Nitrogen Oxides
Zombie Gas Permits on the March Again
Public (re)-Hearing on the Last Three Dallas Gas Sites.……including the newly-discovered "Rawlings Gas Refinery"
This Thursday
1:00 pm
Dallas City Hall
6th Floor
City Council Chambers
Press Conference followed by City Plan Commission Mtg
This is the "do-over" hearing demanded by the Mayor in order to win approval of these permits – after the first one in December resulted in denial.
Come and defend this victory or they'll steal it away from us.
Dallas Residents at Risk, the alliance of groups that we work with on this issue, will be holding a press conference at 1:00 pm – just like we did before the much-publicized January 10th reconsideration vote – and then heading into the CPC meeting at 1:30. Show up early because we'll be talking about a surprising new development in this fight and bringing you up to date with the latest information.
It's important to demonstrate that opposition to these permits is growing, so if you haven't made it down to City Hall before, Thursday is the day to come.
If you're a regular, then you know how much warm bodies in the audience mean to the moment.
They would have been no news coverage on the 10th without all of us standing up and publicly "shaming" the CPC over its "reconsideration vote" in person. You can't do that by e-mail or petition. We need you there. We need you clapping for the good guys. We need you hissing the bad guys. We need you. There is no substitute.
Looking for material for your testimony? Here are some things we know now about these sites that we didn't when the CPC turned them down in December…..
* Neither the Park Board nor City Council ever voted to allow surface drilling in parks. In fact, city staff assured the City Council in 2008 that would be NO surface drilling in parks. So where did Trinity East get the idea it could have two of its drill sites on city park land (The newly-named Luna Vista Golf Course and near-by gun range)? That's a really good question that nobody at Dallas City Hall has attempted to answer.
* One of the Trinity East sites now contains a large gas refinery and compressor station in addition to a pad site for 20 wells. This facility will become the 10th largest air polluter in Dallas the moment it comes on line, releasing 75-100 tons of air pollution every year only 600 feet away from the City's new Elm Fork Soccer Complex on Walnut Hill.
* Last September, the City of Dallas denied a new permit to a rock crushing facility near the Elm Fork Soccer Complex because its 17 tons of annual air pollution was deemed too threatening for children's health. However, five months later, the city is advocating allowing the operation of a gas refinery and compressor station that is estimated to release some 75-100 tons of air pollution a year. Why is 17 tons of air pollution a health threat but 100 tons is OK? Another great question nobody at Dallas City Hall has answered.
* Trinity East knew when it signed its leases with the City that drilling in parkland and the floodplains was prohibited. So why is the City of Dallas still saying its afraid of a lawsuit by Trinity for backing out of the deal if the permits are denied?
We can win if we keep showing up and asking questions.
Please show up this Thursday.
Guess What? That “Drilling” Permit is Really for a Refinery
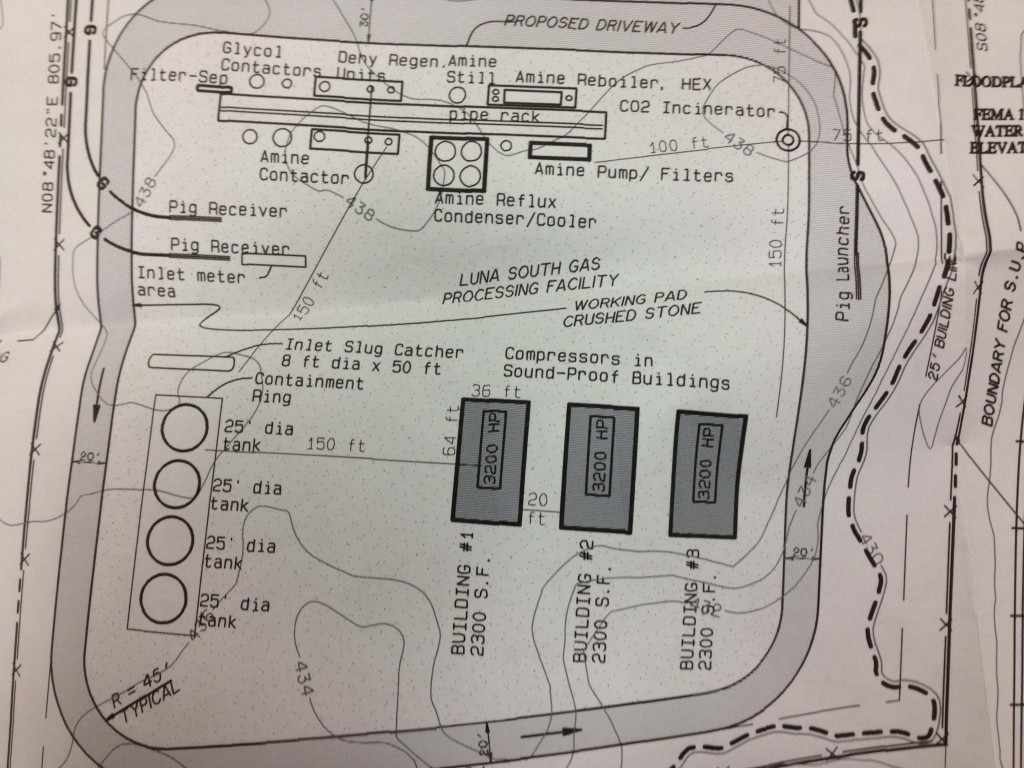 Under the guise of "gas drilling," Dallas City Hall and industry are pressing for approval of a permit that would locate a gas refinery only 600 feet from the new Elm Fork soccer complex, and immediately give birth to one of the ten largest air polluters in the City of Dallas, as well as one of its most toxic.
Under the guise of "gas drilling," Dallas City Hall and industry are pressing for approval of a permit that would locate a gas refinery only 600 feet from the new Elm Fork soccer complex, and immediately give birth to one of the ten largest air polluters in the City of Dallas, as well as one of its most toxic.
"There's a huge toxic Trojan Horse hiding in what the City and Trinity East describe as just a gas drilling permit," charged clean air activist Jim Schermbeck of Downwinders at Risk. "In fact, the Elm Fork permit allows for the building of a gas refinery that houses at least three giant compressors as well as an entire acid gas removal unit that strips off hydrogen sulfide, one of the most dangerous substances in the gas patch."
A motion to "reconsider" the Dallas City Plan Commission's 7-5 December 20th rejection of the Elm Fork permit and two other Trinity East gas sites is being advocated by CPC Chair and Mayoral appointee Joe Alcantar at this Thursday's meeting. If successful, the "reconsideration" would require the CPC to hold a second hearing and re-vote on the permits less than a month after denying them.
Opponents say the move is an act of desperation on the part of the Mayor and City Manager to protect a secret deal that was made between the City and Trinity East when the company first paid for mineral rights leases on city owned land. In interviews, the Mayor himself has said that a "deal was cut." Residents say the public was left out of that deal.
But after making calls to City Hall, Schermbeck is convinced that no one in Dallas city government is aware that the "gas drilling permit" being proposed by Trinity East is actually a permit to build a large gas refinery in the Trinity River floodplains.
"They're in way over their heads. City attorneys are still describing this as a drilling permit, but that's not what takes up most of the acreage on this site – it's all about the refinery."
During the December 20th City Plan Commission hearing on the permit, Trinity East representatives stated that the three proposed compressors alone – huge locomotive sized diesel-powered engines that produce thousands of horsepower in order to move gas through pipelines – would release 25 tons of air pollution each every year for an annual total of 75 tons.
That number would immediately place the facility among the city's ten largest air polluters according to the latest state emission totals from 2010. It would join power plants, asphalt and roofing materials manufacturers, and chemical plants as one of the city's biggest "stationary sources" of pollution.
However, Schermbeck thinks Trinity is low-balling their total air pollution impacts by not including other on-site refinery sources like its battery of storage tanks and "acid gas removal" operation that's designed to strip dangerous hydrogen sulfide off of natural gas streams through a series of acid baths and heat.
Hydrogen Sulfide is a harmful and toxic compound. It is a colorless, flammable gas that can be identified by its "rotten egg" odor. This invisible gas is heavier than air, travels easily along the ground, and builds up in low-lying, confined, and poorly ventilated areas. It acts as a chemical asphyxiant through inhalation exposure and its effects are similar to cyanide and carbon monoxide, which prevent the use of oxygen.
The equipment to strip off Hydrogen Sulfide from raw gas is large, complicated and dangerous. Site plans show a 200 foot long "pipe rack" with at least 20 "point sources" or stacks, apart from the compressors, where pollution could be released into the atmosphere.
"This isn’t a facility you want near parks or kids," said Schermbeck. "Yet, the City of Dallas seeks to put it just 600 feet away from its new huge soccer complex that’s meant to attract thousands of kids for hours every week."
Such a gas facility also challenges regional smog goals. A 2012 study from the Houston Advanced Research Center found that "routine emissions from a single gas compressor station can raise ozone levels by 3 parts per billion (ppb) as far as five miles downwind, and sometimes by 10 ppb or more as far as 10 miles downwind."
The Trinity East numbers don't reflect the release of greenhouse gas pollution either, which could be enormous from a facility the size of the refinery being proposed. Gas processing plants can release 20 to 80,000 tons of greenhouse gases a year. By comparison, the entire inventory of greenhouse pollution from all Dallas industrial sources in 2005 was 25,000 tons a year.
None of this information was brought up at the December 20th CPC hearing on the Elm Fork permit because the permit request in its current form was only a couple of weeks old when it went to the CPC and the compressors were a last-minute addition to an older, pending request.
Citizens were lucky to get a crowd to even show up five days prior to Christmas, and Schermbeck believes no one at Dallas City Hall bothered to notice that one of the so-called drilling permits was a refinery permit.
"Because it had no expertise of its own, and it was ignoring citizens, City Hall was completely reliant on the company's version of what the permit was for, and Trinity East probably didn't want to admit they were stuffing one kind of permit inside of another. The City didn't perform its due diligence. The result is that it's been completely played by the company."
Schermbeck recounted that he could find no one at City Hall who had any idea of how Trinity East arrived at their "25 tons a year" air pollution figure, knew what kind of specific pollutants that tonnage included, or, most importantly, thought it would be good to know this information before the city handed the company a permit to operate an inner-city gas refinery.
"Mayor Rawlings and the City Manager seem content to give Trinity East a blank check to pollute Dallas air," he said.
A closer look at the refinery site plans also reveals equipment that is fundamentally at odds with the way Trinity East and the gas industry has been portraying what kind of gas Dallas has underneath it.
Up to now, gas operators have been saying Dallas gas is "dry" and without a lot of extra hydrocarbons found in "wet gas" further west. But the acid gas removal units and Glycol conductors proposed for the Elm Fork refinery are built for wet gas.
Schermbeck suggests that perhaps either the City has been mislead about the nature of the gas it owns or the nature of the Trinity East site. He theorized that instead of the Dallas refinery being built for dry Dallas gas, it might be aimed at wet gas coming from the west.
"Dallas would get none of the royalties, but all of the pollution."
Mad? Go to this link now and send an e-mail to the Dallas City Council and City Plan Commission that says you oppose these gas permits and the "reconsideration" of their denial by the Commission:
https://www.downwindersatrisk.org/featured-citizen-action
Do it Now.
Another Win for Your Lake of Air
 Late Thursday night Downwinders at Risk, as part of the Dallas Residents at Risk alliance, won a victory that citizens weren't supposed to win. Late Thursday night Downwinders at Risk, as part of the Dallas Residents at Risk alliance, won a victory that citizens weren't supposed to win.
Immediately after Thanksgiving, Dallas Mayor Mike Rawlings and City Manger Mary Suhm had plotted to speed the approval of the first gas drilling permit in Dallas. One left over from 2008 that would be exempt from the new drilling ordinance now in the works. One that included a compressor station and allowed for the drilling in city parks and flood plains. City Hall believed it had greased the tracks with threats of gas company lawsuits and given the City Plan Commission no choice but to approve the permit. Just to be sure, they scheduled the Plan Commission vote for December 20th, a time guaranteed to result in smaller crowds of opposition at City Hall. But something happened to make things go a little off-script. Responding to calls for help, enough Dallas residents showed up to articulately speak against the permit for more than an hour. They represented hundreds of neighborhood groups, the environmental community and public interest organizations like the League of Women Voters. If the raw numbers didn't match earlier attendance, the people that did show up represented real constituencies numbering in the thousands. When the vote was finally called at 7:30 pm Thursday evening, we won 7 to 5. The "grandfathered" gas drilling permit would not be approved by the Plan commission. To overturn this decision, the City Council must find 12 votes – a super majority – in favor of the permit at its mid-January meeting. This was not the result Dallas City Hall was counting on the Thursday night before Christmas. But thanks to supporters like you, it was the result that happened. Just as we mobilized opposition to Midlothian cement plant pollution, and helped organize Frisco residents to close down an obsolete and dangerous lead smelter, Downwinders is drawing a line in the Shale in Dallas and leading a push back against irresponsible urban drilling. And, against very long odds, we're winning….again. We do this to protect your lake of air. You ingest an average of 200 gallons of water every year, or about five bathtubs' worth. But you inhale approximately two million gallons of air every year – your own small lake of air.
In DFW, chances are your lake of air is going to have smog in it, along with some soot, some Sulfur Dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds, as well as an assortment of other manufactured If your tap water was dirty brown and had lots of particles in it, you'd probably choose to drink bottled water. But when the air is dirty brown and has lots of particles in it, your lungs don't have a choice about the air they can use. Downwinders at Risk is here for one reason and one reason only: to defend your lake of air. Whether your air is threatened by smelters, gas rigs, cement plants or too-common smog, we're working to clean it up. For our efforts, Downwinders was proud to receive the first-ever GreenSource DFW award for Outstanding Grassroots Group in 2012. Looking ahead to 2013, your lake of air faces new threats, including worsening new permits by the Midlothian cement plants to burn large volumes of industrial garbage, and indiscriminate aerial spraying of pesticides by local governments. Downwinders at Risk will fight these threats with the combination of good science and citizen activism that's made us the foremost clean air group in DFW. But we need your help to do it. Our work depends on contributions from folks like you who appreciate what we do. Our annual budget is usually only around $30-50,000. We do all the work we do with an amount of money larger groups spend annually on office furniture or travel. We don't get money from a parent group in Washington or New York. Our board members are all from DFW. They're ordinary citizens like you, not rich patrons. Small donations make up a very large percentage of what we take in every year. We couldn't do what we do without you. In the time it took you to read this message, you've inhaled a couple of more gallons of air. Don't you think it should be clean air? You keep supporting us; we keep working for you – and surprising the opposition with victories that citizens in Texas just aren't supposed to be able to pull-off. That's our promise. Thanks for your consideration and Please click here to safely and securely donate online, or send checks to Downwinders at Risk, PO Box 763844, Dallas, TX 75376. Your donation is greatly appreciated and will be wisely spent. Thanks.
|
Traffic Pollution Linked to Autism
 Along with a higher risk of asthma, children who are born and live their first year closer to major freeways also suffer a significantly elevated risk of autism. That's the conclusion of a new study by the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles.
Along with a higher risk of asthma, children who are born and live their first year closer to major freeways also suffer a significantly elevated risk of autism. That's the conclusion of a new study by the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles.
"Compared to 245 California children who were not autistic, the researchers found that 279 autistic children were almost twice as likely to have been exposed to the highest levels of pollution while in the womb, and about three times as likely to have been exposed to that level during their first year of life.
They found that children exposed to the highest amount of "particulate matter' – a mixture of acids, metals, soil and dust – had about a two-fold increase in autism risk. That type of regional pollution is tracked by the Environmental Protection Agency.
Volk and her colleagues also saw a similar link between autism and nitrogen dioxide, which is in car, truck and other vehicle emissions.
'This is a risk factor that we can modify and potentially reduce the risk for autism,' wrote Dawson in an email to Reuters Health."
It's been estimated by the Centers for Disease Control that autism affects one in every 88 children born in the United States.
A new federal Particulate Matter standard is under consideration by the EPA and could be announced this year. It's been linked to other neurological diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimers.
Red Alert for Dec 20th: Dallas Wants to Drill Like It’s 2009
 This is a heads-up to all Dallas residents: Dallas City Hall – the building, the people, everything – has climbed into a time machine and traveled all the way back to 2010.
This is a heads-up to all Dallas residents: Dallas City Hall – the building, the people, everything – has climbed into a time machine and traveled all the way back to 2010.
This has allowed the City council and staff to ignore citizen demands for a more protective gas drilling ordinance, the defeat of a council member who advocated drilling, the creation and conclusion of a task force for helping write a new ordinance, and a bunch of public hearings over the last two years – all so that Dallas City Hall can now just go ahead and do what the gas operators originally asked it to do at the beginning.
The first Special Use Permit request from a gas well operator to allow drilling in Dallas since 2010 will be on the agenda at the December 20th Dallas Plan Commission meeting at City Hall. It concerns a new request to drill by XTO (Exxon-Mobil) at the old Navel Air Station in southwest Dallas, near the Grand Prairie line, that was submitted on November 16th.
Time it's taken the City of Dallas to write a new drilling ordinance in Dallas: 24 months and counting
Time it took XTO to get its new drilling request heard despite not having that new ordinance yet: 20 days
You can read about the sudden jump into municipal action here behind the DMN paywall.
"XTO’s latest requests are apparently on a fast track, headed to the City Plan Commission….
A new, tougher Dallas drilling ordinance is in the works but has not been approved or even published for review, so the existing ordinance would govern the XTO applications, based on the city’s legal view that one set of rules should apply throughout the process."
Every Dallas City Council member appoints a representative to the City Plan Commission. Dallas residents should call their own City Council member (info here), or their Plan Commission appointee (download a list and contact info here) and tell them to reject this XTO request and any others that try to get processed before a new drilling ordinance is in place.
Here's the media release that Dallas Residents at Risk put out this morning about the sudden turn around:
Dallas Officials Consider Throwing Away Years of Work on New Gas Drilling Ordinance and Simply Let Fracking Begin
Have Mayor Rawlings and the Dallas City Council made a decision to move ahead with existing, pending and even new gas drilling applications without taking any action on the new “fracking” ordinance that has been in the works since 2010?
Two weeks ago, Exxon-owned gas company XTO filed a new gas drilling application—because their previous bid to drill at Hensley Field was denied by the Dallas City Plan Commission two years ago. Then the City Council appointed a special Gas Drilling Task Force, whose members met every week for eight months to consider proposals for a new ordinance. They finished their work in February of this year and issued their official recommendations, yet the City Council has not even begun drafting a new ordinance. The only rumored exception: City officials may consider simply changing the existing ordinance to allow fracking in floodplains, which would be necessary for gas company Trinity East to move ahead with its plans to drill in floodplain areas along the Trinity River. Neighborhood groups and environmental advocates say that’s unacceptable.
"This is the largest retreat of leadership that I can ever remember on such an important public health and environmental issue,” said Jim Schermbeck, Downwinders at Risk. “After three years of citizen complaints, a task force created, convened and concluded, expert and public testimony, and all Dallas residents get is a pair of shrugged shoulders from Mayor Rawlings and the Council? It's a bad joke."
There have been several major scientific studies surrounding the risks of fracking since Dallas officials began debating the new ordinance. Community leaders worry that new evidence pointing to health and safety risks for residents living near drilling sites will simply be ignored.
“So what if there's a 66% higher cancer risk within a half mile of a gas well; so what if already bad Dallas smog is made worse; so what if we still have no idea what chemicals will be used for fracking in Dallas,” said Claudia Meyer of the Mountain Creek Neighborhood Alliance. “It's as if the Mayor and Council are closing their eyes, plugging their ears, and desperately hoping to make all these new facts go away by just pretending they never happened.”
The new drilling applications leave Dallas officials exactly where they started, with the City Plan Commission being asked to shoulder the responsibility of deciding on whether to allow fracking to go forward. Advocates say the Commission should decline this offer and let the City Council do what it said it was going to do: Draft and pass a new gas drilling ordinance first.
“If we were only going to end up where we started, what was the point of a task force, or public hearings or anything that's happened since permitting stopped because the City wanted a new drilling ordinance,” said Zac Trahan with Texas Campaign for the Environment. “This is complete and utter dereliction of duty and public trust by the elected officials of this city on one of the most important public health and environmental questions to face Dallas in decades."
Does Pollution Discriminate? The Coal Plant Edition
 A new NAACP report examining the locations and impacts of all 378 coal-fired power plants in America found that those living near the plants were disproportionately poor and members of minority groups. More often than not, the worst-performing coal plants were also in predominately poor and minority communities.
A new NAACP report examining the locations and impacts of all 378 coal-fired power plants in America found that those living near the plants were disproportionately poor and members of minority groups. More often than not, the worst-performing coal plants were also in predominately poor and minority communities.
"Coal Blooded: Putting Profits Before People" failed 75 plants on their environmental justice impacts and found those same plants were responsible for a heavier pollution burden. 14% of sulfur dioxide emissions and 13% of all smog-forming nitrogen oxide emissions from all U.S. power plants came from just those 75 power plants.
The four million people living near those 75 plants are among the poorest and more isolated communities of color. The average per capita income within three miles of the 75 failing plants is $17,500, and nearly 53 percent of the people are minorities.
One of those 75 failing plants is in Texas according to the report's graphics, but the plants aren't listed by state in the Appendix. All coal fired plants in the immediate DFW region have been closed for a while based on their advancing age and voluminous pollution, but that may not be the case in places like San Antonio or Austin. Stay tuned for a clarification.
Hell Freezes Over: Why the New Federal Report on Midlothian Matters
Everything in italics and "quotation marks" below is a direct quote from the latest chapter of the ATSDR's (Agency for Disease Registry and Toxic Substances) "health consultation" on the impact of certain kinds of industrial air pollution on the local population.
You should take five minutes to glance over the sentences. They've taken a better part of a decade and a great deal of citizen persistence to make it to print. You can read them now only because of a petition to ATSDR by local Midlothian residents, spearheaded by Sal and Grace Mier in 2005, prompted the Agency to get involved.
They're also rarer than hen's teeth. Because the words actually come together in sentences to conclude human health was likely harmed by the pollution from Midlothian's three cement plants and steel mill, as well as recommend decreasing that pollution.
Among grassroots activists, ATSDR has a notorious reputation for issuing reports that are "inconclusive by design." The joke is that the agency never met a facility it couldn't learn to live with. And sure enough, previous chapters in this saga have disappointed. Just two years ago, ASTDR's shoddy work in investigating health impacts in Midlothian and elsewhere across the country was the subject of a Congressional hearing.
These ATSDR reports generate no new data. Instead, they are retrospective looks back at the available sampling/monitoring information and a piecing together of possible exposure paths and levels. As such, they're only as good as the data they can digest. In Midlothian's case, that means they're completely dependent on state monitoring – criticized by citizens for years as being inadequate. Nevertheless, with this latest report, citizens have been somewhat vindicated because of what even that inferior sampling revealed.
The health impacts described in this latest report are also limited to what are called "Criteria Pollutants" – old school substances like lead, soot, sulfur dioxide, and ozone that have been regulated by the Clean Air Act for decades. They do not apply to more exotic kinds of air pollution like endocrine disruptors, which there's little or no monitoring for at all.
So there are a lot of missing pieces, but the ATSDR's conclusions and recommendations have an impact on your lungs and maybe your own local fight, even if you don't have a Midlothian zip code. For the first time a federal agency known to avoid coming to any conclusion about anything was forced to say that human health was adversely affected by the operations of industry in Midlothian.
There's a public meeting on this report on December 6th from 7 to 8:30 pm at the Midlothian Conference Center.
Health Consultation/Assessing the Public Health Implications of the Criteria (NAAQS) Air Pollutants and Hydrogen Sulfide MIDLOTHIAN AREA AIR QUALITY MIDLOTHIAN, ELLIS COUNTY, TEXAS
NOVEMBER 16, 2012 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Division of Community Health Investigations
Recommendations:
"Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) should take actions to reduce future SO2 emissions from TXI to prevent harmful exposures."
"TCEQ should take actions to reduce future PM2.5 emissions from TXI and Gerdau to prevent harmful exposures."
"TCEQ should continue efforts to reduce regional ozone exposures."
"TCEQ should insure that levels of these air pollutants do not increase to levels of concern in the future."
"TCEQ should conduct ambient air monitoring to characterize exposures to persons located downwind of the Ash Grove and Holcim facilities and take actions to reduce SO2 emissions from these facilities if harmful exposures are indicated."
"TCEQ should conduct appropriate ambient air monitoring to characterize exposures to persons located downwind of the Ash Grove and Holcim facilities and take actions to reduce PM2.5 emissions from these facilities if harmful exposures are indicated. In addition, particulate matter monitoring is needed in residential areas that are in immediate proximity to the facilities’ limestone quarries."
"In ATSDR’s judgment, one notable gap in monitor placement is the lack of monitoring data for residential neighborhoods in immediate proximity to the four industrial facilities, where fugitive emissions (those not accounted for in stack emissions) likely have the greatest air quality impacts."
Human health was likely harmed, and is still threatened by industrial pollution from Midlothian
From Sulfur Dioxide:
"Breathing air contaminated with sulfur dioxide (downwind of TXI's cement plant and the Ameristeel steel mill) for short periods could have harmed the health of sensitive individuals.…ATSDR cannot determine if harmful exposures to SO2 have been occurring downwind of the Holcim and Ash Grove facilities."
"All 24-hour values in Midlothian were lower than EPA’s former standard. However, the World Health Organization’s health comparable guideline is 8 ppb (WHO, 2006). This value was exceeded at both the Midlothian Tower and Old Fort Worth Road stations in most years of monitoring through 2008…"
"Overall, in the years 1999 to 2001, Old Fort Worth Road (monitoring site north of TXI) ranked among the stations with the highest 24-hour average sulfur dioxide concentrations in the state. As sulfur dioxide emissions from TXI Operations decreased in following years, so did the measured concentrations at this station."
From Particulate Matter, or Soot:
"Public health concern is warranted for adverse health effects from long-term exposure to PM 2.5 in Cement Valley"
"In the past (1996–2008), annual average PM 2.5 levels measured were just below the range of concentration proposed by EPA for lowering the annual average standard…Moreover, many of the annual average PM 2.5 concentrations were above the more conservative WHO health guideline (10 μg/m3)."
"No PM 2.5 monitoring data are available to evaluate exposures downwind of the Ash Grove facility. Furthermore, although annual average PM2.5 levels detected at the Holcim monitor indicate possible harmful levels…."
"We estimated that annual average PM2.5 levels in the vicinity of the Gerdau Ameristeel monitor, from 1996 to 1998, could have ranged from about 22.6 to 26.4 μg/m3, which is above both the current and proposed EPA standard. Using EPA’s approach, the 3-year average level might have been above the NAAQS standard of 15 μg/m3 for these years in the vicinity of the Gerdau Ameristeel monitor. Applying this same approach to annual average PM10 data from other monitors suggests that PM 2.5 levels could have been close to the current and proposed PM2.5 standard, especially for the Wyatt Road, Old Fort Worth Road, Gorman Road, and Midlothian Tower monitors."
"Consistent with the other pollutants discussed earlier, the estimated annual PM 2.5 emissions listed for these facilities are among the highest for Ellis County and also rank high among industrial sources statewide."
From Lead:
"Past lead air exposures during the period 1993 to 1998, in a localized area just north of the Gerdau Ameristeel fence line, could have harmed the health of children who resided or frequently played in this area….In the mid-1990s, the lead levels measured in this area ranked among the highest lead concentrations measured statewide."
From Smog:
"Scientific studies indicate that breathing air containing ozone at concentrations similar to those detected in Midlothian can reduce lung function and increase respiratory symptoms, thereby aggravating asthma or other respiratory conditions. Ozone exposure also has been associated with increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, medication use by persons with asthma, doctor’s visits, and emergency department and hospital admissions for individuals with respiratory disease. Ozone exposure also might contribute to premature death, especially in people with heart and lung disease. School absenteeism and cardiac-related effects may occur, and persons with asthma might experience greater and more serious responses to ozone that last longer than responses among people without asthma."
"The Midlothian Tower site recorded ozone concentrations above the level of the NAAQS for several years (TCEQ, 2011b), and the Old Fort Worth Road site has been measuring ozone concentrations close to the level of the NAAQS. Based on the data from both monitors, from August 1997 to September 2011, the 8-hour EPA ozone standard has been exceeded 236 times."
From Breathing Multiple Pollutants:
"ATSDR believes that sufficient information exists to warrant concern for multiple air pollutant exposures to sensitive individuals, especially in the past….The ability of the scientific community to fully and quantitatively evaluate the health effects from the mixture of air pollutants people are exposed to is at least ten years away (Mauderly et al., 2010)……The current state of the science limits our ability to make definitive conclusions on the significance of simultaneous exposures to multiple criteria air pollutants. ATSDR’s conclusions are based on our best professional judgment related to our understanding of the possible harmful effects of air pollutant exposures in Midlothian and our interpretation of the current scientific literature; therefore, these conclusions are presented with some uncertainty."
From New Production:
"Reductions in SO2 levels in Cement Valley have occurred since late 2008 resulting in exposures to both sensitive individuals and the general public that are not expected to be harmful. These reductions may be caused, in part, by declining production levels at local industrial facilities. Future harmful exposures in Cement Valley could occur if production rises to at least previous levels and actions are not taken to reduce SO2 emissions."
Regulatory "Safe Levels" Very Often Aren't
"Past SO2 exposures were not above the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standard in place at that time but were above the current standard."
"Past lead air exposures were not above the EPA standard at that time but were above the current standard.…The scientific community now believes that the current standard (15 μg/m3) for fine PM (measured by PM2.5) is a better indicator of possible long-term health effects from PM exposures than was the former EPA annual average standard for PM10 (EPA, 2006b)."
Shocking Study: Air Pollution Regulations Improve Public Health
 One of the most basic arguments of industry opponents of clean air regulations is that they really don't do that much to improve public health. Given all the studies concluding that increases in air pollution lead to increases in illness and death, this argument is every bit as plausible as denying global warming at this point. But that doesn't stop industry and their supporters in elected office quit trying.
One of the most basic arguments of industry opponents of clean air regulations is that they really don't do that much to improve public health. Given all the studies concluding that increases in air pollution lead to increases in illness and death, this argument is every bit as plausible as denying global warming at this point. But that doesn't stop industry and their supporters in elected office quit trying.
Out of New York and via the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology comes a three year study (2004-2006) that tracks decreases in ozone pollution to increases in public health, specifically fewer hospital admissions for respiratory problems. Overall, a decrease of about 9% in ozone pollution lead to an 11% decrease in hospitalizations. That's significant, bordering on one-to-one percentage point drop.
The study followed the progress of the EPA's NOx Budget Trading Program (BTP), a cap and trade system established for East Coat states to help them reduce their ozone, or smog pollution, that ran from 2004 to 2008, when it was replaced by the older, Bush-era version of the EPA's cross-stare pollution rules. It looked at all of New York in terms of eight regions throughout the state. Drops in smog averaged 9% but were substantially lower during the critical summer "ozone season."
According to the folks at the Environmental Health News:
"Regulations do work to lower pollution, which in turn can improve respiratory health.
Ozone levels decreased across the state of New York and hospital admissions for respiratory disease dipped in half of the regions studied after the EPA's regulatory program started. There were also notable decreases in hospital admissions for certain respiratory illnesses, most age groups and most health insurance groups.
The reduced admissions for those on public assistance suggests that low income residents may have benefited the most from air quality improvements. This would be an important achievement since this group often experiences the highest air pollution exposures.
These results are consistent with the limited number of other studies that compare pollution levels and health before and after required air pollution reductions."
It says more about the opposition to new regulations that we still have to have studies proving that less crap in the air means less illness and death. This has been a settled scientific fact for some time. But Industry pays big money for it to be a still-disputed political fact.
GAO: Fracking is Overwhelming EPA, Has Many Unknown Risks
 GAO stands for Government Accountability Office. We bet you didn't think there was such a thing.
GAO stands for Government Accountability Office. We bet you didn't think there was such a thing.
The GAO is in business to issue reports on how government works and doesn't work. It's the audit and investigative arm of the Congress. Today comes news that the Office has issued two new reports on fracking – one on how federal regulators are coping with the new responsibility of overseeing so much new drilling in so many new places all at once, and one on the possible risks posed by fracking to the public health and the environment.
GAO says fracking is overwhelming the resources of the federal agencies assigned to watchdog the process and industry:
"Federal and state agencies reported several challenges in regulating oil and gas development from unconventional reservoirs. EPA officials reported that conducting inspection and enforcement activities and having limited legal authorities are challenges. For example, conducting inspection and enforcement activities is challenging due to limited information, such as data on groundwater quality prior to drilling. EPA officials also said that the exclusion of exploration and production waste from hazardous waste regulations under RCRA significantly limits EPA’s role in regulating these wastes. In addition, BLM and state officials reported that hiring and retaining staff and educating the public are challenges. For example, officials from several states and BLM said that retaining employees is difficult because qualified staff are frequently offered more money for private sector positions within the oil and gas industry."
And the GAO says there are a lot of unknown risks to fracking based on the evidence so far:
Oil and gas development, whether conventional or shale oil and gas, pose inherent environmental and public health risks, but the extent of these risks associated with shale oil and gas development is unknown, in part, because the studies GAO reviewed do not generally take into account the potential long-term, cumulative effects. For example, according to a number of studies and publications GAO reviewed, shale oil and gas development poses risks to air quality, generally as the result of (1) engine exhaust from increased truck traffic, (2) emissions from diesel-powered pumps used to power equipment, (3) gas that is flared (burned) or vented (released directly into the atmosphere) for operational reasons, and (4) unintentional emissions of pollutants from faulty equipment or impoundments–temporary storage areas. Similarly, a number of studies and publications GAO reviewed indicate that shale oil and gas development poses risks to water quality from contamination of surface water and groundwater as a result of erosion from ground disturbances, spills and releases of chemicals and other fluids, or underground migration of gases and chemicals. For example, tanks storing toxic chemicals or hoses and pipes used to convey wastes to the tanks could leak, or impoundments containing wastes could overflow as a result of extensive rainfall. According to the New York Department of Environmental Conservation's 2011 Supplemental Generic Environmental Impact Statement, spilled, leaked, or released chemicals or wastes could flow to a surface water body or infiltrate the ground, reaching and contaminating subsurface soils and aquifers. In addition, shale oil and gas development poses a risk to land resources and wildlife habitat as a result of constructing, operating, and maintaining the infrastructure necessary to develop oil and gas; using toxic chemicals; and injecting fluids underground. However, the extent of these risks is unknown. Further, the extent and severity of environmental and public health risks identified in the studies and publications GAO reviewed may vary significantly across shale basins and also within basins because of location- and process-specific factors, including the location and rate of development; geological characteristics, such as permeability, thickness, and porosity of the formations; climatic conditions; business practices; and regulatory and enforcement activities."
So now we have the Director of the US Centers for Disease Control's Environmental Health agency saying that, "We do not have enough information to say with certainty whether shale gas drilling poses a threat to public health," along with the GAO saying the extent of the risks posed by fracking to our air, water, and land are largely unknown. How many more red flags do you need?
Even a Few Weeks of Cleaner Air Can Make A Big Difference
 We can't tell you how many times a resident from DFW will go on a business trip or vacation to a less-polluted place and report an almost instant shedding of the ill effects of dirty air, only to have an almost equally fast re-acquaintance with those effects once they return. Could air pollution really make that much of a difference in so little a period of time?
We can't tell you how many times a resident from DFW will go on a business trip or vacation to a less-polluted place and report an almost instant shedding of the ill effects of dirty air, only to have an almost equally fast re-acquaintance with those effects once they return. Could air pollution really make that much of a difference in so little a period of time?
As it turns out, yes.
Via an new study recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers found that the Chinese government's decision to close down Beijing's polluting factories and take cars off the road during the 2008 Olympics resulted in a remarkable short-term improvement in cardiovascular health. It's the first major study to look at the immediate effects of air pollution in young healthy adults.
In a synopsis published by Environmental Health News, one of the authors describes the study and its importance:
"For the 5-month study from June to November, the researchers recruited 125 resident doctors with an average age of 24 from a centrally located hospital. Half were male, and all were healthy with no history of diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
The researchers measured heart rate, blood pressure and six markers of cardiovascular diseases in blood samples before, during and after the games. The markers included C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, soluble CD40 ligand, soluble P-selectin concentrations and white blood cell count (WBC).
Two markers associated with blood clotting significantly decreased from pre-Olympic to the during-Olympic period: P-selectin levels dropped by 34 percent and von Willebrand factor levels were reduced by 13 percent. After the games, when the pollution control measures were removed, most markers rose back to pregame levels. But two markers – P-selectin and systolic blood pressure – worsened and showed a significant increase compared to the levels during the games.
Air pollution emissions were also measured at similar times. Levels of most air pollutants during the games decreased up to 60 percent compared to their pregame levels, depending on the type of pollutants. For example PM2.5 dropped 27 percent, nitrogen dioxide 43 percent and sulphur dioxide 60 percent. After the games when pollution controls were removed, emissions rose to higher levels than were measured before the games started.
This study suggests that even young healthy people can benefit from short-term air pollution reduction and supports efforts to quantify and understand the benefits and costs of air pollution control measures."
The next time a politician complains about the cost of air pollution controls, make sure and ask them if they're for preventative heart disease treatment. When they say yes, please remind them that keeping crap out of our air that would otherwise end up in our lungs is such preventative care.



