Posts Tagged ‘Dallas air quality’
New Comments from EPA on DFW Air Plan: It Won’t Work
 This plan won't work.
This plan won't work.
That's the simple message from the three pages of new comments Region 6 EPA staff submitted to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality last month concerning its anti-smog plan for DFW.
That message begins with the cover letter, written by Mary Stanton, Chief of the State Implementation Plan Section for Region 6. "… additional local and regional ozone precursor emission reductions will be necessary to reach attainment by 2017."
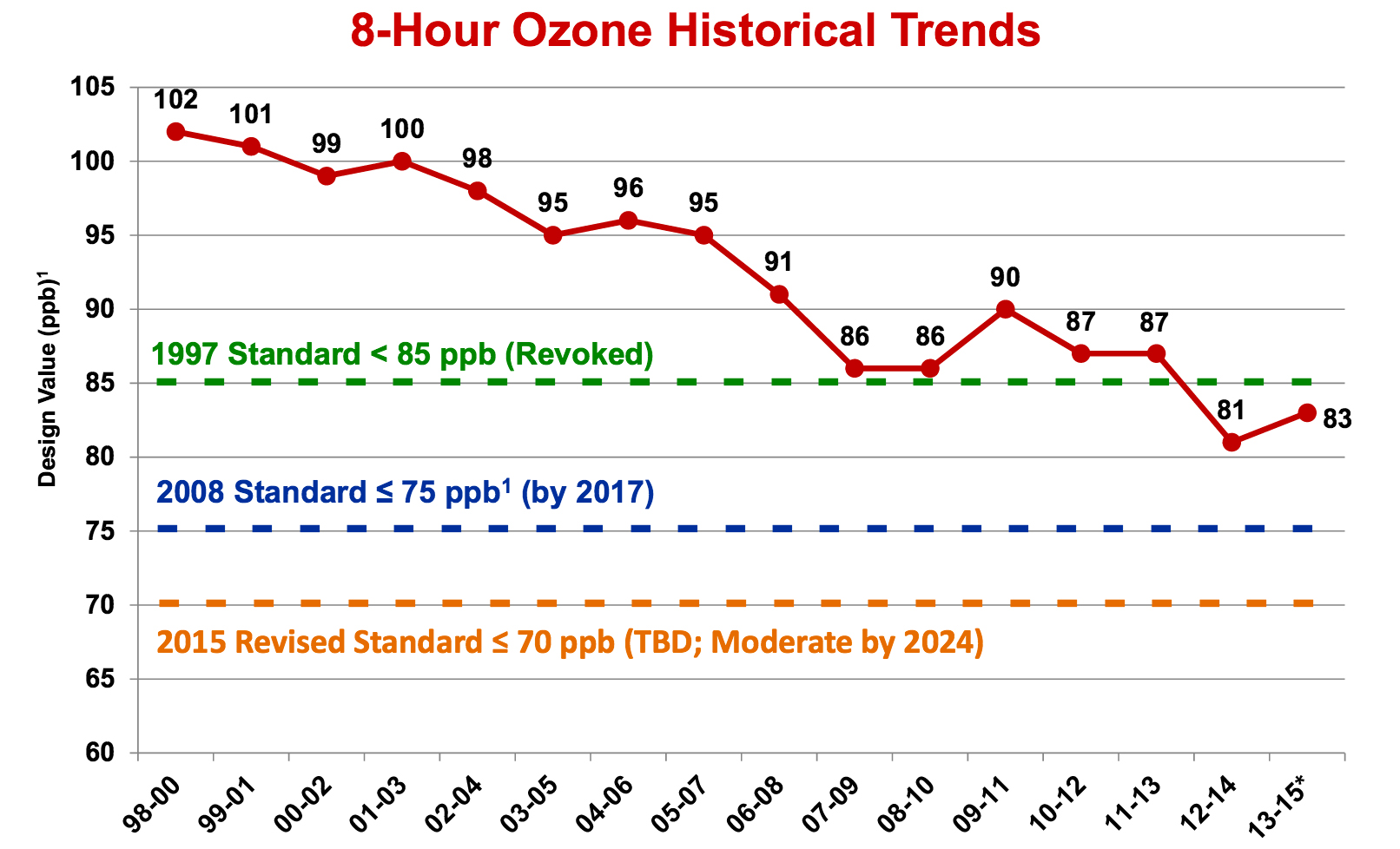
How much in reductions? EPA estimates an additional 100-200 tons per day more in cuts of smog-forming pollution will be necessary to achieve compliance with the current 75 parts per billion ozone standard. "Without emission reductions on this scale, it is unlikely that the area will attain by the attainment date.”
To give you some idea of how large a number that is, TCEQ calculates that all gas and oil air pollution in DFW equals 78 tons per day, the Midlothian cement plants belch out over 18 tons per day, and all the power plants in the immediate DFW area, 21 tons per day. Totaled, those three sources add up to 117 tons of pollution a year.
All the cars and trucks on DFW roads are said to add up to 180 tons per day of pollution.
So the decrease in pollution EPA is saying is necessary to get down to the current ozone standard is huge.

But take a look at those obsolete East Texas coal plants outside the boundaries the DFW nonattainment area. TCEQ says they account for a total of 146 tons per day. Add Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) which can get you up to 90% reductions in coal plant emissions, or close them down completely, add decreases from new controls on the cement kilns and oil and gas sources, and you're well on your way to amassing 200 tons a day of cuts in pollution.
Which do you think is more attractive to most DFW residents: permanently parking their cars, or putting new controls on the coal plants? Even though the coal plants harm the whole DFW airshed more than any other major source, they're not held accountable to the same regulatory requirements as sources closer to the center of the urban core, but which have less impact. Our cars must have special gasoline formulas in summer, we have to have HOV lanes, and we still go through Ozone Action Days, but the coal plants party like it's 1979. TCEQ is taking a hands-off approach to the plants and as a result the DFW region will continue to be in violation of the smog standard or huge cuts from other sources will be necessary.
TCEQ could have added new controls to the coal plants to the plan, but it chose not to. In fact, there are no new controls in the state's plan on any major sources of air pollution affecting DFW. EPA's new comments go to the heart of that choice. "Without additional emission reduction measures, we don’t see how the area will meet the standard of 75 ppb by the end of the 2017 ozone season," writes EPA staff.
EPA goes on to say TCEQ's computer modeling supporting it's do-nothing plan is "unrealistic," severely underestimating future smog levels, and delivering projections of decreases "that seem unlikely to be reached."
 With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
That's the pattern TCEQ has already established with its "screw you" response to the EPA's comments about the part of the plan dealing with "Reasonably Available Control Technology," or RACT, last February. This second part decides what new controls should be required of major sources of air pollution within the 10-County DFW "non-attainment" area – like the Midlothian cement plants and the thousands of oil and gas facilities checkerboarding the western half of the Metromess.
TCEQ says nothing new is required. EPA disagrees. EPA told TCEQ last year it had to do a new RACT review and lower the kiln's emission limits to account for a new generation of technology or it would have to reject the state's plan. TCEQ ignored the request, daring the EPA to disapprove. EPA seems more than willing to take them up on the offer.
And so while you're waiting for the state's computer modeling and suspect math to be rejected by EPA in July, you can probably expect to see EPA officially rejecting the RACT part of the state's plan sooner – maybe as soon as the next 60-90 days.
Despite the TCEQ going out of its way to submit an unacceptable plan to EPA, if the Agency pulls the trigger and begins a federal takeover of the DFW air plan, the Commission and the whole of Texas State Government will cry bloody murder about the usurpation of the state's authority and once again proclaim how "out of control" the EPA is on their way to filing suit.
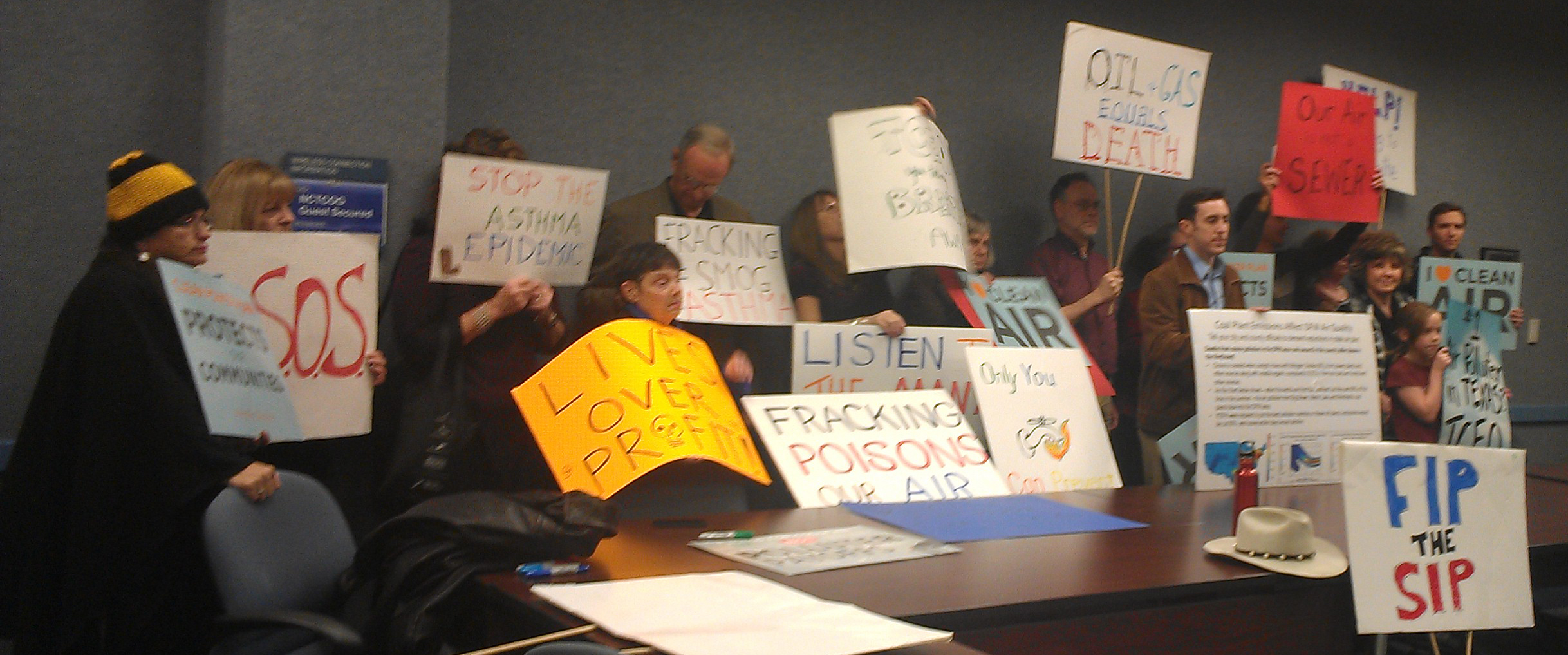 This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
And as always, it's why you, and people you know should:
Citizens To Form Posse, Demand State Enforce the Clean Air Act at Thursday Hearing on New DFW Air Plan
 (Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
(Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
“We’re asking residents to come out and get sworn into a citizens posse to help us make the state follow the Clean Air Act,” said Jim Schermbeck, Director of the local clean air group Downwinders at risk, one of the leading opponents of he new plan. “Austin is going to ridiculous, Monty Python-like lengths to avoid new controls on the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and local gas facilities in this new plan – even though those controls are now commonplace in each industry.”
Thursday’s public hearing centers on a new plan to comply with the federal ozone standard of 75 parts per billion (ppb) by 2018. DFW has never achieved such a low level of smog, and only this last year dipped below the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the first time with the help of cooler, wetter summer.
EPA says a state plan like the one the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is proposing for DFW must include “all Reasonable Available Control Technologies,” and “all Reasonable Available Control Measures” to get lower smog levels as “expeditiously as possible.” EPA defines these as technologies as ones that are “technically and economically feasible.” But according to Schermbeck, the state of Texas is deliberately ruling out local use of pollution controls already adopted by industry that could speed cleaner air.
He cited three examples. Selective Catalytic Reduction, or SCR acts much like the catalyst on cars, only on a much larger scale for industrial plants. It’s already in use on at least half a dozen European cement plants where it’s reduced smog-forming pollution by up to 90%, and on many coal-fired power plants across the world and in the US, where it achieves the same results. Yet the TCEQ DFW air plan doesn’t require SCR on the largest single sources of smog pollution in the region, the Midlothian cement plants, or the East Texas coal plants that are known to impact DFW air quality, saying the technology isn’t “feasible.” TCEQ maintains this stance even though the Holcim cement plant in Midlothian has announced plans to include an SCR unit on one of its own kilns.
“Here’s a pollution control technology already in operation and achieving great results, with a cement plant in North Texas already adopting it, but the state’s position is that it isn’t ‘feasible’. It’d be comical if it wasn’t delaying cleaner air for over 6 million people that haven’t had it in decades.”
Besides ignoring SCR on cement and coal plants, Schermbeck said the TCEQ has also ruled-out electrification of large gas compressors as “infeasible” – despite the widespread use of electric compressors In the Barnett Shale already and the requirement of municipalities like Dallas and Southlake to allow nothing but electric compressors within their city limits. According to a 2012 study by the Houston Advance Research Consortium, compressors could increase downwind ozone levels as much as 3 to 10 parts per billion. There are at least 647 large compressors in the DFW “non-attainment area” covered by the TCEQ air plan.
“Requiring just these three technologies that are already on the market and being used in their respective industries could reduce air pollution by thousands of tons a year and help us achieve compliance with the new federal ozone standard much quicker,“ said Schermbeck. He said they all pass the test of being feasible according to EPA definitions. “By law, they should be required.”
Instead, the state is relying exclusively on a new federal gasoline mix being introduced in 2017 to achieve the required 75 ppb standard by 2018. Although it’s expected to help lower ozone levels across the country, it won’t get DFW down to the level of 75 ppb alone. To make the plan work on paper, the state has had to estimate oil and gas pollution downward in a way Schermbeck and others claim is unrealistic.
“Basically, the state’s approach is to do absolutely nothing for the next three years and hope the federal gasoline change brings it “close enough” to the lower standard. But hope is not a plan.”
Schermbeck said his group would be passing out badges to members of their clean air posse and recruiting residents to persuade the EPA to reject the state’s proposal. The federal agency has the final say. But there’s also always court – where many clean air rules for the state of Texas have been decided over the last 20 years. “If government won’t enforce the law, we may have to do it ourselves.”
