Citizen Action
How the Dallas Climate Plan Baits and Switches on Air Pollution

A little after 5 pm Monday February 3rd, the Office of Environmental Quality and Sustainability (OEQS) at Dallas City Hall released its draft recommendations for the city’s climate “action” plan. There are 93 “action items” including transportation, buildings, green spaces, water management, solid waste, and urban agriculture. Most are without imagination or timelines, meaning that even the most milk toast-like recommendations being made will have to be fought for tooth and nail to be done in a timely manner.
Like the department that generated them, the list of recommendations is effusive about stormwater management and tree-planting and silent on more challenging issues such as inequitable pollution burdens and the City’s own reliance on natural gas. It once again puts the spotlight on the lack of any environmental health expertise at Dallas City Hall in the decision-making process. When Dallas OEQS staff talk about the environment, what they really mean is “conservation” – a definition that’s been obsolete since at least the 1970’s.
There’s no better example of how this tunnel vision affects policy than OEQS staff invoking DFW’s chronically poor air quality (i.e. an environmental health problem) to sell the need for its Climate Plan…only to see the actual Plan ignore poor air quality as a serious health issue that could use some innovative thinking.
For over a year now, anytime you saw a Climate Plan presentation by Dallas OEQS staff, it always cited DFW’s smog problem as something that would only get worse as the climate crisis played out. “Everyone here is probably aware of DFW’s longtime air quality problems” or some approximate was the standard riff. And of course, everybody was. Heads nodded. Audience members were sometimes asked if they knew anyone with asthma and hands immediately shot up. That was the point. The selling point.
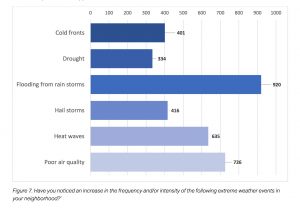 Because, until recently at least, the abstract nature of “the climate crisis” made it difficult to get people excited about the idea of a plan. Staff/Consultants needed a hook. And that hook was something everyone could relate to and probably already knew about: DFW’s three decades of violating the Clean Air Act. If you look at the results of the Ctiy’s online survey asking about frequency or intensity of climate change effects, “Poor Air Quality” was the second most cited concern. Among the City’s own handpicked crew of “stakeholders” advisors, it tied for first, along with buildings/energy use, getting more votes than parks, “nature-based approaches,” and renewable energy.
Because, until recently at least, the abstract nature of “the climate crisis” made it difficult to get people excited about the idea of a plan. Staff/Consultants needed a hook. And that hook was something everyone could relate to and probably already knew about: DFW’s three decades of violating the Clean Air Act. If you look at the results of the Ctiy’s online survey asking about frequency or intensity of climate change effects, “Poor Air Quality” was the second most cited concern. Among the City’s own handpicked crew of “stakeholders” advisors, it tied for first, along with buildings/energy use, getting more votes than parks, “nature-based approaches,” and renewable energy.

And yet, in those same City Staff presentations that highlighted poor air quality as a reason to have a Climate Plan, air quality itself was completely absent in the staff’s list of anticipated recommendations. It wasn’t that they just didn’t have much to say. They had nothing to say. There wasn’t even a category for air quality.
So Downwinders complained. Loudly. Staff and consultants sprang into action and came up with a category of recommendations officially called…“Other,” the theme of which was “air quality standards” and “public education.” Opportunities cited included “location-specific initiatives (e.g. downtown)” and “Programs targeted outdoor workers (e.g. Landscapers, construction workers).”
 So sure, we have a chronic air pollution problem that warrants a $500,000 consultancy fee to construct a plan, but in that plan we’re only going to continue to inform people of that problem and maybe do some kind of vague thing relating to the poor souls who work outside (limit hours, hand-out free oxygen, help find new employment, or maybe free health check-ups? Doesn’t give a hint). By the way, only the public education part of that slide made it to last Monday. Construction workers and landscapers are still up a creek.
So sure, we have a chronic air pollution problem that warrants a $500,000 consultancy fee to construct a plan, but in that plan we’re only going to continue to inform people of that problem and maybe do some kind of vague thing relating to the poor souls who work outside (limit hours, hand-out free oxygen, help find new employment, or maybe free health check-ups? Doesn’t give a hint). By the way, only the public education part of that slide made it to last Monday. Construction workers and landscapers are still up a creek.
Along with those snippets of text on the “Other” slide were large color pictures of the “Breathe Easy” 5K run sponsored by The Jerome Alston Memorial Foundation in May…during Ozone Season. We’ll give the City staff credit. In terms of public education, there might not be a better way to personalize the seriousness of DFW’s air pollution problem than having North Texas smog cause an emergency asthma attack while you’re running in it. But liability could be an issue.
As late as the final round of public meetings last Fall, staff still didn’t have an “Air Quality” category but said they would have “something” when the plan was published.
Turns out “something” looks a lot like nothing.
Among the 93 “actions” listed in the Plan’s draft, the category of Solid Waste gets nine recommendations. Water Resources 15. Urban Ag 14. The brand new category of “Air Quality” has four – the fewest of any category in the plan. It’s practically stamping “Last-Minute Desperation” on the whole subject.
And tell us if any of these recommendations sound like anything you might have already heard about…

Let’s take them from the top.
The very first thing out of the gate, the lead-off, sexiest, out-of-the-box recommendation for improving air quality is…. somehow talk the State into adding more obsolete, state-run air monitors at some unspecified time in the future.
If you can, forget that the State environmental agency – the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) – is a model for the Trump Administration. Forget that its official position is that smog is waaaaay overrated as a health threat. In other words, forget that this is akin to hiring Charlie Sheen to babysit your only child.
It’s not the baked-in, in-your-face cynicism of City staff knowing the state has every reason not to do this that’s so offensive. It’s the same cynicism applied to knowing full well what will happen even if the state says yes to the request: no real improvement in local information about air quality. Those state monitors are big, slow, and sparse. They run two hours or more behind real time. They’re hard to find online. They’re needlessly expensive and take up lots of real estate that has to be purchased. Their placement is decided by TCEQ and city staff, not the communities most in need of them. There is no stated OEQS goal for the number of monitors to acquire, or suggestions about where new monitors should be. No language in the recommendation about wanting real time monitoring or more modern equipment. It’s just an expansion of an already-obsolete system the state only runs because federal law requires them to (for now).

OEQS wants more of these lumbering and obsolete monitors from the state.
So let’s say the City talks the state into doubling the number of state PM 2.5 monitors in Dallas. Victory! The discussion will then be where to place the second slow, hard-to-find PM monitor for all of Dallas County’s 2.5 million residents.
Left unsaid in this recommendation is something we already know. For a year now Staff has tried to move that single Dallas County PM monitor located on Hinton Street north of Downtown to somewhere in Southern Dallas. Apparently the state has made that hard-to-impossible and so for the purposes of having something, anything, to recommend for this climate plan, staff recommends more monitors – knowing there’s a snowball chance in Hell of getting them. It’s the perfect bureaucratic out.
Most importantly the City remains a spectator to the reporting to its residents of how bad their air is. Its staff doesn’t have to make any environmental health judgments as they’re busy promoting tree planting. They leave that up to the people who couldn’t care less about how much pollution you’re breathing.

In the wake of recent Gulf Coast chemical plant accidents, the TCEQ is under heavy criticism for its lack of current air monitoring technology. The system it operates in DFW hasn’t changed in over 20 years. TCEQ won’t even put an air monitor in the only DFW “non-attainment” county that doesn’t have one – Wise – where smog levels have been predicted to be even higher than in DFW proper.
Recommending a modest expansion of circa-1999 technology is the opposite of a “best practices” answer for our gap in local air quality knowledge. The most alarming thing about this recommendation is that it got made at all.
The one-liner stapled at the end about offering free health screenings “with Dallas County” (who’s already in the business) in “areas with poor air quality” is incredibly condescending. Here’s the ultimate “settlement house” approach to a social ill – addressing the symptoms but not the cause. “Well, we can’t do much to enforce code or keep those batch plants out of your backyard, but by God we’ll be around every 6 months to keep track of your asthma until you die from it.”
How does OEQS staff know where those “areas with poor air quality” are now unless they’re out monitoring them? Which they clearly do not want to do. Given there’s only one official PM monitor for all of Dallas County, how are they defining “areas with bad air?” If they’re making educated guesses where those “areas” are based on other factors besides monitoring, why not name those factors and the “areas?” OEQS goes out of its way to avoid using the words “environmental justice” even as it makes recommendations based on the concept.
Recommendation #2 – let’s build our own “non-regulatory” air monitoring network sometime in the unspecified future with unspecified non-profits and community partner volunteers and put an unspecified number of monitors in unspecified places, for which we unspecified criteria. And these monitors “could be used to “to track progress for air quality improvements based on strategic initiatives deployed in CECAP, and the comprehensive plan.”
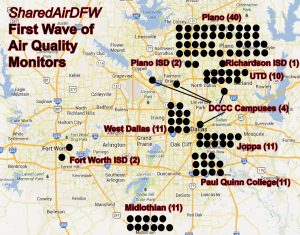
This is actually a great idea. It’s such a great idea that a specified alliance of local governments, non-profits, and community partners are already doing it in specified locations with specified monitors. Their effort is about to deploy over 100 locally-built air monitors that will increase PM 2.5 monitoring in Dallas County by 4000%. It’s called the SharedAirDFW Community Air Quality Monitoring Network and the City of Dallas officially walked out of it last year over a public participation requirement and a desire to refrain from being the source of bad news about bad air.
Dallas city staff is consistent in believing that telling you about air pollution is absolutely, positively necessary – they just want someone else to do it.
Having walked away from the SharedAirDFW network, OEQS set out to make one up of its own using the City Hall-friendly Nature Conservancy as its non-profit partner. The “Breath Easy” plan was to put 9-12 PM and smog monitors on the same number of DISD campuses, grow trees and implement anti-idling zones at those schools and see if asthma attacks/rates dropped in 24 months (2 growing cycles). Everyone seemed to agree how important a project this was and the city raised $500,000 or more to buy 12 very nice Aeroqual (Recommended by Downwinders since 2017!) air monitors. Everyone but the Dallas independent School District, who nixed the idea last summer. This detail somehow escaped the presentation staff gave to the City Council’s Quality of Life Committee on the Breath Easy project in September 2018.

An Aeroqual stationary air monitor like the 12 Dallas owns…but isn’t using
So far the City of Dallas is 0 for 2 in making their own recommendation a reality when it had the chance. But wait! Remember those 12 monitors the City bought for the defunct Breathe Easy project? They’re just sitting somewhere. They’re already paid for but aren’t being used. OEQS could implement this recommendation of theirs on its own tomorrow if it wanted to by placing these 12 monitors in locations based on where the most industrial facilities are and where the most air pollution complaints come from. Overnight it could have its own fleet of “non-regulatory” monitors in the field, with all the benefits cited by staff.
But there’s no mention of those 12 monitors, or of the City Hall’s ability to accomplish this goal on its own, right now, without waiting. Because it doesn’t want to. It wants someone else to do it.
Recommendation #3 . It’s that forlorn public awareness recommendation showing up in the form of continued support for an ozone season air quality campaign run by a group that did its part to make smog an issue for years. There’s no harm to this but there’s also no help. This campaign will go on for as long as DFW is in violation of the Clean Air Act and doesn’t mention climate change.
Finally, there’s recommendation #4. Perhaps (but perhaps not) heavy industry that pollutes a lot shouldn’t be close to homes. This is coming straight-faced from a OEQS that’s approved the last four batch plants seeking permits to set-up shop in Joppa and the South Central Corridor…next to homes. Do as we recommend, not as we actually, you know, do.

The TAMKO asphalt shingles plant and multiple diesel locomotives operate next to Austin’s asphalt batch plant…and residents in Joppa
When it says the City will review zoning, that’s not a special environmental health screening of sites. It’s just part of upcoming land use planning processes that will already be used to re-examine all zoning on a neighborhood-by-neighborhood level. They’re riding coat tails. The OEQS doesn’t make recommendations about suggested buffer zones, where those zones should be, or what criteria the city should use in pursuing buffer zones. And it doesn’t even say the City’s neighborhoods need any buffer zones between homes and industries at all, just that it may want to consider them at an unspecified time by an unspecified body for unspecified neighborhoods. Have we mentioned the staff at City Hall really really doesn’t like to deal with environmental health issues?
We get it. They had to have something or you’d be reading our criticism about the absence of ANY specific air quality recommendations, no matter how lame. And there are other items in other categories that will inevitably produce decreases in air pollution of all kinds – bus and vehicle fleet electrification being among the lowest-hanging fruit.
But City Hall’s cynical use of DFW’s air pollution problem to win support for a plan that ends up doing nothing about it directly makes these “Air Quality” recommendations particularly contemptuous.
What would more sincere “air quality” recommendations look like?
1. Acknowledging an historic imbalance in the air pollution burdens borne by Dallas neighborhoods and a commitment with a deadline to inventory the City’s air pollution threats by council district and zip code. You c an’t fix what you don’t measure. Right now there’s no map of where concentrations of air pollution are in Dallas.
an’t fix what you don’t measure. Right now there’s no map of where concentrations of air pollution are in Dallas.
2. Acknowledging there’s no safe level of PM air pollution, i.e., no amount of exposure that isn’t capable of doing harm. Acknowledging People of Color are exposed to more, and higher levels of PM pollution than their white peers. These conclusions, supported by a multitude of good studies, including ones from EPA, are basic in prioritizing where to reduce air pollution in Dallas.
3. Recommendation to write an Environmental Equity Provision into City Code to discourage and prohibit siting new polluters in those zip codes hosting more permitted polluters than the citywide average, beginning in 2021.
 4. Recommendation to quit siting polluters in any floodplain beginning in 2021.
4. Recommendation to quit siting polluters in any floodplain beginning in 2021.
5. Recommend a 2025 deadline for the electrification of all railroad switch yard operations in Dallas.
6. Recommend 1500 foot buffer zones on either side of new major highways where homes, day care centers, and schools would be prohibited from locating. Applied to existing highways as uses within 1000 feet come up for new permits and zoning.

7. Recommend the immediate amortization and relocation of the GAF asphalt shingle factory in West Dallas and the TAMKO shingle factory in Joppa. These factories are among the City’s largest industrial polluters in Dallas, accounting for over 420 tons of air pollution in 2017 alone. They operate in the middle of dense urban residential areas populated primarily by People of Color. They need to be relocated elsewhere. Building new facilities will automatically trigger modern pollution controls requirements. They’ll be cleaner and doing business in a less harmful location.
8. Recommendation to rewrite city codes giving incentives for cleaner industries and more requirements for dirty ones.
9. Join UTD’s SharedAirDFW Community Air Monitoring Network – plug OEQS’ 12 unused monitors into the Network and begin to take responsibility for telling Dallas residents what their air quality actually is.
 10. Acknowledge the conflict of interest the City has in producing and selling gas from its landfill recovery operation and commit to electrification of all city-owned vehicles by 2025. Dallas’ own city-run McCommas Bluff methane gas recovery facility is the fourth largest air polluter in Dallas, releasing over 160 tons of air pollution in 2017 alone. Recommend contracting only with electric vehicle fleets for additional services. Los Angeles recently committed to an all electric garbage truck fleet in five years, and Dallas could do the same – but it still wants to use its own landfill gas to power combustion vehicles.
10. Acknowledge the conflict of interest the City has in producing and selling gas from its landfill recovery operation and commit to electrification of all city-owned vehicles by 2025. Dallas’ own city-run McCommas Bluff methane gas recovery facility is the fourth largest air polluter in Dallas, releasing over 160 tons of air pollution in 2017 alone. Recommend contracting only with electric vehicle fleets for additional services. Los Angeles recently committed to an all electric garbage truck fleet in five years, and Dallas could do the same – but it still wants to use its own landfill gas to power combustion vehicles.
11. Implement stronger enforcement of the city air quality and nuisance ordinances, including hiring new staff and publicizing how to request an investigation.
12. Beginning in 2025 begin collecting municipal clean air mitigation fees of $50 a pound on permitted air pollution from major sources to incentivize pollution controls and pay for new staff. In 2017 such a fee would have collected over $1 million.
13. Implement no idling zones in all Dallas warehouse districts.
14. Recommend Low-Emission Zones in Downtown Dallas where combustion vehicles are banned or restricted, permanently or on a schedule. Consider expanding to other parts of Dallas such as Deep Ellum and Bishop Arts where congestion is already a problem.
15. Recommend PM pollution protection be designed into new bus shelters.
16. Recommend establishment of an Electric Bus Procurement Pool with DISD, DART, Trinity Metro, other area schools districts, and transit companies for cheaper purchases of electric buses.
17. Restoration of t he Dallas Environmental Health Commission.
he Dallas Environmental Health Commission.
18. Hiring a City of Dallas Environmental Health Scientist.
DFW does have a chronic bad air problem. The Climate Crisis will make it worse. It is a legitimate area of policy planning in any thoughtful, modern Climate Plan.
Just not this one.
Downwinders Welcomes New Board Members
November brought a round of new board members joining our ranks. It also brought an historic milestone. For the first time in our 25 year history, we’re now governed by a board whose majority is composed of people of color.
 Marsha Jackson
Marsha Jackson
A year ago not many people at Dallas City Hall knew Marsha Jackson’s name. That’s not the case this December. Ms. Jackson is both the founder of her own neighborhood group, Neighbors United, and the citywide Southern Sector Rising Campaign for Environmental Justice. She’s also the nearest neighbor to Shingle Mountain, Dallas’ largest illegal dump and the highest profile symbol of environmental racism in North Texas since the RSR lead smelter clean-up in the early 1990’s. Like Luis Sepulveda almost 30 years ago Marsha Jackson’s name has become synonymous with the fight for Environmental Justice in Dallas.
Michelle McAdam
Michelle is a long-time friend of Downwinders who finally decided to join the board. She was a student in the very first year of our College of Constructive Hell-Raising, where she met her unlikely Southern Dallas doppelganger and provided us with one of our favorite college stories. She’s a true Daughter of Dallas nobility but instead of resting on our laurels or trust funds, she’s worked tirelessly her whole adult life for people who haven’t been as fortunate, including being on staff at the International Rescue Committee and now as an Economic Empowerment Specialist at New Friends New Life, a group working to transition women out sex trafficking or exploitation.
 Justina Walford
Justina Walford
Justina is a former District 4 City Council candidate, Southern Dallas dog rescuer and advocate, and member of the Southern Sector Rising Campaign Steering Committee. She’s also Director of the annual Women Texas Film Festival. Born and raised in Southern California, Justina owned a theater in Hollywood during the early 2000’s where she produced full length plays and storytelling events that included her original work.
Amber W ang
ang
Amber has degrees from Rice in Mechanical Engineering and trouble-making from our own College of Constructive Hell-Raising. She’s Technology Manager at the Victory
Co-Working space Hatchways and has bravely decided to help us in developing more sustainable local funding source. At Rice Amber led a student design organization that developed pro bono solutions for nonprofit organizations and social ventures in the Houston community. We hope she can do the the same for us.
The Only Thing Missing in Dallas’ Climate Plan “Focus on Equity” is…any measure of Equity

A staff presentation focusing on Dallas environmental equity lacks any metrics for comparing residential pollution burdens, or even for measuring the success of its own outreach effort.
So how does City Hall know what environmental “equity” looks like?
According to management guru Peter Drucker, “If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.”
Then what does it mean that a full year into a Dallas climate planning process heavily touted as reflecting the city’s emphasis on “equity” there’s still no map showing how pollution burdens are distributed across Big D? And what does it tell you when a presentation meant to advertise the inclusiveness of the City’s outreach effort for its climate plan doesn’t document participation by residents of color?
It tells you that despite all the rhetoric on the subject, Dallas City Hall isn’t serious about environmental justice yet.

Office of Environmental Quality and Sustainability Susan Alvarez presents the City’s climate plan through “an equity lens.”
Exhibit A: “Dallas’ Climate Action Through an Equity Lens.” 



This was a presentation that Susan Alvarez, Assistant Director of the City of Dallas Office of Environmental Quality & Sustainability, gave as part of Eastfield College’s Sustainability as a Social Justice Practice: Developing Resilient Strategies held last Friday, November 8th.
Context is everything and so it’s important to note that the entire thrust of both the Conference and the City’s specific presentation was aimed squarely at how to respond to current environmental challenges in an equitable and just way. Here was a chance for Dallas OEQS city staff to display their embrace of equity as it relates to the climate plan it’s been paying a half-million dollars to consultants to construct. It was their very own EJ report card.
Equity and the Climate Plan:
And sure enough, there was no turning away from Dallas’ racist history in Alvarez’ presentation. Maps showing the City’s chronic segregation and poverty were included, as well as allusions to the Trinity River as the city’s dividing line between Haves and Have-Nots. Alvarez spoke about the current “Redlining Dallas” exhibit at City Hall that traces the City’s history of racism across 50 feet of photographs and stories.
In fact, just about every impact of the City’s official segregation was referenced, except for the one you’d expect.
There was not a single slide or sentence expended on the disproportional environmental impacts of 100 years or more of Dallas racism. No maps of where heavy industry zoning is allowed in the City. No maps of where most of the City’s largest polluters are located. No maps of what zip codes or Council Districts have the highest pollution per capita numbers. No references to past environmental justice struggles with the City like the West Dallas RSR fight, or gas drilling.
Watching the presentation you’d get the impression that racism infected every aspect of life for Dallas residents of color except for their exposure to pollution. But of course, we know that’s not true.
During this and other presentations on the climate plan-in-progress, staff go out of their way to point out that industry makes up “only 8% of emissions.” But if you’re interested in applying “equity” to this number the next slide should show the audience where that industry is distributed in Dallas – a map showing you where industrial polluters are allowed to set-up shop. A slide to show you the amounts of permitted pollution by Zip Code, or maybe actual 2017-18 emissions by Council District. But there is no next slide.
If there were, it would show that most of that industry is located in predominantly Black and Brown neighborhoods. Racist zoning is at the heart of not just banking, education, and employment inequities in Dallas. It also means the dirtiest industries have always been located in close proximity to people who were institutionally considered Second-Class citizens.
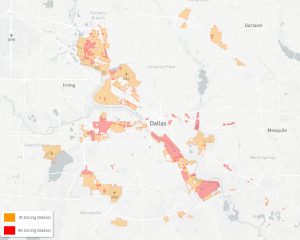
This one slide is already more information on Dallas environmental equity than you’ll find in the entire City staff presentation on equity and the climate plan
Disproportional exposure to industrial pollution by residents of color is not just AN equity issue. It’s THE single most important equity issue when you’re speaking about environmental justice in Dallas. The City’s Black and Brown residents are more likely to be exposed to harmful pollution than their white peers because the City’s own zoning designed it that way – but you’d never know it watching this presentation, on equity, at the social justice conference.
The “Redlining Dallas” exhibit that Alvarez cited thinks so. Along with other insidious effects of racism, it gives space to the RSR clean-up fight Luis Sepulveda and his West Dallas Coalition for Environmental Justice waged in the early 1990’s. But there was no mention of that fight or any other Dallas examples during the presentation on equity, at the social justice conference.

Staff referenced every other kind of red-lining on display at the City Hall exhibit – except the one most relevant to the topic.
Nor was there any mention of how much industry was located in the Trinity River floodplain, doing business in Black and Brown neighborhoods founded because the City wouldn’t allow these so-called “undesirables” to live anywhere else but side by side with “undesirable” industries. Alvarez made the point in the presentation that climate change means more flooding in general and more severe flooding. The next slide should show who and what is affected by that new flooding risk. A slide showing what percentage of heavy industry is located in the flood plain. A slide showing what the racial make-up and income levels are of those who’ll be more affected by increased flooding…and contamination. But there was no next slide, in the presentation on equity, at the social justice conference.
If you don’t have accurate maps of the inequities plaguing the status quo, how do you know when or if you’re ever getting rid of them? How do you judge success without a baseline?
PR, Process and Equity:“I don’t think it’s important to say I’ve got four black people in my stakeholders group.”
Alvarez lowered expectations for the presentation by saying it would only look at the question of equity in how it was applied to the City’s climate plan “community engagement.” No actual equity policy options from other plans were on the table, just how well the plan’s public relations campaign did.
Not very well, she admitted. In fact the initial meetings and publicity were so anemic that she said the professional PR folks at Earth X had a come-to-Jesus-meeting with staff about a reboot. So that’s tens of thousands of dollars wasted on PR consultants only to be usurped by better free advice from locals.

A meeting of the Dallas climate plan advisory group.
In her recounting of the climate plan’s PR rollout and planning process Alvarez gave an overview of the mechanics. “X” number of meetings attracted “X” numbers of people. The City’s survey got “X” number of responses. An “X” number of people serve on an advisory stakeholders group.
Considering the very specific circumstances of the presentation, the next slide should have been how the results of those attending meetings, or completing a surveys, or advisory committee memberships reflect Dallas’ population as a whole. How do we stack up to who we’re representing? According to the Statistical Atlas Dallas is approximately 25% Black, 41% Hispanic , 30% White and 3% Asian. So the next slide should compare what percentage of those attending climate plan meetings, or completing surveys, or becoming advisory committee members were Dallas residents of color vs the city demographics.
But there was no next slide about how inclusive the City’s climate plan community outreach or advisory process has been in the presentation on equity, at the social justice conference.
In response to a question about the lack of such information Alvarez said it was irrelevant to the topic at hand. “I don’t think it’s important to say I’ve got four black people in my stakeholders group.”
Since the advisory group membership is only listed online by organizational affiliation it’s impossible for anyone outside the meetings to know what the ethnic or gender make-up of it is. There are 39 separate entities listed. 25% of that number would be nine to ten black people.
In elaborating, Alvarez challenged the idea that mapping Dallas’ racial or ethnic disparities in pollution  burdens was necessary to understanding “Dallas’ Climate Action Through an Equity Lens.” She more or less stated it didn’t matter. (the presentation was recorded by Eastfield College and Downwinders has asked for access to it in order to quote Alvarez accurately).
burdens was necessary to understanding “Dallas’ Climate Action Through an Equity Lens.” She more or less stated it didn’t matter. (the presentation was recorded by Eastfield College and Downwinders has asked for access to it in order to quote Alvarez accurately).
Nothing could better summarize the kind of Catch-22 “don’t confuse me with the facts” approach to “equity” the City staff has taken in regards to environmental racism than the belief that actual data about Dallas environmental racism is of no use to the study or remedying of Dallas’ environmental racism.
And nothing makes a better case for the need to pass environmental justice reforms the Southern Sector Rising Campaign is advocating at Dallas City Hall, including an environmental justice provision in Dallas’ economic development policy, restoration of the Environmental Health Commission, and creation of a Joppa Environmental Preservation District. If residents want environmental equity considered in city policy they’re going to have to enlist their City Council members, do it themselves, and enact reforms like these.
The same is true as City Hall ramps up to take on citywide land-use planning in its “forwardDallas!” process early next year. When staff recently released the City’s “equity indicators” report, there was an indicator for everything but the environment. It only reinforced the idea that the environment, and environmental justice, are still after-thoughts in Dallas city government. Residents will have to arm themselves with the information the City staff can’t or won’t provide. They should start with the recent Legal Aid report “In Plain Sight” that demonstrates deep neglect for code and zoning regulations in Southern Dallas.
And it also goes for the climate plan. Southern Sector Rising’s first recommendation for the city’s climate plan last May was “Remove industrial hazards from the flood plain.” On the other hand, the idea of land use reforms in the floodplain hasn’t appeared in any official literature or presentation associated with the city’s climate plan.
Grist recently published an article about the Providence Rhode Island climate planning process that looks to be the exact opposite of the model Dallas has adopted. But that city benefited from having an environmental justice infrastructure already in place when the climate crisis assignment arrived. Where’s the home for Environmental Justice in Dallas City Hall? Right now, it’s with staff that doesn’t think metrics about equity are important, in its presentation on equity, at the social justice conference.
Listen to Our New Chair Get Interviewed By D Magazine

Downwinders at Risk’s new Chair Evelyn Mayo gets a huge shout out in D magazine’s popular online manifestation with her very own “Earburner” podcast.
D magazine reporter Matt Goodman and D Managing Editor Tim Rogers interview Evy about her new report on Southern Dallas zoning for Legal Aid, her Roller Derby years in Singapore, and of course, Particulate Matter.
CLICK HERE to link to the podcast and learn more about one the new dynamic leaders of Downwinders at Risk.
“SharedAirDFW” is DFW’s New Regional Air Quality Monitoring Network
Monitors are being assembled.
Software is being written.
Community meetings are happening.
Downwinders is helping build the region’s
first 21st-Century Air Network
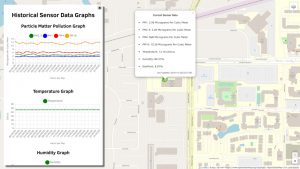
The first images from the mapping app UTD students are building for the new SharedAirDFW Air Quality Monitoring Network. Here data is being received by monitors already installed on the UTD campus. Residents will be able not only to see current conditions but levels over the last 24 hours or more.

One of the over 100 new SharedAirDFW air quality monitors being built in the UTD laboratory that will be distributed throughout DFW, including Joppa, West Dallas, Southern Dallas, and Midlothian.

UTD students working with Downiwnders’ consultant Robert “the map” Mundinger on the SharedAirDFW mapping app software and interface.

By this time next year the Network plans on having over its first 100 air quality monitors distributed throughout DFW, including the “front line” communities of Joppa, West Dallas, Southern Dallas and Midlothian.
____________________________________
Real Time Air Quality Information is Coming to DFW
It’s taken years of work and a lot of patience but with any luck a new citizen-friendly regional air monitoring network will debut in 2020.
Under the working title of “SharedAirDFW” over 100 new custom-built air quality monitors are being distributed throughout the DFW region in the next 12 months that will be able to give residents real time information about the air they breathe for the first time. When it’s up and running, it’ll be the first network of its kind in Texas and one of the largest in the U.S.
Based out of the University of Texas at Dallas laboratories and fueled by its graduate students, as well as Downwinders’ grant monies, these monitors will offer real time information through a easily accessible app.
Right now a handful of official EPA monitors provide air quality readings up to one or two hours behind real time conditions. SharedAirDFW willl increase the number of calibrated air quality monitors in DFW by a factor of four while giving readings updated every few seconds.
Almost half of the new monitors are going to front line communities in the DFW area: 33 monitors purchased by Downwinders are going to Joppa, West Dallas, and Midlothian, while another 11 purchased by Paul Quinn College are slated for the Southern Dallas neighborhoods surrounding its campus.
Joppa residents will get a preview of the system at a December 5th community roll out involving UT researchers, Habitat for Humanity, Paul Quinn, and local elected officials. Community events in Midlothian and West Dallas will follow.
This is one of the most important projects Downwiders has helped birth in its 25 year history. We’ll be bringing you updates as we get closer to bringing the whole system online. Thanks for you support.
The Only Public Hearing in the Nation on the Trump EPA Rollback of Methane Emission Rules for Oil and Gas is in Dallas: 8am to 6pm Thursday October 17th
 October 17th is also the date of the only public hearing being offered on one of the most far-reaching rule-rollbacks of the Trump administration – allowing more methane to be released from the nation’s oil and gas wells. And it’s right here in Dallas.
October 17th is also the date of the only public hearing being offered on one of the most far-reaching rule-rollbacks of the Trump administration – allowing more methane to be released from the nation’s oil and gas wells. And it’s right here in Dallas.
In August, the Trump EPA officially proposed its rollback of the methane emissions regulation put in place by the Obama administration. This one-day hearing in Dallas is the single chance for citizens to speak-up and be heard in person. You can bet industry will be out in force to support it.
As many of you already know, Methane pollution is less plentiful than CO2 but is approximately 85 times more potent as a climate destroyer. This is part of what makes it so important to decrease emissions.
But Methane is also a surrogate pollutant for a host of chemicals called VOCs – Volatile Organic Compounds – like the carcinogen Benzene. When you decrease methane emissions from an oil or gas well, you’re also decreasing VOC emissions across the board.
Many VOCs are dangerous toxins and as a class of chemicals contribute to smog. Downwinders at Risk landmark 2015 study of smog sources in DFW identified 50 tons a day of VOCs from regional gas wells and production facilities that contributed up to almost 4 parts per billion of smog.
 Rolling back the Obama Administration rule to limit methane emissions means more toxic exposures to thousands of residents in DFW living within hundreds of feet of wells and facilities. it also means our chronic, three-decade old smog problem, which got worse this summer for the first time in five years, will keep going further south.
Rolling back the Obama Administration rule to limit methane emissions means more toxic exposures to thousands of residents in DFW living within hundreds of feet of wells and facilities. it also means our chronic, three-decade old smog problem, which got worse this summer for the first time in five years, will keep going further south. It’s no coincidence that these hearings take place during working hours when professional lobbyists can attend but working people can’t. Nevertheless DFW residents must step up and represent all those folks from around the US who are not being given a chance to speak.
The public hearing will be held at the Earle Cabell Federal Courthouse, 1100 Commerce Street, in Dallas, in the Red River and Live Oak conference rooms on the 7th floor. According to the official notice, “Because this hearing is being held at a U.S. government facility, individuals planning to attend the hearing should be prepared to show valid picture identification to the security staff to gain access to the meeting room.”
To register to speak, you have to use the online registration form available at https://www.epa.gov/controlling-air-pollution-oil-and-natural-gas-industry/proposed-policy-amendments-2012-and-2016-new or contact Virginia Hunt at (919) 541-0832 to register to speak. The last day to pre-register to speak at the hearing will be October 14, 2019.
Testify downtown and then come and hear Dr. Bullard testify at Paul Quinn.
Dr. Robert Bullard in Dallas Oct 17th at Paul Quinn to Unveil New Report

Environmental Justice issues in Dallas will get a higher profile next week as the “Father of Environmental Justice” comes back to Big D to help promote the release of a new landmark report on zoning in Southern Dallas.
 Texas Southern University’s Dr. Robert Bullard is no stranger to DFW, having included a chapter on the struggle to get the West Dallas RSR lead smelter Superfund Site cleaned-up in his 1994 book “Unequal Protection.” But it was 1990’s “Dumping on Dixie” that’s widely recognized as the very first comprehensive look at what he termed “environmental racism” in the US – how rural Southern communities of color became national dumping grounds.
Texas Southern University’s Dr. Robert Bullard is no stranger to DFW, having included a chapter on the struggle to get the West Dallas RSR lead smelter Superfund Site cleaned-up in his 1994 book “Unequal Protection.” But it was 1990’s “Dumping on Dixie” that’s widely recognized as the very first comprehensive look at what he termed “environmental racism” in the US – how rural Southern communities of color became national dumping grounds.
Dr. Bullard returns to Dallas on Thursday October 17th for a full day of appointments and visits concluding with a presentation that evening at Paul Quinn College of a new Legal Aid of Northwest Texas report on the continuing impact of racist land use policy in Dallas’ “Southern Sector.”
Entitled “In Plain Sight” this Legal Aid effort is a blockbuster.
It’s the first close-up look at industrial zoning in Southern Dallas, comparing what’s on the books versus what’s actually taking place on-site. And it’s Dallas residents themselves who did the investigation, with teams of unofficial neighborhood inspectors visiting each site, taking pictures, and recording observations. In effect, it’s a citizen report card on the City’s enforcement of its own land use policies in the most neglected, abused parts of Dallas.
Inspired by the example of the now notorious Shingle Mountain illegal dump, which was allowed to operate by the City of Dallas without either the correct Certificate of Occupancy or the correct zoning, the study finds there are plenty of other examples of this kind of “non-compliance” throughout Southern Dallas. In fact, violation rates were found to be extremely high in some neighborhoods. It’s Exhibit A for why there must be systematic zoning reform in Dallas.
There are lots of events happening on the17th, but you really don’t want to miss the roll-out of this important, game-changing report and a chance to meet and talk to a living legend.

Marsha Jackson standing in her backyard
Update: A 21st Century Regional Air Monitoring Network for DFW is On Its Way
 me technical and bureaucratic hitches, momentum is starting to build toward the 2020 operation of a true 21st Century DFW regional air quality monitoring network.
me technical and bureaucratic hitches, momentum is starting to build toward the 2020 operation of a true 21st Century DFW regional air quality monitoring network.
A small army of University of Texas at Dallas graduate students are assembling over 100 solar-powered wireless air monitoring units to be dispersed throughout the metro area. A third of those have been purchased by Downwinders for placement in Joppa, West Dallas, and Midlothian. 40 or more or going to Plano. Three Dallas County Community College campuses are receiving one, along with the Fort Worth and Richardson school districts.
And now news has come that Paul Quinn College has received an EPA grant to purchase 11 of these monitors for placement around its Southern Dallas campus. Downwinders is working to coordinate the location of its Joppa area monitors with Paul Quinn to provide Southern Dallas with its own mini-network of monitors.
Meanwhile another group of UTD students are working on the mapping software and app residents will be able to use to access the data in real time. They’re being led in this effort by Robert “The Map” Mundinger, who Downwinders hired for the job. All in all, Downwinders has now invested almost $50,000 in this network, which we hope will become a model for the rest of Texas and the nation.
Texas Misusing 17-Year Old Rural Air Pollution Model to Permit Inner-City Joppa Asphalt Plant

One of these is not like the other
What if you found out an industrial polluter was operating in your densely-populated neighborhood and the state told you not to worry because an obsolete computer model of the polluter’s releases 17 years ago and 500 miles away, in a desert, performed by the polluter themselves, said everything was OK?
That’s exactly the situation Joppa residents find themselves in as the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) goes through the motions of renewing one of the permits of the many industrial polluters located in the community.
 Austin Industries’ asphalt batch plant sits next to the Marietta Martin (TXI) concrete batch plant in Joppa, and both are in the Union Pacific switch yard and all of those are adjacent to the giant Tamko asphalt roofing factory.
Austin Industries’ asphalt batch plant sits next to the Marietta Martin (TXI) concrete batch plant in Joppa, and both are in the Union Pacific switch yard and all of those are adjacent to the giant Tamko asphalt roofing factory.
Austin has applied to the TCEQ for a renewal of its 10-year old air permit for its Joppa plant and gave notice last December. Legal Aid of NorthWest Texas requested a contested case hearing on behalf of the Joppa Freedman’s Town Association and Downwinders at Risk requested one on behalf of resident Jabrille McDuffie.
To absolutely no one’s surprise, TCEQ’s Executive Director recommended against such a hearing at the beginning of August in comments mailed out to all parities. He argued that contrary to the opponent’s claims there was sufficient evidence that Austin Industries permit in Joppa was following the law and was “protective of human health.” Previous “air quality analysis,” the Executive Director says, have concluded such already.
The entire basis of that “air quality analysis” is the computer air modeling performed by Austin Industries’ hired contractors and supposedly double-checked by the state…in 2002.
Just like any other computer model, it all depends on the variables: volume of air pollution, local meteorology, stack height, local “receptors” aka people or animals who live by or near the facility, and even local terrain. Winds do one thing to air pollution on the open plains and another in the middle of a city block.
Because of these variables, an Exxon refinery that wants to build a facility in Houston with the exact same design as is has in Arkansas still has to submit a separate computer model to account for the distinct surroundings in the new location. The one from Arkansas just won’t do for Houston.
Or at least that’s the way things are supposed to work. But like so much else in Southern Dallas these days, things aren’t working the way they’re supposed to.
According to the TCEQ the Austin Asphalt facility is a portable asphalt batch plant operation. That means it wasn’t built specifically for its current Joppa site. It was moved there and it can be moved somewhere else.
In 2002 it first operated in Hockley County, a rural part of Northwest Texas near Lubbock some 400 miles west of Joppa. It moved to its current location in Joppa in 2008.
In 2002 the TCEQ let Austin Industries use what’s called a “SCREEN3” air model to determine if the air pollution from its asphalt batch plant’s was a threat to anyone in Hockley County. Again unsurprisingly, the firm hired by Austin Industries to do the computer modeling found it was “protective of human health.”
TCEQ says the Austin Industries’ asphalt plant has never been subject to any additional “impacts evaluation.” besides this 2002 review.
That means the only air modeling ever done for this Austin asphalt plant was while it was operating in rural Hockley County in 2002. There has been no air modeling of the plant since it came to Joppa in 2008.
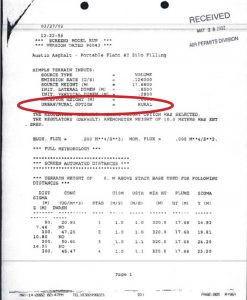
In 2002 the Austin plant was in West Texas and used a rural air model. In 2019 they’re still using for it for operation in Joppa.
Besides the most obvious and important difference in population density between unincorporated Hockley County near Lubbock and inner city Dallas, all of the variables in the 2002 modeling apply only to the Hockley County location. Meteorology, stack height, and surrounding terrain among them. In fact, the entire model was defaulted to a “rural” versus “urban” option in 2002. This renders the modeling scientifically useless in its current location in Joppa.
But that uselessness isn’t keeping the Executive Director of the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality from citing it to justify renewal of Austin’s air permit.
There’s also the matter of the age and limitations of the SCREEN3 model. In 2011 EPA replaced it with something called the “AERSCREEN” model. In doing so the agency called the old model “outdated“ and said “there are no valid reasons” to keep using SCREEN3.
And it’s not just the EPA. State environmental agencies, like the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality, have quit accepting SCREEN3 modeling.
Alex De Visscher, Associate Professor and Canada Research Chair in Air Quality and Pollution Control Engineering at the University of Calgary, writing in an 2013 text book entitled “Air Dispersion Modeling: Foundations and Applications,” said SCEEN3 is a “product of a previous generation of air dispersion modeling” and “is no longer a recommended model… it does not allow for multiple sources, and it does not include atmospheric chemistry or deposition.”
These exclusions are important. There are multiple sources of Particulate Matter 2.5 air pollution at Austin Industries’ plant in its Joppa location, including piles of raw material, and industrial combustion at the site. SCREEN 3 modeling didn’t and wouldn’t reflect these multiple sources of pollution. And of course when you’re talking about PM 2.5 pollution, as you are with an asphalt batch plant, the atmospheric chemistry and deposition, or fallout, is critical.
TCEQ’s own air modeling guidelines say so:
“Air dispersion models utilize dispersion coefficients to determine the rate of dispersion for a plume. Dispersion coefficients are influenced by factors such as land-use / land-cover (LULC), terrain, averaging period, and meteorological conditions. Evaluating the LULC within the modeling domain is an integral component to air dispersion modeling. The data obtained from a LULC analysis can be used to determine representative dispersion coefficients. The selection of representative dispersion coefficients may be as simple as selecting between rural or urban land-use types. For the ISC, ISC-PRIME, and SCREEN3 models, the dispersion coefficients are based on whether the area is predominately rural or urban. The classification of the land use in the vicinity of sources of air pollution is needed because dispersion rates differ between rural and urban areas.”
The TCEQ itself says it makes a fundamental difference whether the air model for a polluter is run for urban or rural terrain. Yet for over a decade TCEQ and Austin Asphalt have misused the results of a “rural” computer model to misleadingly assure inner-city Joppa residents that the company’s asphalt plant posed no harm.
What’s more, the modeling performed in 2002 only examined “asphalt vapors,” a made-up, vague pollutant category that can’t be monitored or measured. It didn’t examine Particulate Matter 2.5 pollution or specific Volatile Organic Compounds that make up those “vapors” and was therefore incomplete in the extreme.
So despite all the verbage the TCEQ’s Executive Director uses to tell Joppa residents th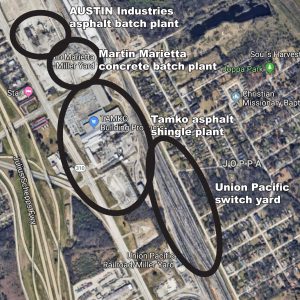 at past “air analysis” has shown Austin Industries’ plant to be protective of human health, in truth the only “analysis” ever done was performed 17 years ago in a sparsely-populated rural location 400 miles away from its current location, with what TCEQ admits are totally inaccurate modeling inputs by company consultants. It didn’t include all priority pollutants or even all sources of air pollution from the facility and the model used is now considered obsolete by EPA, modeling experts, and other state environmental agencies.
at past “air analysis” has shown Austin Industries’ plant to be protective of human health, in truth the only “analysis” ever done was performed 17 years ago in a sparsely-populated rural location 400 miles away from its current location, with what TCEQ admits are totally inaccurate modeling inputs by company consultants. It didn’t include all priority pollutants or even all sources of air pollution from the facility and the model used is now considered obsolete by EPA, modeling experts, and other state environmental agencies.
Joppa residents deserve better.
In its response to the Executive Director, Downwinders at Risk specifically requested TCEQ delay further regulatory action on this permit renewal until it can conduct a modern comprehensive air modeling impact analysis for Austin Asphalt’s current operation in Joppa that requires an evaluation of all on-site sources of pollution, including fugitive and mobile sources, on the Austin Asphalt site, off-site near-by sources of pollution within a three kilometer (1.86 mile) radius of Austin Asphalt’s facility, and representative monitored background concentrations obtained from local Joppa neighborhood monitoring as well as modeling of permitted maximums emission rates form all sources.
On September 11th the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality will take up the Austin Industries permit renewal at its headquarters in Austin. Both Legal Aid and Downwinders at Risk representatives will be present to answer any questions from the Commissioners but will not be allowed to make any statements. We’ll let you know the outcome.
One might reasonably ask why the City of Dallas itself isn’t fighting this permit renewal? After all in 2007, the city took on a string of proposed coal-fired power plants that it said would increase air pollution for Dallas. But to date that same city has never bothered to try and stop an industrial polluter from opening shop or renewing its permit in one of its most abused neighborhoods.
might reasonably ask why the City of Dallas itself isn’t fighting this permit renewal? After all in 2007, the city took on a string of proposed coal-fired power plants that it said would increase air pollution for Dallas. But to date that same city has never bothered to try and stop an industrial polluter from opening shop or renewing its permit in one of its most abused neighborhoods.
This dishonest use of a irrelevant model by the state’s discredited environmental agency shows why it’s imperative the City of Dallas – and all municipalities in Texas – change the way they do business and be proactive in addressing their environmental justice and environmental health issues in their own city limits.
Too often city representatives default to state or federal officials on the environment when they should be the first line of defense, not the last. City officials’ reliance on a failed state agency to perform its job as environmental protector is what caused Shingle Mountain. It’s what caused this situation in Joppa. To change that means changing both policies coming out of City Hall and current City Hall culture. Environmental Protection is a Do-It-Yourself proposition these days.
DFW Holcim Cement Plant Seeks to Burn 100% Petroleum Coke
Increases Predicted in Air Pollution, including 100 more tons of PM a Year
Holcim Cement’s Midlothian cement plant has requested a permit application to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to release an additional 2700 tons per year of Carbon Monoxide and burn 100% Petroleum Coke in its Kiln #2. Holcim estimates these change will set of federally-mandated reviews for increases in emissions of Particulate Matter (PM), Nitrogen Oxide (NOx), Sulfur Dioxide (SOx), and Carbon Monoxide (CO).
Notice of the company’s permit amendment was published in the Midlothian Mirror earlier in the  month.
month.
Holcim is one of three very large cement plants doing business just south of I-20 in Midlothian in what is the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. The other two are TXI and Ash Grove. These are not batch plants. These are where the batch plants get their product. With annual air pollution emissions in the thousands of tons, any one of these kilns would easily be the largest “stationary” industrial source of air pollution in North Texas. Combined, they represent a mega source of air pollution for DFW.
Review of the numbers in the permit application show the company wants to scrap its current limit of a little over 4000 tons a year for Carbon Monoxide and replace it with a higher 7112 ton per year ceiling. In addition, the difference between actual emissions and proposed changes could result in 100 tons more of Particulate Matter, 260 more tons of smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide, and 1700 additional tons of Sulfur Dioxide.
 Missing from the permit analysis is the impact of the changes on CO2 climate crisis pollution. Petroleum Coke is nothing but carbon. It releases a lot of CO2 when burned. Burning 100% Petroleum Coke at Holcim will significantly increase this kind of air pollution. Cement plants are already a huge source of CO2 worldwide and Texas leads the country in CO2 pollution.
Missing from the permit analysis is the impact of the changes on CO2 climate crisis pollution. Petroleum Coke is nothing but carbon. It releases a lot of CO2 when burned. Burning 100% Petroleum Coke at Holcim will significantly increase this kind of air pollution. Cement plants are already a huge source of CO2 worldwide and Texas leads the country in CO2 pollution.
Overall, it’s the largest requested air pollution increase from any of the three Midlothian kilns in a very long time. And it reveals how badly the snake-bit 20th Century Holcim plant is aging.
Holcim’s current air pollution levels are already way out of sync with the other two, newer cement plants in Midlothian, and the Holcim facility has had a long troubled history with what its owners claim is a problem with the area limestone – the same patch of limestone the other two plants use. Holcim is already releasing 14 times the amount of four major air pollutants compared to Ash Grove’s 2014 renovated plant, and three times the amount of those same pollutants as TXI. This permit amendment would make the difference even starker.
Clearly Holcim has a problem child cement plant. Since Kiln #1 opened in 1999 it’s never performed to expectation. Because it would otherwise have set off a national non-attainment area for Sulfur Dioxide, Holcim had to add scrubbers to the plant before it even opened. When Kiln #2 was added in 2000, Holcim predicted it would cut pollution in half. Instead it doubled air pollution and by EPA decree the company had to add new pollution controls and buy Downwinders at Risk an independent scientist to monitor their operations. Now Holcim is saying their longstanding plan to reduce Carbon Monoxide pollution at that second kiln just didn’t work out and they need to increase their CO “permit allowables” by over 2700 tons a year.
Even for a very large cement plant, that’s a significant increase in pollution. CO pollution is a red flag for poor combustion, which is always worrisome when you’re looking at a facility of Holcim’s size that’s burning a flame at 2400 degree flame 24/7/365. Poor combustion at a cement plant burning tires and industrial waste, as Holcim does, or even coal and Petroleum Coke, means the creation of more “Products of Incomplete Combustion,” or “PICs.”
PICs are bad news. Dioxin – the poison in Agent Orange – is a PIC but there are thousands more. Some are extremely toxic. Holcim is already releasing 168 times more CO than the newer Ash Grove plant – located just across Highway 67, and nine times more than former Bad Boy TXI. That’s a lot of potential PICs. Something isn’t right in the basic design of the plant to make it so inefficient, but instead of investing in a new plant, Holcim just wants to increase its pollution levels.
There’s a second part of Holcim’s request that’s even more disturbing. Besides the increase in CO pollution, Holcim is seeking approval from the State to burn 100% Petroleum Coke as a fuel for its Kiln #2.
Cement kilns need a cheap source of fuel. Since 1960 the Midlothian kilns have burned gas, coal, hazardous waste, tires, used oil, car inards, plastic packaging, and other “industrial wastes” to keep a flame at 2400 degrees F or hotter. But never 100% Petroleum Coke.
Pet Coke is a refinery waste high in BTU value and sulfur content. It’s very dirty. It’s basically solid carbon. In the application submitted by Holcim, the company says Particulate Matter pollution could go up by 100 tons per year. There’s also a very good chance of increases in smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides and Sulfur Dioxide pollution. Separately there’s also a significant but undocumented increase in CO2 that will occur because of Pet Coke’s composition, so this is a very bad Climate Crisis move as well.
Holcim says not to worry – most of these increases are on paper only and they’re not really changing the emissions, just “refining them.” But with the plant’s history, it’s more likely air pollution will increase, and not by a little bit.
TCEQ’s permit engineer assigned to the Holcim case says this is only a preliminary application and that the company will have to answer more questions about pollution increases, and more importantly will have to stage a “test burn” to see what the impact of burning 100% Pet Coke will actually be (under ideal conditions when everyone is looking over their shoulder). Many long time observers of the modern TCEQ under Governor Greg Abbott are skeptical any of this will happen before Holcim gets their permit however.
Because of the increased volumes of pollutants, this application will be generating an official response from Downwinders requesting at least one public meeting for a briefing on the permit and objecting to any increase in PM and NOX, insisting on test burns using 100% Pet Coke before the permit is approved, and protesting any increase in Climate Crisis pollution.
There’s two responses you can take right now to oppose Holcim’s permit amendment:
1) You can request a public meeting in Midlothian to have the TCEQ and company brief the public on the permit amendment and have the opportunity to ask questions
CLICK HERE TO SEND AN EMAIL NOW TO THE TCEQ
AND ALL LOCAL STATE REPRESENTATIVES AND SENATORS
Requests should be addressed to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality as well as local State Representatives and Senators – not just those representing Midlothian.
TCEQ:
By email:
https://www14.tceq.texas.gov/epic/eComment/
bbohac@tceq.state.tx.us
By mail:
TCEQ, Office of the Chief Clerk, MC-105, P.O. Box 13087 Austin, Texas 78711-3087
Texas State Senators
St. Senator Brian Birdwell/Midlothian: Brian.Birwell@senate.texas.gov, 512-463-0122
St. Senator Royce West/Southern Dallas County: royce.west@senate.texas.gov 512-463-0123
St. Senator Beverly Powell/ Southern Tarrant County: beverly.powell@senate.texas.gov 512-463-0110
Texas State Representatives
Rep. John Wray/Midlothian: john.wray@house.texas.gov 972-938-9392
Rep Yvonne Davis/ Southern Dallas County: yvonne.davis@house.texas.gov 512-463-0598
Rep. Carl Sherman/Southern Dallas County: carl.sherman@house.texas.gov 512-463-0953
Rep. Chris Turner/ Southern Tarrant County/Arlington: Chris.Turner@house.texas.gov 512-463-0574
Contact all of these folks individually, or you can send them and the TCEQ the same email requesting a public meeting on Holcim’s permt via Downwinders’ ClickNSend feature. Leave your own personal message too.
2) Request a Contested Case Hearing
If you feel you’ll be affected by Holcim’s new air pollution, you have a right to ask for a contested case hearing – a formal legal proceeding that sets a higher bar for Holcim to get a permit. In order to request a Contested Case hearing, you must send the TCEQ Chief Clerk:
1) YOUR NAME, or GROUP NAME
2) MAILING ADDRESS AND TEL #
3) APPLICANT’S NAME AND PERMIT #: Holcim, Air Quality Permit 8996 and PSDTX454M5
4) THIS EXACT STATEMENT: ” I/We request a contested case hearing.”
5) A DESCRIPTION OF HOW YOU WILL BE HARMED BY HOLCIM’S AIR POLLUTION
6) THE LOCATION OF YOUR HOME OR BUSINESS AND THE APPROXIMATE DISTANCE TO THE HOLCIM CEMENT PLANT TO THEM.
7) A DESCRIPTION OF HOW YOU USE THE PROPERTY AFFECTED BY HOLCIM’S AIR POLLUTION (HOME OR BUSINESS OR RECREATIONAL)
8) A LIST OF DISPUTED ISSUES
Example: 1. Any increase in PM Pollution from Holcim will be harmful to my health and enjoyment of my property, 2. There has been no evaluation of the PM, NOx, SOx, or CO emissions of burning 100% Petroleum Coke in Kiln #2, 3. There has been no evaluation of the burning 100% Petroleum Coke in Kiln #2 on increase in CO2 4. Holcim’s cement plant isn’t applying Best Practices and Best Available Control Technology for emission reductions of PM, CO, NOx, and SOx.
Send your request to the TCEQ’s Chief Clerk:
By email:
https://www14.tceq.texas.gov/epic/eComment/
bbohac@tceq.state.tx.us
By mail:
TCEQ, Office of the Chief Clerk, MC-105, P.O. Box 13087 Austin, Texas 78711-3087

