Posts Tagged ‘Greg Abbott’
A Guide to the State’s War on the Clean Air Act
 There's been a lot of activity lately on the many-fronted war the State of Texas is conducting against the Clean Air Act. What about a brief status report:
There's been a lot of activity lately on the many-fronted war the State of Texas is conducting against the Clean Air Act. What about a brief status report:
1) Mercury Rules
Thursday's headline was that Supreme Court Justice Roberts denied the attempt by Texas and 18 other states to delay the implementation of EPA's new, more protective limits on release of toxic Mercury pollution from coal plants. In 2013, three out of the top five largest Mercury polluters in the whole country were Texas coal plants.
It was only last summer that majority of the entire Court ruled EPA hadn't followed protocol in weighing costs to the coal industry versus public health benefits, and sent the standard back to the Agency to be rewritten. Not an especially big deal.
Texas, along with other states, sought an injunction from Justice Roberts to stop the timeline for implementation of the rules until the rewrite was finished. Roberts denied the request and so EPA is allowed to continue writing the rules and now expects to release the revised edition next month. One indication of how much trouble the rules are in, or not, is the speed and format of Robert's actions. He ruled on the case only a day after the EPA had submitted its brief, and ruled on it unilaterally, not bothering to convene the full Court.
The practical implications of the rules are reductions in the use of coal with higher Mercury content, better Particulate Matter pollution control equipment, and specific carbon absorption control technology aimed at Mercury. Many Texas coal plants have already taken steps to comply with the standards and it seems like almost all have applied for extensions to the original deadline.
2) Haze Rules
Earlier this week, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton announced the state was suing the EPA for rejecting its lackadaisical plan to protect national parks from haze air pollution, also mostly coming from coal plants. Just three Luminant coal plants – Big Brown, Martin Lake and Monticello – release 40% of all Texas’ Sulfur Dioxide air pollution.
Late last year, EPA announced it found the state's lightning-fast 140-year plan to do absolutely nothing somehow inadequate, and begin to draft one of its own that would require "scrubbers" for Sulfur Dioxide pollution at nine coal plants across the state. It also concluded Texas had intentionally downplayed the impact of the coal plants on park air quality in computer modeling submitted to EPA .
Texas is suing to prevent the EPA from enforcing its plan to require scrubbers and asking the court to accept the original Texas plan as reasonable. Pending.
3) Sulfur Dioxide Non-attainment Areas in East Texas
In mid-February, EPA announced it intended to declare areas surrounding three East Texas coal plants as out of compliance with national Sulfur Dioxide pollution limits and declared them in official "non-attainment" of the Clean Air Act. Big Brown, Monticello, and Martin Lake power plants were found to be causing the violations in ambient air quality using computer modeling results first run by the Sierra Club, and then analyzed by the EPA. Boundaries were drawn for the new non-attainment areas that include all or parts of Freestone, Anderson, Rusk, Gregg, Panola, and Titus counties.
Final action by EPA on the non-attainment area classification is scheduled for this summer. Then it will be up to the state to submit a plan for action. We can all write the script from there. It ends in a court ruling.
Eventually, these East Texas non-attainment areas are another tool by EPA's to raise the costs of operating the oldest, most polluting coal plants to better reflect their toll on public health. Plants could lower their Sulfur Dioxide emissions by importing more "Cleaner Coal" from Wyoming and/or paying for those scrubbers the Haze Rules requires too.
4) DFW Clean Air Plan
DFW is in "non-attainment" for ozone, or smog pollution. It has been since 1991. The State has submitted a plan to EPA that sits back and watches federal fuel changes reduce smog-forming pollution by 20-40 tons per day. The problem? EPA estimates it will take cuts of 100-200 tons per day to get down to the current ozone standard of 75 parts per billion. The state says it sees no reason for more cuts.
This is the state plan up for comment at the the now infamous "F*** the TCEQ" public hearing in Arlington in late January, with final submission to EPA by the state this summer.
But between now and then one of the headlines you should see will be EPA rejecting the part of the state's plan dealing with pollution control technology. EPA has already telegraphed their intention to do so, and they don't have to wait for the state's final submittal deadline to act.
This will, of course, be followed by the state's suing the EPA for daring to enforce the Clean Air Act when Austin won't. But it won't keep the EPA from doing exactly what it did in the Haze Rule fight – write its own clean air plan for DFW.
And that will be our chance to make the greatest leap forward in local air quality in a decade.
New Comments from EPA on DFW Air Plan: It Won’t Work
 This plan won't work.
This plan won't work.
That's the simple message from the three pages of new comments Region 6 EPA staff submitted to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality last month concerning its anti-smog plan for DFW.
That message begins with the cover letter, written by Mary Stanton, Chief of the State Implementation Plan Section for Region 6. "… additional local and regional ozone precursor emission reductions will be necessary to reach attainment by 2017."
How much in reductions? EPA estimates an additional 100-200 tons per day more in cuts of smog-forming pollution will be necessary to achieve compliance with the current 75 parts per billion ozone standard. "Without emission reductions on this scale, it is unlikely that the area will attain by the attainment date.”
To give you some idea of how large a number that is, TCEQ calculates that all gas and oil air pollution in DFW equals 78 tons per day, the Midlothian cement plants belch out over 18 tons per day, and all the power plants in the immediate DFW area, 21 tons per day. Totaled, those three sources add up to 117 tons of pollution a year.
All the cars and trucks on DFW roads are said to add up to 180 tons per day of pollution.
So the decrease in pollution EPA is saying is necessary to get down to the current ozone standard is huge.

But take a look at those obsolete East Texas coal plants outside the boundaries the DFW nonattainment area. TCEQ says they account for a total of 146 tons per day. Add Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) which can get you up to 90% reductions in coal plant emissions, or close them down completely, add decreases from new controls on the cement kilns and oil and gas sources, and you're well on your way to amassing 200 tons a day of cuts in pollution.
Which do you think is more attractive to most DFW residents: permanently parking their cars, or putting new controls on the coal plants? Even though the coal plants harm the whole DFW airshed more than any other major source, they're not held accountable to the same regulatory requirements as sources closer to the center of the urban core, but which have less impact. Our cars must have special gasoline formulas in summer, we have to have HOV lanes, and we still go through Ozone Action Days, but the coal plants party like it's 1979. TCEQ is taking a hands-off approach to the plants and as a result the DFW region will continue to be in violation of the smog standard or huge cuts from other sources will be necessary.
TCEQ could have added new controls to the coal plants to the plan, but it chose not to. In fact, there are no new controls in the state's plan on any major sources of air pollution affecting DFW. EPA's new comments go to the heart of that choice. "Without additional emission reduction measures, we don’t see how the area will meet the standard of 75 ppb by the end of the 2017 ozone season," writes EPA staff.
EPA goes on to say TCEQ's computer modeling supporting it's do-nothing plan is "unrealistic," severely underestimating future smog levels, and delivering projections of decreases "that seem unlikely to be reached."
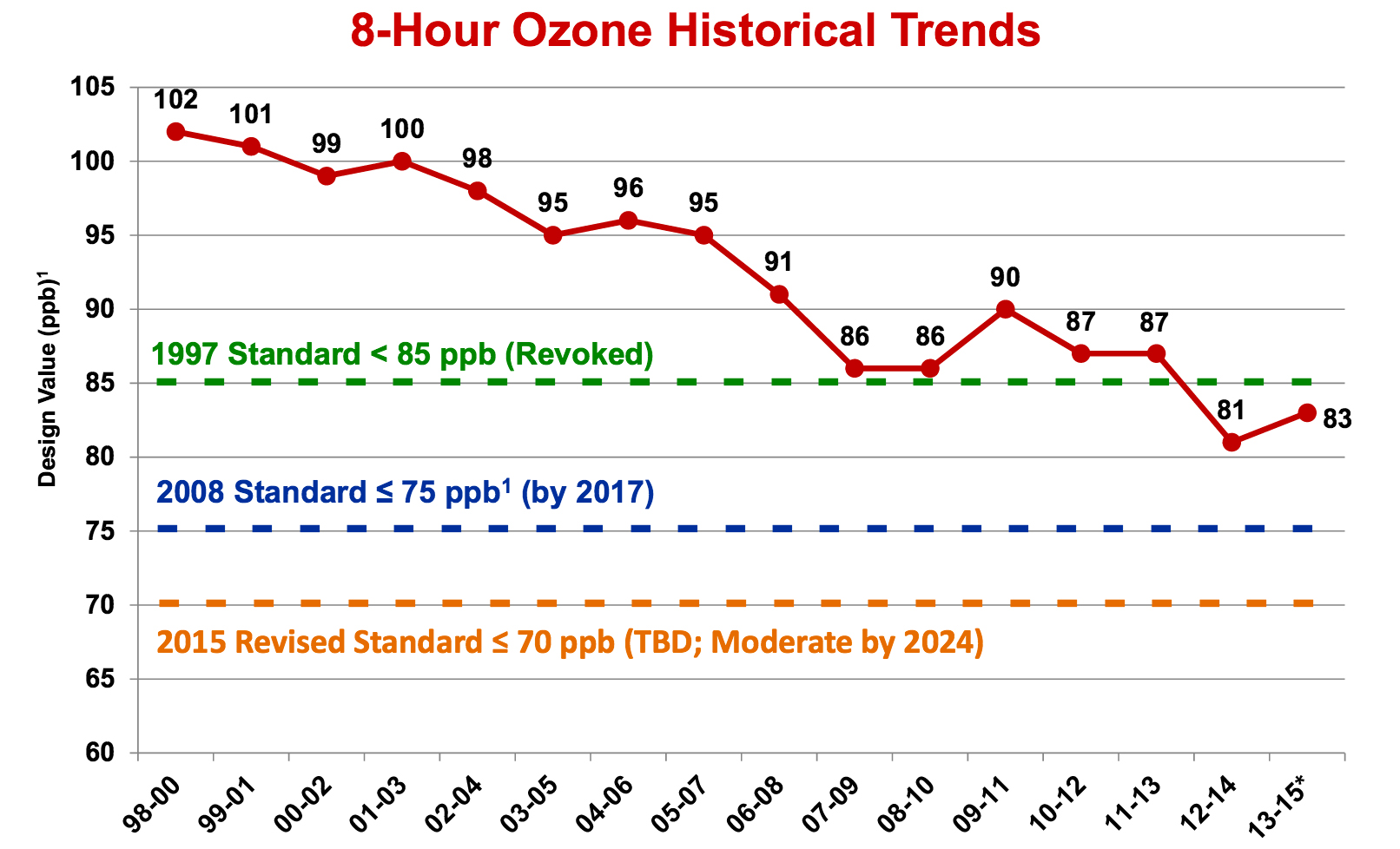 With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
That's the pattern TCEQ has already established with its "screw you" response to the EPA's comments about the part of the plan dealing with "Reasonably Available Control Technology," or RACT, last February. This second part decides what new controls should be required of major sources of air pollution within the 10-County DFW "non-attainment" area – like the Midlothian cement plants and the thousands of oil and gas facilities checkerboarding the western half of the Metromess.
TCEQ says nothing new is required. EPA disagrees. EPA told TCEQ last year it had to do a new RACT review and lower the kiln's emission limits to account for a new generation of technology or it would have to reject the state's plan. TCEQ ignored the request, daring the EPA to disapprove. EPA seems more than willing to take them up on the offer.
And so while you're waiting for the state's computer modeling and suspect math to be rejected by EPA in July, you can probably expect to see EPA officially rejecting the RACT part of the state's plan sooner – maybe as soon as the next 60-90 days.
Despite the TCEQ going out of its way to submit an unacceptable plan to EPA, if the Agency pulls the trigger and begins a federal takeover of the DFW air plan, the Commission and the whole of Texas State Government will cry bloody murder about the usurpation of the state's authority and once again proclaim how "out of control" the EPA is on their way to filing suit.
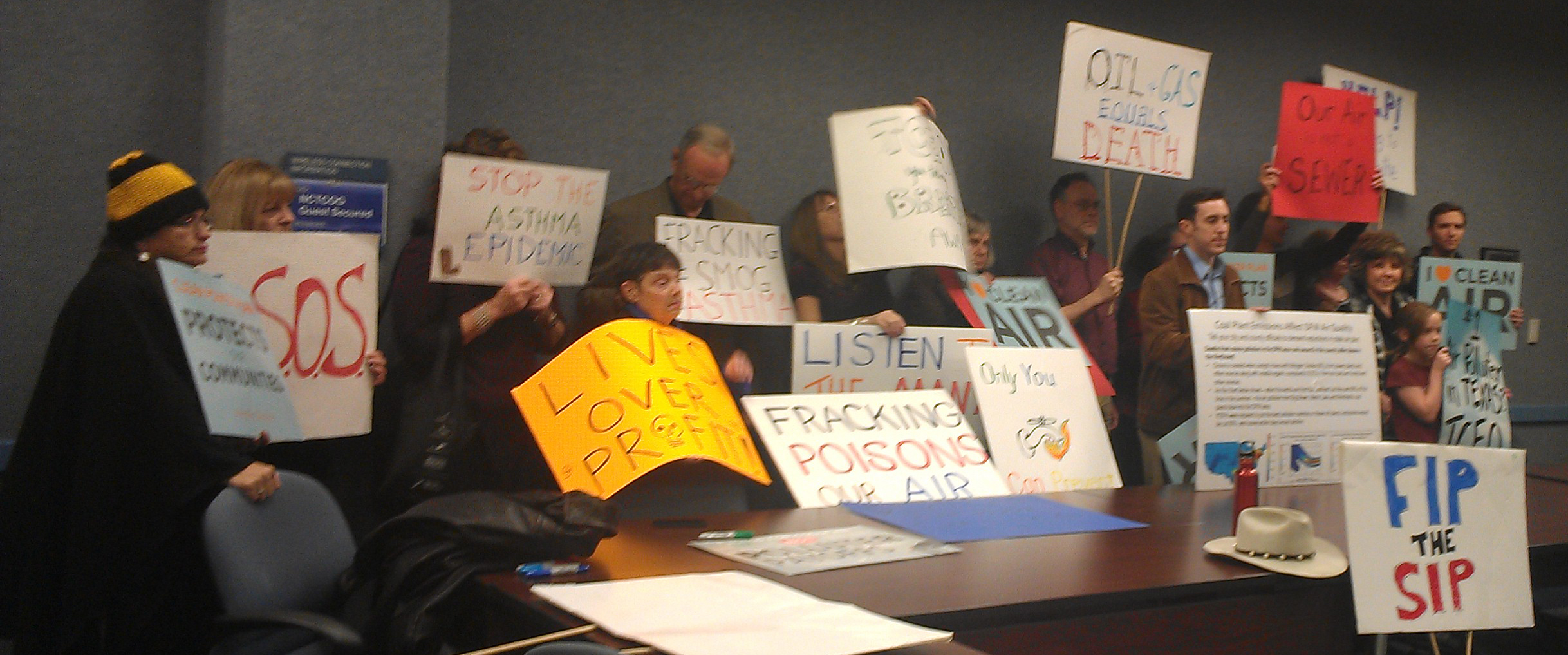 This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
And as always, it's why you, and people you know should:
State Re-Submits Illegal DFW Smog Plan, Dares EPA to Reject It

(Dallas)– In an unprecedented rebuke to the Environmental Protection Agency, Texas has refused to provide critical data EPA says it needs to approve the state’s controversial anti-smog plan for DFW, which requires no new pollution controls despite more than two decades of chronic bad air.
Texas' refusal to cooperate with EPA puts its plan, scheduled to be approved by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality December 9th, on a collision course with the federal agency.
Although EPA gives state governments authorization to write smog plans for their own metropolitan areas, it still has final approval based on criteria listed in the Clean Air Act. EPA disapproval of the State's DFW plan would trigger the possibility of a federal takeover of the air planning process.
That would be fine with local air quality activists, who've been pushing for the EPA to take over the job of writing a new clean air plan for North Texas since the State unveiled its first draft last year. They say TCEQ's official position that smog isn't harming public health means the Commission can't be trusted to write an effective anti-smog plan. When the state announced a plan imposing no new controls on any sources of air pollution despite DFW being in continual violation of the Clean Air Act for the last quarter century, they feel they were proven right.
"It's as if the state is too embarrassed to do what EPA is asking for fear of finding facts that don't match its ideology," said Jim Schermbeck, Director of the local clean air group, Downwinders at Risk.
He noted among the most important missing items in the State’s final plan published November 20th was a "Reasonably Available Control Technology"(RACT) study for the Midlothian cement plants, as well as answers to the impact of controls on other sources like the East Texas coal plants and oil and gas facilities that EPA posed in its eleven pages of official comments on the first draft last February. Application of modern pollution controls to all major sources of air pollution in a smog-plagued region is a key component of the Clean Air Act.
In official comments last February, EPA specifically requested the state perform a new study of what kind of smog controls should be required of the three Midlothian cement plants immediately south of DFW. EPA warned lack of such a study would mean the plan would be disapproved:
"Failure to conduct a thorough RACT analysis for cement kilns which would include appropriate emission limits would prevent us from approving the RACT portion of the attainment plan submittal.”
By turning-in the same version of the technology review originally criticized by EPA, without any new additional analysis, the TCEQ began a bureaucratic game of "Chicken," daring the EPA to deny approval.
"If you're EPA, I don't see how you take this any other way than a big raised middle finger from Austin," said Schermbeck. "The question is: What's EPA gonna do about it now?"
Also missing in the final state version are any responses to other EPA's concerns and questions about the plan's chances of actually lowering smog levels and the possibilities of reducing smog with new controls on other sources, such as,
“How would a reduction in NOx emissions from utility electric generators in the counties closest to the eastern and southern boundaries of the DFW area impact the DFW area?”
EPA was already openly skeptical about the chances of the state’s plan succeeding without requiring any additional cuts in pollution. Stating “it would be difficult to see” how the plan meets its required 2017 deadline, the Agency concluded “we believe it is likely that additional reductions will need to be included to demonstrate attainment.”
TCEQ’s resubmitted plan doesn’t have any additional reductions. Failure of a state plan to show how it can reach the smog standard by 2017 would be cause for EPA to assume the job itself.
Evidence suggests the state is purposely overlooking the air quality benefits of controls on large industrial sources of air pollution affecting DFW.
In late October, Downwinders at Risk released a new study of its own. It paid for University of North Texas engineers to build a clone of the State’s DFW air computer model and run a series of control scenarios the state hasn’t performed in almost a decade. Using the TCEQ’s own numbers it showed new controls on the cement kilns, coal plants, and gas compressors in the Barnett Shale would lower smog levels enough to meet the current federal smog standard. DFW hasn’t met a federal standard for smog since once was created in 1991.
Dismissing the results as “limited,” TCEQ officials nevertheless agreed with them – since they were based on their own model. The State argues those new controls are not yet technically or economically feasible – despite their being commonplace around the world, in the US, and even in Texas.
This question is one of the keys to the standoff with EPA: are the proposed new controls for industry “Reasonably Available” or not? If they are, they must be included in the air plan. If not, they remain off the table. EPA makes the first call on a definition, and any aggrieved party can sue to expand or contract it.
Because it’s a national hot spot for smog, DFW is only one of a handful of US metro areas that even had to submit a clean air plan this last cycle. EPA computer modeling predicts the area will still be in violation of the Clean Air Act in 2015 unless significant reductions in pollution are made.
This summer saw the North Texas regional smog average rise twice in one hot August week, retreating from gains made during last year’s cooler, wetter summer. DFW once again has higher annual smog levels than Houston. Both cities remain well above the current standard.
According to the American Lung Association, the 10 county DFW “non-attainment” area for smog includes approximately 150,000 asthmatic children, 350,000 adults with asthma, and over 600,000 adults with cardiovascular disease or COPD – all of whom are at risk from the region’s bad air.
“The lungs and lives of seven million residents are being held hostage by a state government that doesn’t think smog is a problem and isn’t willing to require new pollution controls to reduce it, “ Schermbeck pleaded
“Expecting the State of Texas to enforce Environmental laws in 2015 is like expecting the State of Mississippi to enforce Civil Rights laws in 1965. Our only hope is federal intervention.”
EPA will Be Issuing Power Plant Permits in Texas Despite Greg Abbott’s Campaign for Governor
 There was never really any question, but just in case you were wondering, EPA will indeed be taking over the permitting of power plants in Texas based on new greenhouse gas emission rules.
There was never really any question, but just in case you were wondering, EPA will indeed be taking over the permitting of power plants in Texas based on new greenhouse gas emission rules.
The U.S. Court of Appeals slapped down Texas Attorney General Greg Abbott's recent challenge to the Environmental Protection Agency on Friday, one trying to keep the EPA from considering such emissions when they permit new facilities or approve large modifications on old ones.
