Posts Tagged ‘Lead’
Was Lead Contamination the Major Cause of 20th Century American Crime?
 That's the hypothesis that Kevin Drum makes in the latest issue of Mother Jones, and he has a lot of evidence to back it up.
That's the hypothesis that Kevin Drum makes in the latest issue of Mother Jones, and he has a lot of evidence to back it up.
For years, scientists have known about the link between lead exposure in children and decreasing IQ levels. More recently, researchers have discovered more subtle effects in terms of anti-social behavior and AHHD diagnosis. Now, modern toxicology is to the point where most leading researchers say there is no level of lead a child can be exposed to that doesn't have the potential to effect his or her personality.
What if you were to use what we know now about the effects of lead contamination on young minds and playback the last 70 years of American history?
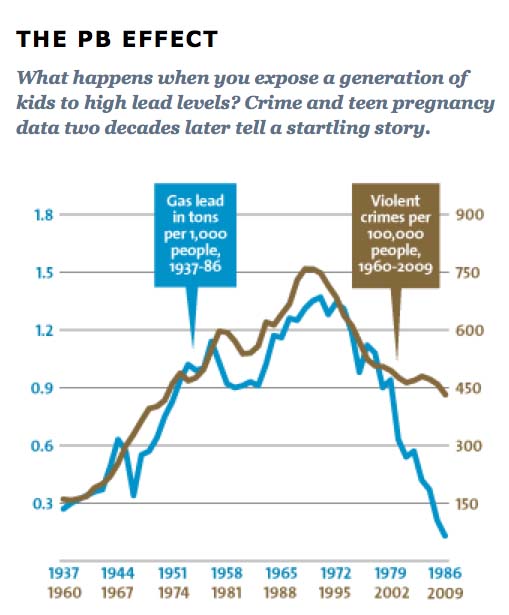
The biggest source of lead in the postwar era, it turns out, wasn't paint. It was leaded gasoline. And if you chart the rise and fall of atmospheric lead caused by the rise and fall of leaded gasoline consumption, you get a pretty simple upside-down U: Lead emissions from tailpipes rose steadily from the early '40s through the early '70s, nearly quadrupling over that period. Then, as unleaded gasoline began to replace leaded gasoline, emissions plummeted.
Gasoline lead may explain as much as 90 percent of the rise and fall of violent crime over the past half century.Intriguingly, violent crime rates followed the same upside-down U pattern. The only thing different was the time period: Crime rates rose dramatically in the '60s through the '80s, and then began dropping steadily starting in the early '90s. The two curves looked eerily identical, but were offset by about 20 years.
So Nevin dove in further, digging up detailed data on lead emissions and crime rates to see if the similarity of the curves was as good as it seemed. It turned out to be even better: In a 2000 paper (PDF) he concluded that if you add a lag time of 23 years, lead emissions from automobiles explain 90 percent of the variation in violent crime in America. Toddlers who ingested high levels of lead in the '40s and '50s really were more likely to become violent criminals in the '60s, '70s, and '80s.
Dr. Howard Mielke of Tulane, who's analyzed the blood lead data collected from Frisco and found the samples higher than the state average, makes an appearance in Drum's article because of a large new study overlaying neighborhood lead exposure to neighborhood crime in six American cities. They match up precisely.
Read the short version of the article here. Here's an interview with Dr. Mielke.
No one knew a lead additive in gasoline would produce such an impact. Because we didn't do the toxicology. Lead was introduced in gasoline in the 1920's when the modern industrial age was just hitting its stride. Now there are some 80,000 chemicals in the marketplace, only a handful of which have been tested thoroughly, including lead, because we're still not doing the toxicology BEFORE the chemical is used in widespread commerce.
Cancer. Birth Defects. Endocrine Disruptors. Why is it so inconceivable to some that the thousands of untested chemicals coursing through the veins of our economy can't have unintended consequences just like leaded gasoline, on their own or in combination with each other? What new epidemics are we instigating even now?
Good Friday: Exide Smelter Closing Today
 Sometimes, all it takes is the slightest push of an index finger, or a focused exhaling of breath.
Sometimes, all it takes is the slightest push of an index finger, or a focused exhaling of breath.
Sometimes the house of cards is so precarious, so unstable, that any challenge, no matter how slight, can send the established structure to the ground.
A year ago a small, newly-formed citizens group that had just staged its first action was struggling to convince the City of Frisco to quit supporting co-existence with an outlaw lead smelter and instead kick it out of town.
Today, that smelter will stop operating.
Community activism rarely pays off as quickly or as spectacularly as it has with the curious case of the Exide lead smelter. But when it does, it's reason to pause and give thanks and remind ourselves that such things are still possible.
Because truth be told, this historic effort was directed by a group of Frisco residents that was never larger than 10 people strong. Please just think about that. Less than a dozen people challenging their local status quo are responsible for this huge victory for public health.
Downwinders' often tells its supporters that, like the Woody Allen quote about life, 90% of social change is about just showing up. The system so often goes completely unchallenged, that you'd often be surprised what happens when you just show up and start asking embarrassing questions. When you start poking at the house of cards.
As their campaign proceeded, this small group of committed people attracted the support of hundreds, and then thousands of their fellow residents. They forced the city to see the contradiction between the continued operation of a circa-1960's smelter and the reality of 2012 Frisco. They held up a mirror and re-framed the relationship between smelter and town. And the contradiction was so great, so at odds with the new perception of Frisco, that the established political support the smelter had enjoyed in town for decades dried up. Young couples with kids concerned about a lead smelter they never heard of before outnumbered Good Ol Boys in City Hall and the Chamber of Commerce. The old establishment was undone by the very demographics of change they'd unleashed a decade or so earlier.
There is still much work to do. A half-century of contamination blankets the smelter site, as well as an undetermined number of off-site "hotspots." Exide wants to leave a permanent landfill behind in the middle of Central Frisco, while the City is breezing along with plans to turn a piece of land right across the street from the smelter site into the city's largest park. Downwinders will be helping citizens monitor the cleaning-up of the smelter site for at least the next two years.
But as of today there is no more lead pollution coming out of the Exide smokestacks. No more daily fallout of poison. No more new layers of lead being laid down in the topsoil of Frisco. That is a pretty remarkable thing considering where we were 365 days ago.
So raise your glasses tonight to the hardy folks of Frisco Unleaded and the improbability of the impossible happening in record time. Here's to Colette McCadden, Henrik Ax, Shiby Matthew, Matt Vonderahe, Jeannette Sandin, Meghan Green, and Eileen Canavan, all residents who decided they would stick their neck out and start showing up and asking questions, much to the consternation of the Powers That Be. May they all have Frisco parks, and schools, and streets named after them.
It's not always this easy, but the fact that it was this time should give us hope about the power of pushing back.
