCR unit is planned for Holcim's idle Kiln #2 while a more common Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer will be built for its operating Kiln #1. Both technologies are being installed to meet new EPA emission standards for hydrocarbon pollution from cement plants. Those standards themselves were championed by Downwinders and other citizen groups in 2009, with over 200 people showing up at an EPA hearing the the DFW Airport Hotel to support them.
The deadline for compliance with the new standards is September 2016. However, restarting of Kiln #2, and the introduction of SCR in Midlothian, is dependent on local demand for Holcim's cement, which is still recovering from weak demand during the recession. That lack of demand could delay the technology's inauguration until after 2016.
Nevertheless, according to Schermbeck, Holcim's application for a permit to install SCR makes it's more likely that all of the Midlothian cement plants, and others in EPA "non-attainment areas" for smog pollution around the country, will be adopting it sooner rather than later.
"Holcim's application sets a precedent that's hard to ignore by regulators in Austin and Washington. For the first time a US cement plant has expressed enough confidence in SCR to make it a technically and economically-viable choice for pollution control. There's no going back."
SCR is widely considered to be the most advanced form of pollution control for cement manufacturing, capable of reducing smog-forming pollution by 90% or more, along with significant reductions in Particulate Matter, metals, and Dioxins.
Although about half a dozen European cement kilns are successfully operating the technology, U.S. plants have refused to endorse it. Two EPA-sponsored pilot tests of SCR are being conducted at Indiana and Illinois cement kilns as part of court-ordered settlements. Holcim's application for its Midlothian kiln is the first time and American cement plant is voluntarily approving SCR use.
Although it's not coming in time to impact the current DFW clean air plan, due to go to public hearing in January of next year, Holcim's application will put SCR on the agenda for the next such plan.
Just two weeks ago, EPA staff recommended a new ozone, or smog, standard of between 60 and 70 parts per billion over an eight hour period versus the current limit of 75 ppb. Adoption of a stricter standard is expected to occur by late next year, meaning a plan to meet that standard will be gearing up sometime in the next three to five years. By that time, Holcim's SCR unit should have a track record that can be cited as a reason for all the Midlothian cement plants to use it.
Schermbeck noted that just last month representatives of the TCEQ told a regional air quality meeting in Arlington that SCR was neither an economical nor technically feasible pollution control option for the Midlothian cement plants. He said Holcim's application belies that claim.
A public meeting on the Holcim permit application is being scheduled for early November.
Arrival of SCR on the scene marks the latest and the most dramatic milestone in the transformation of the local cement industry since Downwinders at Risk was founded 20 years ago to stop the burning of hazardous wastes in the Midlothian kilns.
After a 14-year battle, TXI halted its hazardous waste-burning operations in 2008. Downwinders then pursued a six-year "green cement" campaign to replace all seven obsolete and dirtier wet kilns with newer "dry kiln" technology. That campaign ended in 2012 with the announcement that Ash Grove would shutter its three wet kilns and build a new dry kiln in their place. That plant is due to go on line this year.
Adoption of SCR remained a goal of the group through four different DFW clean air plans going all the way back to 2000. Schermbeck said his group made incremental progress each time, winning small and large battles that directly lead to today's news.
"Holcim's application for SCR is the latest testament to the persistence and focus of a small group of committed citizens who have pulled and pushed the U.S. cement industry into the 21st Century one step at a time."
Ask the State and Holcim To Finally Give DFW “the Holy Grail” of Cement Pollution Control Technology
 Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
That's right. Holcim is asking the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) to OK a permit that will result in a "major modification" of its Midlothian plant and could produce significant amounts of new pollution before it even decides what the major modification is going to be. Anywhere else in the country this might be a bit odd, but hey, it's Texas, where Rick Perry's TCEQ has a rubber stamp standing by for anything industry requests.
Holcim's permit request is being prompted by a problem complying with new federal regulations limiting a kind of pollution called Total Hydrocarbons, or THCs. These are also sometimes referred to as "Volatile Organic Compounds." Think Benzene, and other kinds of hazardous flammable gases. In its permit application Holcim says it needs to add new controls to reduce THC to levels and come under the new federal standard. Fair enough. The company then says that it's still trying to decide between two different types of controls and will make up its mind after getting the permit and seeing how well its choice works out on one of its two separate giant kilns. That's the bogus part.
But wait, there's more! The two technologies Holcim is considering installing in Midlothian are: 1) A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, or RTO, which is a fancy way of saying setting them on fire and flaring them off, and, 2) A Selective Catalytic Reduction unit, or SCR, which is a tower of treated metal honeycombs that pick up pollution as the plant exhaust passes through them. RTOs are already installed on American cement plants, including TXI's huge Midlothian kiln just a few miles down Highway 67 from Holcim. On the other hand, up to now full-scale commercial SCR units have only been installed on European cement plants and in fact, the Portland Cement Association has lobbied long and hard to keep them out of the US for fear of raising the pollution control bar too high for all of the country's cement plants.
That's because SCR is more expensive to build and maintain than most cement plant control devices. But for the money, you get the Holy Grail of cement plant pollution control technology.
Most of the European cement plants that have SCR units install them to remove another type of pollution from their stacks – Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). If that sounds familiar, it's because NOx is a major smog-forming pollutant, and DFW has so much of it that the region has never been in compliance with the Clean Air Act standard for smog. And you'll never guess which facilities are the single largest sources of NOx pollution in North Texas. Or maybe you will: the Midlothian cement plants. That's why Downwinders at Risk has made it a point to campaign to require all three Midlothian cement plants – Holcim, TXI and Ash Grove – to install SCR….since all the way back in 2001, when the first European units were deemed a success at a German cement plant. SCR can remove 80 to more than 90% of all NOx coming out of a cement kiln. The 6500 tons of NOx a year that the Midlothian cement plants are permitted to release could be reduced to 650 tons with the application of SCR.
Now, as it turns out, SCR units are great not only at capturing large amounts of NOx pollution, but all kinds of other industrial pollution coming out of cement plants as well. Like THCs – up to 70% or so, but also Particulate Matter, Metals, Greenhouse Gases, Carbon Monoxide, and Dioxins. It's what's called a multi-pollutant control device because it does such a good job of eliminating a wide variety of nasty stuff from smoke stacks. This is what makes it the state-of-the-art technology for communities hosting kilns. In contrast, RTOs are single-purpose pollution devices aimed just at hydrocarbon removal and aren't designed to remove other kinds of emissions.
So even though Holcim is considering operating SCR because of its hydrocarbon problem, it would have a massive impact on the plant's air pollution across the board. And if Holcim were to set the precedent, the clock would begin ticking on bringing SCR to the other two Midlothian cement plants as well. It would only be a matter of time.
The public comment period for telling the state whether to accept or reject Holcim's permit application ends this Friday, July 11th at 5 pm. (If you're interested in jumping through the hoops to fill out the online form for official comments, you can go here and use Permit Number 8996)
Downwinders is submitting detailed comments praising Holcim for considering SCR, but urging the TCEQ to reject this permit because it's too vague and doesn't commit the company to any partciular technology, including SCR. We've also been collecting letters form local officials and stare legislators that urge Holcim to definitively choose SCR.
Now we're asking you to help us bombard both the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and Holcim's US headquarters in Dundee Michigan in the next 48 hours with the same message to show public support for the company to do the right thing while rejecting a placeholder permit that doesn't commit it to do that right thing.
We want a permit request from the company that says Holcim will definitely install SCR, becoming the first commercial application of this state-of-the-art technology in America.
Using our "Featured Citizen Action" link, you can send such a message to Austin and Michigan in a matter of seconds right now. All you have to do is click here and then send the e-mails. We guarantee there's no more important or easier thing you can do for clean air in North Texas this week than sending these e-mails to the TCEQ Commisisoners and Holcim Corporate leadership. Please help us get the cement plant pollution control technology DFW deserves. It will only take a matter of seconds for you to help us achieve a goal we've been working toward for 14 years. We can do this. But we need your help. Now. Thanks.
Another Chapter of “Why Don’t We See This in Midlothian?”
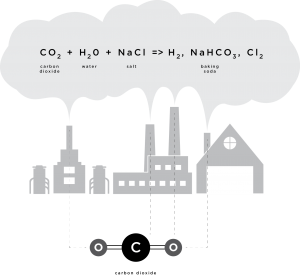 Cement plants are among the world's largest sources of CO2. In order to reduce their carbon footprints, either voluntarily or to comply with new environmental regulations, as well as make a buck, owners are trying out different strategies to turn their Greenhouse Gases into just plain green cash.
Cement plants are among the world's largest sources of CO2. In order to reduce their carbon footprints, either voluntarily or to comply with new environmental regulations, as well as make a buck, owners are trying out different strategies to turn their Greenhouse Gases into just plain green cash.
As far as we can tell, the "SkyMine" pilot-project announced for San Antonio's Capital Aggregates Cement Plant is still on schedule for operation later this year. Employing 50 people, the first-of-its-kind facility will convert the cement plant's carbon dioxide into baking soda and hydrochloric acid that's aimed at oil and gas field use.
Now comes word that a LaFarge Cement Plant in Canada is hooking up with a fuel cell company to make a slightly more progressive product from its GHGs:
"Mantra Energy Alternatives has struck a deal with Lafarge Canada to deploy an electrochemical reduction technology at Lafarge’s No. 9 Road cement plant.
“This will be the first pilot plant of its kind in the world,” said Mantra’s vice-president Patrick Dodd in a press release.
On paper, the technology would convert carbon dioxide, considered the most prolific greenhouse gas, into useful chemicals like formic acid and formate salts. The pilot plant would convert 100 kilograms per day of carbon dioxide emitted from the local cement plant into concentrated formate salts, which sell for about $1,500 per tonne.
Mantra is eying the formic acid for use in its patented fuel cells, which it bills as a significantly less expensive fuel cell with greater power density."
Granted, the manufacturing of oil and gas chemicals sounds more likely for one of the three huge Midlothian cement plants to attempt than diving into the alternative energy business, but at least it's something. The end products can change and adapt but these projects begin to put the infrastructure of a supply and demand system in place while seeing potentially large decreases in CO2 output. In 2014 America, the fastest way to get reductions in GHGs is to make it profitable to do so. These experiments pave the way for that to happen.
There's no question that the TX/ Martin-Marietta, Holcim and Ash Grove cement plants are the largest stationary sources of CO2 in North Texas, or that together, they form a huge GHG hotspot. All the old coal-fired power plants that would have challenged them have been shuddered or converted to gas.
While (forced) modernization at all three plants like the conversion from wet to dry kiln technology has brought all emission totals down, particularly CO2, the fact remains that the huge scale of operations in Midlothian means there's no other facilities that churn it out as much. And yet not one creative idea for how to reduce those huge local emissions has been announced from any of those companies. You can't just use the Texas excuse because the San Antonio experiment is happening despite no immediate government mandate, especially on existing facilities. And you might think that the first company to do so would receive some needed good PR. But nope.
This has been another chapter of "Why Don't We See This in Midlothian?"
Hell Freezes Over: Why the New Federal Report on Midlothian Matters
Everything in italics and "quotation marks" below is a direct quote from the latest chapter of the ATSDR's (Agency for Disease Registry and Toxic Substances) "health consultation" on the impact of certain kinds of industrial air pollution on the local population.
You should take five minutes to glance over the sentences. They've taken a better part of a decade and a great deal of citizen persistence to make it to print. You can read them now only because of a petition to ATSDR by local Midlothian residents, spearheaded by Sal and Grace Mier in 2005, prompted the Agency to get involved.
They're also rarer than hen's teeth. Because the words actually come together in sentences to conclude human health was likely harmed by the pollution from Midlothian's three cement plants and steel mill, as well as recommend decreasing that pollution.
Among grassroots activists, ATSDR has a notorious reputation for issuing reports that are "inconclusive by design." The joke is that the agency never met a facility it couldn't learn to live with. And sure enough, previous chapters in this saga have disappointed. Just two years ago, ASTDR's shoddy work in investigating health impacts in Midlothian and elsewhere across the country was the subject of a Congressional hearing.
These ATSDR reports generate no new data. Instead, they are retrospective looks back at the available sampling/monitoring information and a piecing together of possible exposure paths and levels. As such, they're only as good as the data they can digest. In Midlothian's case, that means they're completely dependent on state monitoring – criticized by citizens for years as being inadequate. Nevertheless, with this latest report, citizens have been somewhat vindicated because of what even that inferior sampling revealed.
The health impacts described in this latest report are also limited to what are called "Criteria Pollutants" – old school substances like lead, soot, sulfur dioxide, and ozone that have been regulated by the Clean Air Act for decades. They do not apply to more exotic kinds of air pollution like endocrine disruptors, which there's little or no monitoring for at all.
So there are a lot of missing pieces, but the ATSDR's conclusions and recommendations have an impact on your lungs and maybe your own local fight, even if you don't have a Midlothian zip code. For the first time a federal agency known to avoid coming to any conclusion about anything was forced to say that human health was adversely affected by the operations of industry in Midlothian.
There's a public meeting on this report on December 6th from 7 to 8:30 pm at the Midlothian Conference Center.
Health Consultation/Assessing the Public Health Implications of the Criteria (NAAQS) Air Pollutants and Hydrogen Sulfide MIDLOTHIAN AREA AIR QUALITY MIDLOTHIAN, ELLIS COUNTY, TEXAS
NOVEMBER 16, 2012 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Division of Community Health Investigations
Recommendations:
"Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) should take actions to reduce future SO2 emissions from TXI to prevent harmful exposures."
"TCEQ should take actions to reduce future PM2.5 emissions from TXI and Gerdau to prevent harmful exposures."
"TCEQ should continue efforts to reduce regional ozone exposures."
"TCEQ should insure that levels of these air pollutants do not increase to levels of concern in the future."
"TCEQ should conduct ambient air monitoring to characterize exposures to persons located downwind of the Ash Grove and Holcim facilities and take actions to reduce SO2 emissions from these facilities if harmful exposures are indicated."
"TCEQ should conduct appropriate ambient air monitoring to characterize exposures to persons located downwind of the Ash Grove and Holcim facilities and take actions to reduce PM2.5 emissions from these facilities if harmful exposures are indicated. In addition, particulate matter monitoring is needed in residential areas that are in immediate proximity to the facilities’ limestone quarries."
"In ATSDR’s judgment, one notable gap in monitor placement is the lack of monitoring data for residential neighborhoods in immediate proximity to the four industrial facilities, where fugitive emissions (those not accounted for in stack emissions) likely have the greatest air quality impacts."
Human health was likely harmed, and is still threatened by industrial pollution from Midlothian
From Sulfur Dioxide:
"Breathing air contaminated with sulfur dioxide (downwind of TXI's cement plant and the Ameristeel steel mill) for short periods could have harmed the health of sensitive individuals.…ATSDR cannot determine if harmful exposures to SO2 have been occurring downwind of the Holcim and Ash Grove facilities."
"All 24-hour values in Midlothian were lower than EPA’s former standard. However, the World Health Organization’s health comparable guideline is 8 ppb (WHO, 2006). This value was exceeded at both the Midlothian Tower and Old Fort Worth Road stations in most years of monitoring through 2008…"
"Overall, in the years 1999 to 2001, Old Fort Worth Road (monitoring site north of TXI) ranked among the stations with the highest 24-hour average sulfur dioxide concentrations in the state. As sulfur dioxide emissions from TXI Operations decreased in following years, so did the measured concentrations at this station."
From Particulate Matter, or Soot:
"Public health concern is warranted for adverse health effects from long-term exposure to PM 2.5 in Cement Valley"
"In the past (1996–2008), annual average PM 2.5 levels measured were just below the range of concentration proposed by EPA for lowering the annual average standard…Moreover, many of the annual average PM 2.5 concentrations were above the more conservative WHO health guideline (10 μg/m3)."
"No PM 2.5 monitoring data are available to evaluate exposures downwind of the Ash Grove facility. Furthermore, although annual average PM2.5 levels detected at the Holcim monitor indicate possible harmful levels…."
"We estimated that annual average PM2.5 levels in the vicinity of the Gerdau Ameristeel monitor, from 1996 to 1998, could have ranged from about 22.6 to 26.4 μg/m3, which is above both the current and proposed EPA standard. Using EPA’s approach, the 3-year average level might have been above the NAAQS standard of 15 μg/m3 for these years in the vicinity of the Gerdau Ameristeel monitor. Applying this same approach to annual average PM10 data from other monitors suggests that PM 2.5 levels could have been close to the current and proposed PM2.5 standard, especially for the Wyatt Road, Old Fort Worth Road, Gorman Road, and Midlothian Tower monitors."
"Consistent with the other pollutants discussed earlier, the estimated annual PM 2.5 emissions listed for these facilities are among the highest for Ellis County and also rank high among industrial sources statewide."
From Lead:
"Past lead air exposures during the period 1993 to 1998, in a localized area just north of the Gerdau Ameristeel fence line, could have harmed the health of children who resided or frequently played in this area….In the mid-1990s, the lead levels measured in this area ranked among the highest lead concentrations measured statewide."
From Smog:
"Scientific studies indicate that breathing air containing ozone at concentrations similar to those detected in Midlothian can reduce lung function and increase respiratory symptoms, thereby aggravating asthma or other respiratory conditions. Ozone exposure also has been associated with increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, medication use by persons with asthma, doctor’s visits, and emergency department and hospital admissions for individuals with respiratory disease. Ozone exposure also might contribute to premature death, especially in people with heart and lung disease. School absenteeism and cardiac-related effects may occur, and persons with asthma might experience greater and more serious responses to ozone that last longer than responses among people without asthma."
"The Midlothian Tower site recorded ozone concentrations above the level of the NAAQS for several years (TCEQ, 2011b), and the Old Fort Worth Road site has been measuring ozone concentrations close to the level of the NAAQS. Based on the data from both monitors, from August 1997 to September 2011, the 8-hour EPA ozone standard has been exceeded 236 times."
From Breathing Multiple Pollutants:
"ATSDR believes that sufficient information exists to warrant concern for multiple air pollutant exposures to sensitive individuals, especially in the past….The ability of the scientific community to fully and quantitatively evaluate the health effects from the mixture of air pollutants people are exposed to is at least ten years away (Mauderly et al., 2010)……The current state of the science limits our ability to make definitive conclusions on the significance of simultaneous exposures to multiple criteria air pollutants. ATSDR’s conclusions are based on our best professional judgment related to our understanding of the possible harmful effects of air pollutant exposures in Midlothian and our interpretation of the current scientific literature; therefore, these conclusions are presented with some uncertainty."
From New Production:
"Reductions in SO2 levels in Cement Valley have occurred since late 2008 resulting in exposures to both sensitive individuals and the general public that are not expected to be harmful. These reductions may be caused, in part, by declining production levels at local industrial facilities. Future harmful exposures in Cement Valley could occur if production rises to at least previous levels and actions are not taken to reduce SO2 emissions."
Regulatory "Safe Levels" Very Often Aren't
"Past SO2 exposures were not above the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standard in place at that time but were above the current standard."
"Past lead air exposures were not above the EPA standard at that time but were above the current standard.…The scientific community now believes that the current standard (15 μg/m3) for fine PM (measured by PM2.5) is a better indicator of possible long-term health effects from PM exposures than was the former EPA annual average standard for PM10 (EPA, 2006b)."
Midlothian Cement Plants Linked to Higher Child Asthma Rates
On the left is a computer-modeling image from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality showing the direction of the predominant downwind plume of pollution from the three Midlothian cement plants - from extreme NW Ellis County, blowing diagnoally across Tarrant County and into Wise County. On the right is the map from the original 2009 Cook Children's Hospital CCHAPS study indicating levels of childhood asthma in the Hospital's service area. It tracks closely with the direction of the plume and asthma levels increase in closer proximity to the cemnt plants. 
According to researchers Patricia Newcomb and Alaina Cyr from the UTA College of Nursing "…the bulk of Tarrant County asthma cases lie directly in the path of southeasterly winds that have historically carried high levels of particulate matter from working cement kilns in a neighboring county. Asthma prevalence increases in a linear configuration within the path of the 'cement plume' as residential location comes closer to the cement kiln area."
Exposure to Particulate Matter pollution, or soot, is a well-known known cause for asthma. It can also make a child's asthma worse.
"This latest study is one more piece of empirical evidence that we need to decrease pollution from the Midlothian cement plants to secure the right of our children to breathe without getting sick, " said Jim Schermbeck, Director of Downwinders at Risk, a local group originally founded in 1994 to oppose the burning of hazardous waste in the Midlothian cement plants.
Proximity to the pollution from the three Midlothian cement plants was the only environmental factor geographically associated with higher concentrations of childhood asthma, ruling out poverty and indoor air pollution. There also wasn't a strong correlation to urban gas drilling, although the authors concede that "urban drilling may play a part as well" in the region's higher than normal child asthma rates, and there was no direct comparison between the geography of drilling activity and area asthma levels.
In 2009, Cook Children's Hospital released its Community-wide Children's Health Assessment and Planning Survey (CCHAPS), the largest examination of childhood health in North Texas ever undertaken. It found that Tarrant County and the western side of the North Texas region suffer childhood asthma rates significantly higher than state and national averages.
In "Conditions Associated with Childhood Asthma in North Texas," published in the October edition of ISRN Allergy, Newcomb and Cyr revisit the Cook study and delve more deeply into its data. "The purpose of this study was to identify significant associations between asthma diagnosis, comorbid conditions, and social problems in children." The complete article can be accessed on the Cook Hospital CCHAPS website page devoted to asthma, under "Special Reports."
Midlothian is the home of the largest concentration of cement plant manufacturing capacity in the United States. It hosts three large cement plants – TXI , Holcim and Ash Grove – with a total of six kilns. They are the largest stationary sources of pollution in North Texas. Reports submitted by the plants themselves show they poured over a million pounds of Particulate Matter pollution into the North Texas air in 2009.
EPA recently announced that it was considering once again delaying the implementation of new federal emission rules, including stricter particulate matter pollution standards, from 2013 to 2015 that have been in the works for two decades. The delay would also water down proposed PM pollution standards. Schermbeck said Newcomb and Cyr's analysis shows the real world costs of such a rollback.
"It's a scientific fact, endorsed by EPA, that inhaling tiny bits of particulate matter can make people sick and even kill them. What this study makes clear is that the agency is senselessly condemning more Tarrant County kids to illness and suffering by delaying rules that were supposed to have been in place in the 1990's. It's time to start saving lives by reducing this kind of pollution."
