Posts Tagged ‘Coal’
Bring the East Texas Coal Plants into DFW’s Smog “Non-Attainment Area” and See How Long They Last……
 Want the Coal Plants to Face the Kind of Regulation
Want the Coal Plants to Face the Kind of Regulation
They've Been Avoiding for Decades?
Click here and send a formal comment letter demanding the coal plants
be included in the new DFW non-attainment area for smog.
Even as we're all waiting to see what EPA decides to do about the current Texas air plan for DFW under the current 75 ppb ozone standard, the regulatory process is gearing-up to administer the new 70 ppb standard.
One of the things which must be decided by the EPA are what geographical boundaries to use for the new standard when it comes to the DFW airshed and its chronic smog condition. Should they stick with the current 10-County configuration or should it be different and/or more inclusive?
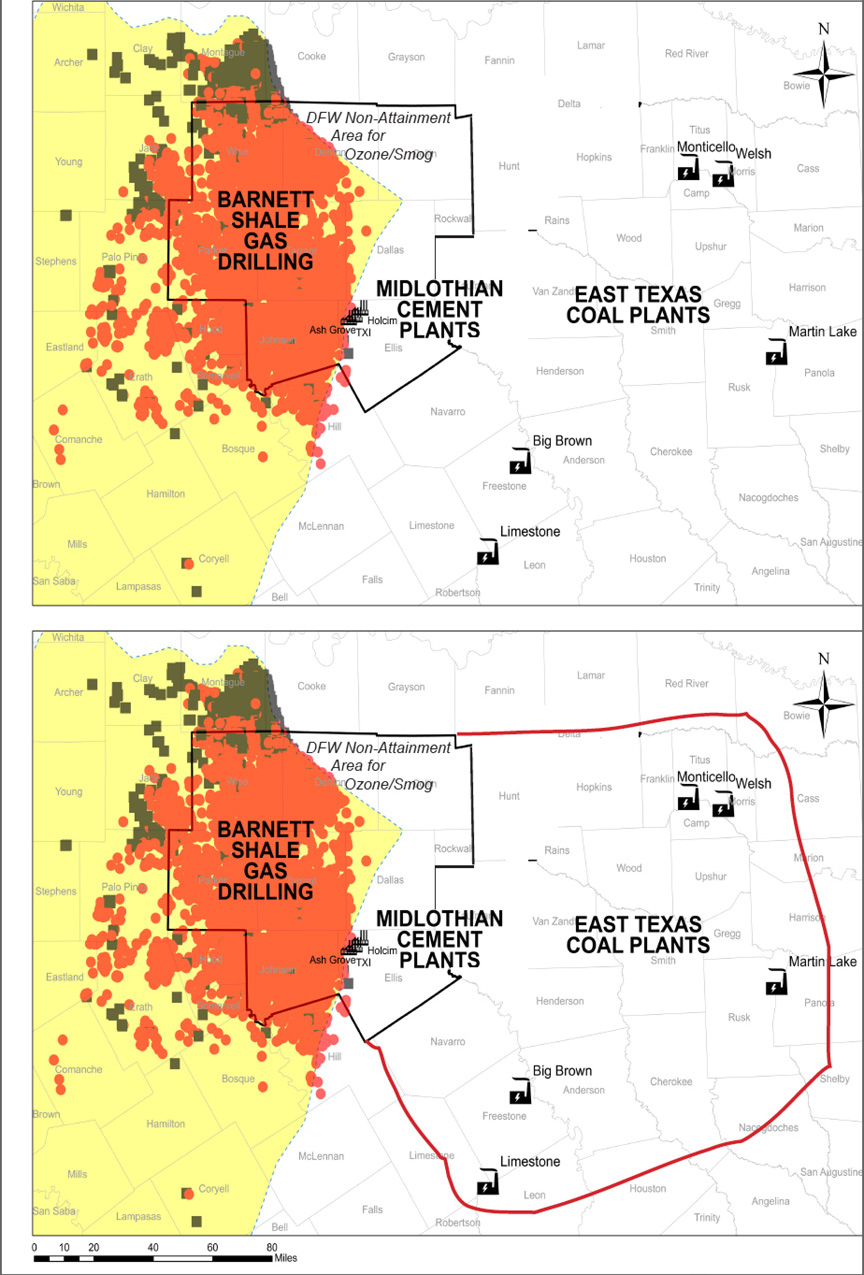
The history of DFW's smog fight is a lengthy chronicle of bringing new counties into the fold despite official resistance. Originally, the DFW non-attainment area was only Tarrant, Dallas, Collin and Denton. Then Rockwall, Parker, and Johnson Counties came in because of their commuter traffic.
Downwinders had to petition the EPA to bring Ellis County and its cement industrial complex into the non-attainment area early in this century after being told repeatedly by state officials that its pollution had no impact on DFW air quality.
More recently, the state argued against the inclusion of Wise County, despite its huge inventory of oil and gas pollution, population of commuters, and more than likely, the highest ozone levels of anywhere in North Texas. EPA decided to bring it in anyway.
We're once again at a crossroads, and it could be the most significant one in a decade.
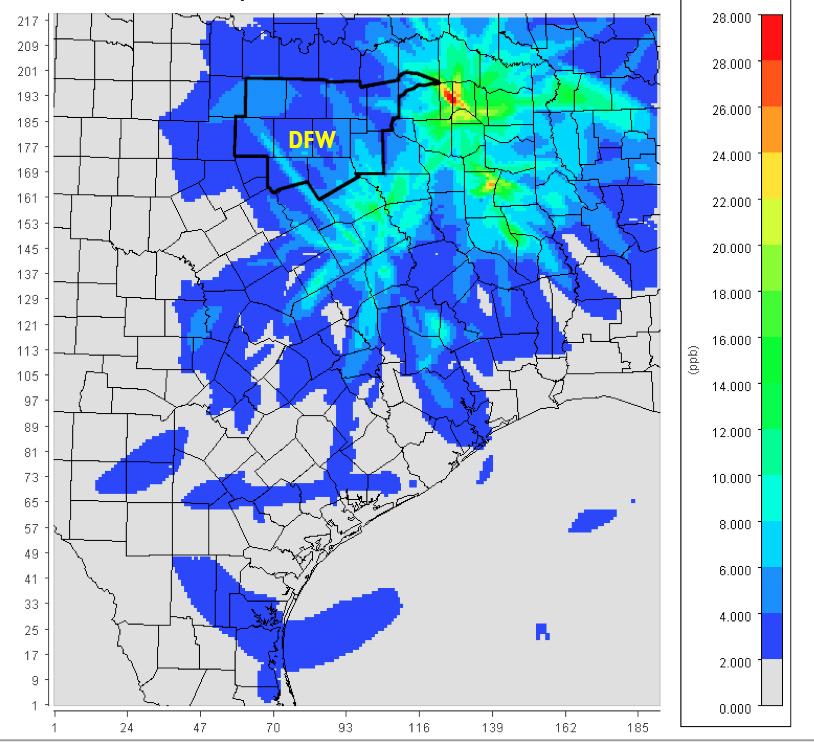 New evidence shows the huge impact the East Texas coal plants have on DFW air quality. Every scenario run by the UNT Engineering Department with the state's own DFW air computer model as part of Downwinder's Ozone Attainment Project demonstrates there's no more effective smog fighting strategy than reducing or eliminating the pollution from these coal plants.
New evidence shows the huge impact the East Texas coal plants have on DFW air quality. Every scenario run by the UNT Engineering Department with the state's own DFW air computer model as part of Downwinder's Ozone Attainment Project demonstrates there's no more effective smog fighting strategy than reducing or eliminating the pollution from these coal plants.
In fact, with a few other measures within the DFW area itself, controlling or eliminating their emissions could bring us in compliance with the 75 ppb standard, something that's not likely to happen otherwise.
Why is it so important to officially bring them into the DFW non-attainment area? Because major sources of pollution like coal plants are regulated differently inside than they are outside the area.
Right now, many DFW businesses are having to pay to operate and maintain pollution control equipment although most emit a tiny fraction of the pollution coming from the coal plants. That's because they're located in one of the ten counties in the DFW non-attainment area. They're held to a higher standard of control than their peers doing business outside those ten counties.
On the other hand, despite their large contribution to DFW's chronic ozone problem, the East Texas coal plants remain untouched by the same regulations and are not held to that higher standard. What sense does that make?
As much sense as it made to keep the cement plants out. As much sense as it made to try and exclude Wise County.
As per usual, the EPA is letting the state have first crack at defining a new DFW smog zone. The state has decided to leave the boundaries the way they are.
 Now, it's your turn to comment on that state decision, and tell Austin and the EPA – which will review the State's recommendations – what you think needs to happen.
Now, it's your turn to comment on that state decision, and tell Austin and the EPA – which will review the State's recommendations – what you think needs to happen.
The state is accepting comments on its decision until April 15th. This time, you can send your comments directly by e-mail instead of having to go through the official Texas Commission on Environmental Quality website
If you want to use our ready-to-send letter, all you have to do is CLICK HERE , sign the letter and add your own comments if you want. Then one more click and it's on it's way to Austin.
If you want to write your own comments:
EMAIL: kristin.patton@tceq.texas.gov
SNAIL MAIL: Kristin Patton, MC 206, State Implementation Plan Team, Office of Air, Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, P.O. Box 13087, Austin, Texas 78711-3087,
FAXED:(512) 239-6188.
All comments should reference "2015 Ozone NAAQS Designation Recommendations."
It’s a Texas vs EPA Cage Match. Winner Takes All …The Air You Breathe
 JOIN OUR TAG TEAM EFFORT TO TAKE DOWN THE STATE OF TEXAS
JOIN OUR TAG TEAM EFFORT TO TAKE DOWN THE STATE OF TEXAS
BUT WATCH OUT – THEY PLAY DIRTY
NEXT THURSDAY EVENING
JANUARY 21st
6:30 PM
616 Six Flags Road
First Floor HQ of the
North Central Texas Council of Governments
There's an important bureaucratic cage match between EPA and the State over how clean your air should be.
The state says just by hitching a ride on already-in-progress federal gasoline mix for cars and trucks, DFW ozone, or smog, will drop to levels "close enough" to the current federal smog standard of 75 parts per billion (approximately 78 ppb) . No new cuts in pollution required.
The EPA says not so fast – "close enough" may not be good enough this time around and you're not following the Clean Air Act in laying back and requiring no new cuts in pollution.
EPA has told Austin a failure to follow Clean Air Act rules will force it to take responsibility for the plan away from the State.
Is this something you want? If so, you should show up and next Thursday evening to give the EPA the political support it needs to pull the rug out from under the State.
WHAT HAS THE EPA ALREADY SAID ABOUT THE STATE'S PLAN?
Along with comments from DFW residents, environmental groups, doctors, industry and elected officials, EPA itself will weigh-in with written comments on the TCEQ plan by the deadline of January 29th.
But we don't have to wait that long to find out what EPA really thinks about what the State is proposing. Last year, EPA provided 11 pages of comments on exactly the same plan.
1) This plan won't work without more cuts in pollution
What EPA Said:
"Based on the monitoring data and lack of additional large reductions in NOx within areas of Texas that impact DFW, it is difficult to see how the area would reach attainment in 2018 based solely on federal measures reductions from mobile and non-road….The recent court decision that indicates the attainment year will likely be 2017 for moderate classification areas such as DFW, makes it less clear that the area will attain the standard by 2017 without additional reductions."
What EPA Meant:
It wasn't looking good when the deadline for reaching the 75 ppb standard was 2018 and the State didn't require any new cuts in air pollution, but now that the deadline is 2017, your do-nothing "close enough" plan is even less likely to work.
2) Your case for doing nothing isn't very good
What EPA Said:
"While the State has provided a large chapter on Weight of Evidence, the principal evidence is the recent monitor data. The monitor data does not show the large drops in local ozone levels and therefore raises a fundamental question whether the photochemical modeling is working as an accurate tool for assessing attainment in 2018 for DFW."
What EPA Meant:
Actual measurements of smog in DFW seem to undercut your claim that the air is getting cleaner faster. Maybe your computer model that's driving the entire plan isn't all that great. (And this was before smog levels went UP after the summer of 2015 – something not predicted by the State's model….)
3) Review pollution limits for the Midlothian cement kilns, or we'll reject your plan
What EPA Said:
"Because of significant changes in the type and number of cement kilns in Ellis County,…TCEQ's rules need to be reevaluated to insure these reductions are maintained, and the emission limits reflect a Reasonably Available Control Technology (RACT) level of control as required by the Clean Air Act…Failure to conduct a thorough RACT analysis for cement kilns which would include appropriate emission limits would prevent us from approving the RACT portion of the attainment plan submittal."
What EPA Meant:
Update your kiln pollution limits, or this part of the plan is toast. (Texas chose not to perform this update, in essence, giving EPA the bureaucratic finger.)
4) Oil and Gas pollution seems to be keeping the region's smog levels higher than they should be
What EPA Said:
"Recent NOx trends (Figure 5-10 in TCEQ's Proposal) indicate a fairly flat NOx trend for several NO monitors in the western area of the DFW area (Eagle Mtn. Lake, Denton, and Parker County monitors). These monitors are in areas more impacted by the growth in NOx sources for Oil and Gas Development that seem to be countering the normal reduction in NOx levels seen at other monitors due to fleet turnover reductions (on-road and Nonroad). These higher NOx levels in the modeling domain that seem to be fairly flat with no change since 2009
raise concern that the area is not seeing the NOx reductions needed to bring the ozone levels down at these monitors."
What EPA Meant:
Since the historically worst-performing air pollution monitors in DFW are located in exactly the same area as a lot of gas and oil activity, and these monitors haven't been seeing the expected decrease in smog you predict, maybe you ought to think about cutting pollution from those oil and gas sources. Like we said, this plan needs more cuts in pollution.
5) Your own evidence supports cuts in pollution from the East Texas Coal Plants
What EPA Said:
"The TCEQ provided an evaluation of emissions from all of the utility electric generators in east and central Texas. However, the discussion in Appendix D on the formation, background levels, and transport of ozone strongly supports the implementation of controls on NOx sources located to the east and southeast of the DFW nonattainment area. How would a reduction in NOx emissions from utility electric generators in just the counties closest to the eastern and southern boundaries of the DFW area impact the DFW area?"
What EPA Meant:
Despite your protests, the State's own analysis shows cuts in pollution from the East Texas Coal Plants have a big impact on DFW smog levels and supports the argument for putting new controls on them. Did you actually run your fancy-dancy computer model to see what would happen if you did that? (No, the State did not. But UNT and Downwinders did.)
WHY WOULD AN EPA PLAN FOR DFW AIR MAKE ANY DIFFERENCE?

If the EPA rejects the State's plan, the clock begins ticking: the State is warned it has to write a new plan and, meanwhile, EPA begins to write its own. If the State doesn't turn in a plan the EPA finds acceptable in 24 months, the EPA plan is implemented instead.
The State has no interest in any new cuts of pollution from any sources. It thinks it's plan is already "close enough."
If the EPA is writing the plan, citizens can use the new UNT study to show the Agency which cuts get the largest drops in smog – using the State's own air model.
We can use Dr.Haley's study to show the approximate economic and public health benefits of those cuts.
More change happens if EPA is writing the plan.Enough to finally get DFW safe and legal air? We don't know until we try. The alternative is doing nothing.
Expect Obama’s New CO2 Plan to Close Those Nasty East Texas Coal Plants? Don’t.
 By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
That's also true for Texas, where besides being Ground Zero for the fracking boom, we also have plenty of wind power and some solar. According to the EPA, the state must cut an annual average of 51 million tons of carbon to reach its target, a reduction of about 21 percent from 2012 emissions. We're well on our way to achieving most of that reduction with current or planned wind, gas, hydro, and solar. (In what might be a first concession that natural gas shouldn't be a long-term "bridge fuel," some analysts think tweaks performed by EPA prior to the Plan's release give more incentives to adopt real renewables earlier rather than leaning on gas in the interim.)
This is mostly good news. We want the wind and solar economies to grow. The trade-off is that, under Obama's Clean Power Plan, the rise of these technologies and their emissions reductions lets the obsolete East Texas coal plants off the hook because you don't need them to close to meet your CO2-cutting goals.
Five of those obsolete coal-fired power plants surround DFW's eastern side in a half circle (Big Brown, Martin Lake, Monticello, Limestone, and Welsh). They are, without a doubt, the worst examples of fossil fuel-generated pollution in Texas. They're huge emitters of Mercury, Particulate Matter (PM), Sulfur Dioxide (SOx), and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx).
These five East Texas coal plants are projected by the state to still be releasing 150 tons a day of smog-forming NOx pollution in 2018. Because of wind direction and volume, that pollution has a very large impact on DFW air quality – probably more than any other single phenomenon. We need those coal plants to either modernize or close ASAP to help solve our chronic smog problem. But from the initial survey of the policy, the Clean Power Plan is not going to force that outcome.
While the Plan probably signals the end of any new coal plants any time soon, or at least none without CO2 solutions like sequestration or capture, the fate of existing coal plants, especially in a state like Texas, is more ambiguous. More likely, they'll continue to linger on, beneficiaries of friendly state-created policies designed to nullify the requirements of the Clean Air Act, like loosening their PM limits by magnitudes.
Now, you might think that a federal goal that's been mostly accomplished without doing anything new would be a no brainer in Austin, but there are increasingly fewer and fewer brains in Austin. Because the state's environmental agencies are now completely ideologically driven, common sense just isn't a factor anymore. Instead of asking "how can we best solve this problem?" the response is now to deny there's a problem at all and go about ginning up anti-federal hyperbole to better position yourself in the Republican Primary.
Consequently, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is seriously considering not turning in a required state plan of how to get the reductions needed by the deadline of 2030. If the state doesn't submit one of its own, then the EPA would write one for them. This has the business community in Texas a little nervous, since they have a lot more influence here than in DC. But citizens, which kind of anti-climate change plan would you rather have Texas abide by – one written by a state agency that denies climate change is happening and is doing everything it can to obstruct policies to prevent it, or one written by a federal agency that's actually acknowledging the obvious and doing something about it?
Regardless of whose plan does what by when, the East Texas coal plants look to be able to ride this federal policy out thanks to an almost two-decade homegrown drive to open up the state to renewables. If we want these coal plants to stop causing problems for us, we're probably going to have to find other leverage points.
One of these leverage points is demanding the state of Texas follow the law and require the coal plants install modern Selective Catalytic Reduction controls as part of the new DFW clean air plan it submitted to EPA this summer for approval. SCR could reduce smog pollution from these plants by 90%. So far, Texas has refused to even acknowledge the need to do so. EPA has requested the state change its mind – without success.
If it wants to, EPA can reject the state's plan for not including these new controls on the coal plants. But we have to encourage them to do so – by petition, and by e-mail.
Consider the five East Texas coal plants the energy sector equivalent of the obsolete "wet" kilns in Midlothian that burned hazardous waste for 20 years. They're technological dinosaurs, on their last legs, but still churning out tons and tons of harmful air pollution as they plod their way to the bone yard. The Clean Power Plan insures they'll be the last of their kind, but it's not a silver bullet.
Why DFW Residents Should Speak in Favor of a Lower Smog Standard at Thursday’s EPA Public Hearing in Arlington
All Day NATIONAL Public Hearing on a New Federal Ozone Standard
Thursday, January 29th, 9am to 7:30 pm
Arlington City Hall, 101 W. Abram
There are only three national public hearings on the possibility of lowering the national federal ozone, or smog, standard. One is in Washington DC, another is in Sacramento, California and the third is right here in Arlington, Texas. We need everyone that can come and speak for 5 minutes on the importance of cleaner air to do so. You know industry and elected officials hostile to the EPA and the Clean AIr Act will be well-represented
To secure your 5-minute speaking slot, e-mail Eloise Shepard and ask for one in the time period during the day on Thursday most convenient for you. Please do it asap: shepherd.eloise@epa.gov.
There are at least two very good reasons why North Texas residents should support a new lower smog standard of 60 parts per billion – the lowest standard under consideration by the EPA.
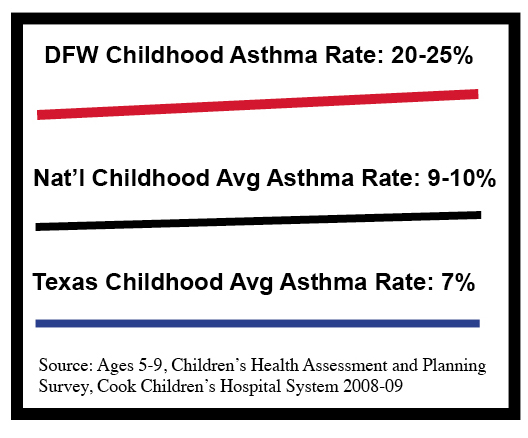 1. DFW has Epidemic Childhood Asthma Rates
1. DFW has Epidemic Childhood Asthma Rates
According to a first-of-its kind survey in 2008 by Cook Children’s Hospital, one out of every four DFW children ages 5-9 suffered from asthma. That was more than twice the national average, and more than three times the average for the state of Texas. Asthma is the most common cause of missed school days and is one of most common causes of Emergency Room visits and hospitalizations.
The DFW Hospital Council estimates nearly 1500 children in Dallas County visited an emergency room or were admitted to a hospital due to asthma in 2012. Dallas County has the highest number of child asthma hospitalization in the state.
According to EPA itself, a new 60 parts per billion (ppb) standard for ozone would eliminate roughly 1.8 million asthma attacks, 1.9 million missed school days, and 6,400 premature deaths nationwide – 95% of all ozone-related deaths. Few regions would benefit more from such a lower ozone standard than DFW.
2. It’s One of the Few Ways to Force Reductions in Harmful Air Pollution in Texas 
Texas is a place where industry rides rough shod over state regulators and citizens don’t have a level playing field to seek relief from the adverse health consequences of air pollution. Tougher federal ozone standards are one of the only ways to reduce air pollution from large local sources like the cement kilns in Midlothian, gas facilities in the Barnett Shale, and coal plants in East Texas.
Lower federal ozone standards over the last two decades, combined with grassroots campaigns have resulted in the lower volumes of smog pollution from the Midlothian cement kilns, plus reductions in other kinds of harmful pollution from the kilns as well, like particulate matter, and carcinogens. A new 60 ppb ozone standard would mean the kilns would have to add state-of-the-art controls to bring down those totals even more – to as much as 90% reductions. The same is true with the East Texas coal plants and with polluting gas facilities. To get down to 60 ppb ozone levels in DFW could mean deep cuts from the largest sources of industrial air pollution in North Texas. Something that probably won’t happen without a new, lower federal ozone standard.
And that won't happen without a lot of you showing up on Thursday to say you want and need cleaner air to breathe. Reserve your 5-minute speaking slot now. It's a good investment if you live in Texas.
Sloshing Back and Forth Between Coal and Gas
 Around 2003 or so, the Dallas Morning News editorial board convened a roundtable of air pollution stakeholders and more or less facilitated a discussion of what could be done to clean up DFW's dirty air. You see, the area still hadn't complied with the 1997 national smog standard and more and more official air quality monitors were in violation of it. Pretty much, just like now.
Around 2003 or so, the Dallas Morning News editorial board convened a roundtable of air pollution stakeholders and more or less facilitated a discussion of what could be done to clean up DFW's dirty air. You see, the area still hadn't complied with the 1997 national smog standard and more and more official air quality monitors were in violation of it. Pretty much, just like now.
There was a memorable moment when one of the "environmentalists" at the table noted that for decades the Texas utility industry had been primarily reliant on natural gas for its power source, then switched almost entirely to coal during the 70's and 80's, exactly when the nation's first national air quality standards were being written and enforced. "Part of the problem is that there doesn't seem to have been any planning for the consequences of the industry switching over from one source to the other just like that. It's like a frenzied mob group of stockbrokers running back and forth between bidders."
"That's the marketplace," huffed a utility industry representative. And indeed it still is. One frenzied run after another back and forth between the two largest sources of fossil fuel.
You know the scene in Pirates of the Caribbean, At World's End where the crew runs back and forth, from each side of the ship, until it eventually turns upside down? It's like that, only with money doing the running. And it never ends.
That DMN discussion was only a decade ago. What happened next shows how quickly those runs can reverse themselves and the conventional wisdom. Fracking technology delivered new shale plays that flooded the market with new gas. So much new gas, that the price of it dropped to historic lows. That caused a huge switch in the utility industry. Gas was cheaper, so the coal-powered plants started to close and be replaced by gas-powered plants. At the same time the chemical industry, which uses voluminous amounts of gas in production of plastics and other products, announced a new wave of domestic construction because of cheaper gas supplies in the US. Finally, in order to prop-up the low gas prices that that are killing profits, the gas industry itself promoted the fuel for transportation use and export.
And students, what happens when all these elaborate plans to take advantage of cheap gas begin to blossom? Demand increases. Cheap gas turns into not-so-cheap gas. And then coal begins to look pretty good again. All of a sudden it's the negative image of 2003, and all that money is starting to run toward coal as gas prices rise.
And what that means is that the higher methane levels causing climate change are replaced by higher CO2 levels causing the same climate change. This is why we need to get out of the rut we're in where our choices are determined by short-term financial gain and not long-term survival.
Government puts its finger on the scales in the marketplace all the time to help this or that industry. Without government guarantees, whole sectors of the economy would not be able to function in a completely unfettered market. This is what the CO2 cap and trade system was designed to do – make the marketplace respond to pressures put there by government in order to achieve a goal of reducing the stuff that will make the place we live less habitable. But it was all a communist plot,or something like that. So in the meantime, we continue to slosh back and forth.
From the Houston Chronicle comes this summary of the latest trends:
After years of declining greenhouse gas emissions, Texas and other states reported sharply higher levels of carbon dioxide in 2012 as electric generating plants began to use more coal when natural gas prices began to rise, according to a study released Thursday.
Citing research done by the Environmental Integrity Project, Texas once again led the nation in CO2 from power plants in 2012, emitting 251 million tons. Florida was a distant second at 120 million tons. Just five states accounted for one-third of the nation's CO2 power plant emissions. Besides Texas and Florida, they include Pennsylvania, Indiana, and Ohio. Needless to say. the old TXU plants in East and Central Texas run by corporate off-spring Luminant are the largest contributors.
The price of gas will continue to go up and coal will be competitive. Or maybe it will go down and coal won't be attractive. Maybe we'll be downwind of lots more coal plant pollution. Or maybe we'll all have a rig or compressor station in our backyard. Who can say? That's the marketplace! The question is, do you want to bet our survival on it?
Perry’s Coal Rush Ends With a Whimper, not a Bang
 In 2006, Governor Perry announced that he was going to fast track over a dozen new coal plant permits in East and Central Texas. There was an instant hue and cry. Not only citizens but cities protested. Believe it or not, the same Dallas City Hall now prostituting itself for gas refineries was actually out organizing a multi-municipality alliance with Houston against the coal plants and Perry. Downwinders launched its now infamous "Smokestack Love" cross-state tour, complete with a 16-foot long parade-quality float with a smokestack-inhaling Perry.
In 2006, Governor Perry announced that he was going to fast track over a dozen new coal plant permits in East and Central Texas. There was an instant hue and cry. Not only citizens but cities protested. Believe it or not, the same Dallas City Hall now prostituting itself for gas refineries was actually out organizing a multi-municipality alliance with Houston against the coal plants and Perry. Downwinders launched its now infamous "Smokestack Love" cross-state tour, complete with a 16-foot long parade-quality float with a smokestack-inhaling Perry.
Unfortunately, opponents weren't able to stop all the plants. A leftover 1980's permit for the Oak Grove lignite plant north of College Station did get approved over the objections of local landowners. But most were derailed by fierce resistance or lower natural gas prices brought on by the heavy exploitation of the Barnett and Eagle Ford Shale plays.
Last Thursday, the final domino of that proposed 2006 wave of new coal plants fell with the announcement that the White Stallion plant near Bay City was being canceled.
"The news marks a victory for opponents of coal in Texas, notably the Environmental Defense Fund and the Sierra Club, who have worked for years to oppose the White Stallion and other coal power projects in the state. At this point, there are no longer any major new traditional coal power plants planned in Texas. All of the new projects are primarily natural gas and wind power, with some solar."
Congratulations to all those who worked so hard to see these bad ideas finished off for good. But remember there are still older coal plants in East and Central Texas that are among the largest point sources of pollution in the state, and the nation. Having now eliminated new potential clean air threats from the last of the Perry-proposed coal rush, the Sierra Club is turning its attention to the existing plants that are long past their prime and need to be replaced with cleaner sources of energy.
