Archive for November 2012
TCEQ Can’t Handle the Truth Over DFW Air Plan Failure
 Here's further proof that Governor Perry has transformed the world's second-largest environmental agency into just another extension of his on-going political campaign.
Here's further proof that Governor Perry has transformed the world's second-largest environmental agency into just another extension of his on-going political campaign.
After waiting for a couple of days for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to say something about the failure of its latest DFW clean air plan to reach a 1997 ozone standard by the end of this "ozone season," Downwinders put out a release on Monday criticizing the agency for leaving the air dirtier than when the plan was begun in 2010.
To succeed, the TCEQ plan had to bring smog numbers down at all DFW monitors to 84 parts per billion or below by the end of this last summer, using three-year rolling averages incorporating readings from 2011 and 2010. The agency blithely predicted it would do just that and even published computer-modeled estimates of what the averages would be at the end of 2012. According to TCEQ we were supposed to see record low ozone levels this summer. So low that there would be no violations of the 1997 ozone standard for the first time since it was implemented.
Although the official EPA regulatory deadline to judge the plan a success or failure is June 15th, 2013, it's fate has already been decided by the data collected the three previous summers. That's important to know. TCEQ doesn't get another summer to prove that it's brilliant plan to sit back and watch people buy cars will work somehow, someway. The Clean Air Act only allows them three years to get their act together per plan. The clock started ticking in 2010. It stopped ticking on November 1, 2012, at the traditional end of DFW's ozone season. That was the practical deadline. All that's left to do is type up the report to EPA and submit it come June 15th of next year. They've run of of time.
But unless you've gone through this process before, or had been following the plan closely, you wouldn't necessarily know this. That was the case with Andrew McLemore, a reporter for the Fort Worth Weekly, who'd been assigned to follow up on the Downwinders release and e-mail the TCEQ for a response.
 What TCEQ spokesperson Lisa Wheeler said to McLemore was that of course the agency never claimed to be able to meet the goal by 2012. We said we'd do it by June of 2013 – the regulatory deadline. Ohhhhh.
What TCEQ spokesperson Lisa Wheeler said to McLemore was that of course the agency never claimed to be able to meet the goal by 2012. We said we'd do it by June of 2013 – the regulatory deadline. Ohhhhh.
This is a great answer for a term paper that's late, but not so much when there's no more summers between now and June of next year to use in your clean air plan. Ozone data for November to June isn't going to do you any good because (unless global warming really accelerates) that's not the time of year we see high ozone numbers. And the plan has to use the highest of the high numbers. Telling McLemore that everyone had to wait until June to know the final results of the DFW air plan was like telling him to wait for the cake to cool for eight months after its' already been taken out of the oven. The thing is done. It's not getting any bigger, or sweeter-tasting, or rounder. It's not changing character or content. It is what it is right now.
TCEQ knows this. Lisa Wheeler knows that there will be no new numbers to add or subtract from that will make any difference. There will be no 2013 average that they can use to change the results from what they are at this moment. It's all already been determined by this summer's miserable showing, and the miserable showing before that in 2011. That's what makes this answer of theirs so incredibly cynical.
Wheeler apparently wanted to confuse McLemore, in essence saying, "Gee we really didn't fail yet – you have to wait until next June to conclude that. We still have time to change the outcome! " But because the data won't change, the results won't change either.
Don't take our word for it. TCEQ has a whole web page devoted to chronicling the proof that the DFW air plan has already failed – http://www.tceq.state.tx.us/cgi-bin/compliance/monops/8hr_attainment.pl
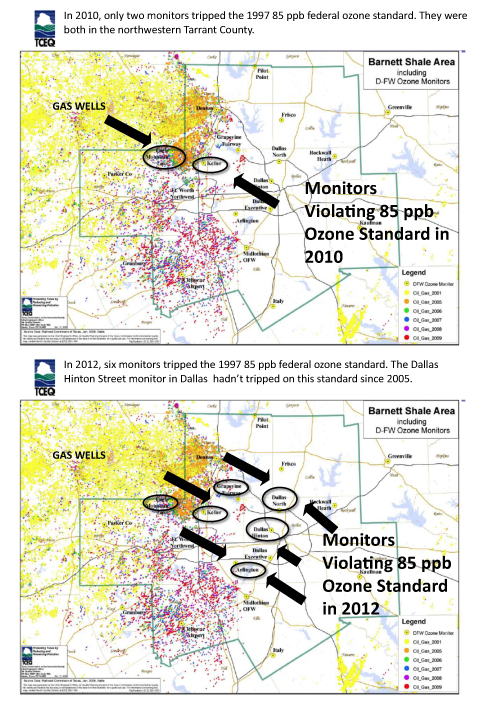
You'll notice this page, titled "Compliance with Eight-Hour Ozone Standard" has only three columns of data, one for 2010, one for 2011, and one for 2012. No column for 2013. You'll also notice that at the end of that three year cycle, there are two sites with running average that are at or above 85 ppb. The results are in. TCEQ's second clean air plan for DFW to reach the old 1997 standard in the last four years has failed. TCEQ just can't man-up and say so.
Not only has it failed. It's actually left DFW air dirtier than when it began. Here's why:
– Two monitors now have a three year running average (design value) of 85ppb or more. This is the same number as 2010, so no change at all on that front.
– The three year average for the region's highest reading actually went up 1 ppb from 2010 (86 ppb), to 2012 (87 ppb), with a spike of 90 ppb last year. Worse than 2010.
– Six monitors saw a violation of the 85 standard this summer by posting a 4th highest reading that was 85 ppb or above. Only one monitor did that in 2010. 2012 is five times worse than 2010 by this measuring stick.
– The location of those violating monitors is of concern because they moved further east from the northwestern corner of Tarrant County where they'd been "contained" – all the way into central Dallas, where the "Hinton St. monitor" near Mockingbird and I-35 recorded a 4th highest reading of 85 ppb or above for the first time since 2005. Also proof things have gotten worse, not better.
So the latest TCEQ DFW clean air plan achieved the following: More numerous and geographically-dispersed violations, with an increase in average levels of air pollution that takes it further away from the 84 it needs to achieve, instead of bringing it closer.
Heckava job.
To fully appreciate the agency's mendacity in its public approach to this failure, all you have to do is ask yourself how TCEQ would have reacted had it somehow achieved the miraculous decrease in air pollution its clean air plan promised. Go look at the front page of the TCEQ website. It has almost as many diatribes against the EPA as it does real environmental policy news, including opinion pieces written by TCEQ Commissioners. Do you think the agency would have waited until June 15th, 2013 to trumpet its success just because of a meaningless, bureaucratic deadline? Neither do we.
The TCEQ is never going to be a trustworthy source of information or expertise in the fight against DFW smog again while Governor Perry is in office. The sooner local officials wise-up and chart their own path, the better.
What Texas House Speaker Joe Straus Really Thinks of “Smokey Joe” Barton
 Texas Monthly's Paul Burka has written about some e-mails that went flying back and forth among Texas Republican lawmakers as the bitter re-districting battle took place over the last 12-15 months. Some of them have become public. One of these reveals what Texas House of Representatives Speaker Joe Straus thinks about Midlothan-area Congressman "Smokey" Joe Barton and his supporters in their attempts to gerrymander a new, more Republican district for the Congressman (since Arlington is getting a bit too purple for his taste). Welcome to the reality based community Speaker.
Texas Monthly's Paul Burka has written about some e-mails that went flying back and forth among Texas Republican lawmakers as the bitter re-districting battle took place over the last 12-15 months. Some of them have become public. One of these reveals what Texas House of Representatives Speaker Joe Straus thinks about Midlothan-area Congressman "Smokey" Joe Barton and his supporters in their attempts to gerrymander a new, more Republican district for the Congressman (since Arlington is getting a bit too purple for his taste). Welcome to the reality based community Speaker.
2nd TCEQ Clean Air Plan in Four Years Fails, Leaves Air Dirtier
 For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
November 1st marked the official end of the eight-month 2012 ozone season. According to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, or TCEQ, its plan was supposed to deliver record-breaking clean air to DFW this summer on its way to bringing the region into compliance with the Clean Air Act for the first time in two decades.
Does Pollution Discriminate?
 Yes. Or rather the forces that shape where pollution and people co-exist.
Yes. Or rather the forces that shape where pollution and people co-exist.
Historically we know that low-income and non-white urban areas are more likely to have polluting factories, Superfund Sites and illegal dumping. In large part, this is because the places within a city where "undesirable" heavy industries were allowed to locate were also traditionally also the only places where "undesirable" people, re: anybody that wasn't white or had a little money, were allowed to live. This is how you get massive segregated public housing complexes built across the street from huge lead smelters, as was the case in Dallas only a few decades ago. But maybe you thought that was all a thing of the past.
Today comes word of a new study out of Yale that confirms that people of color and the poor in the US suffer disproportionately from exposure to one of the most insidious kinds of pollutants – extremely tiny particles of poisonous soot called Particulate Matter 2.5 (that's soot that's 2.5 microns or less in size. A human hair is about 10 microns wide). Researchers looked at air monitoring and demographic data from five cities – Los Angeles, Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, St. Louis and Fresno. It is the first study to "reveal major racial and economic differences in exposures to specific particle ingredients, some of which are linked to asthma, cardiovascular problems and cancer." Not to mention strokes, and debilitating brain diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
"Tiny particles of air pollution contain more hazardous ingredients in non-white and low-income communities than in affluent white ones, new research shows. The greater the concentration of Hispanics, Asians, African Americans or poor residents in an area, the more likely that potentially dangerous compounds such as vanadium, nitrates and zinc are in the mix of fine particles they breathe. Hispanics had the highest exposures to the largest number of these ingredients, while whites generally had the lowest. The findings of the Yale University study add to evidence of a widening racial and economic gap when it comes to air pollution. Communities of color and those with low education and high poverty and unemployment face potentially greater health risks even if their air quality meets federal health standards."
So how does that affect DFW? We need to let studies like this inform our decisions about city planning. In places that have a lot of pollution problems, it's probably a good idea not to keep adding more. Think of where the fracking in Dallas will be taking place – mostly in minority neighborhoods, along the floodplain, with other "undesirable" industries like landfills near-by. Think about the struggle over community control of the CF Hawn freeway re-do of Deadman's Curve in South Dallas where residents want fewer cars going slower instead of more cars going faster. Cars are a big source of PM pollution. Freeways are large conduits for PM pollution. In the last five years there's been a slew of studies showing more asthma and illness the closer you live to a major freeway. Guess which sub-populations get more freeways in their part of town?
There is an environmental equivalent of Affirmative Action that needs to be incorporated into city zoning and planning. One that considers the past historical inequities and current environmental body burden of affected neighborhoods. One that makes sure that society's "undesirables" do not keep getting piled on top of one another
