Posts Tagged ‘Texas’
State Re-Submits Illegal DFW Smog Plan, Dares EPA to Reject It

(Dallas)– In an unprecedented rebuke to the Environmental Protection Agency, Texas has refused to provide critical data EPA says it needs to approve the state’s controversial anti-smog plan for DFW, which requires no new pollution controls despite more than two decades of chronic bad air.
Texas' refusal to cooperate with EPA puts its plan, scheduled to be approved by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality December 9th, on a collision course with the federal agency.
Although EPA gives state governments authorization to write smog plans for their own metropolitan areas, it still has final approval based on criteria listed in the Clean Air Act. EPA disapproval of the State's DFW plan would trigger the possibility of a federal takeover of the air planning process.
That would be fine with local air quality activists, who've been pushing for the EPA to take over the job of writing a new clean air plan for North Texas since the State unveiled its first draft last year. They say TCEQ's official position that smog isn't harming public health means the Commission can't be trusted to write an effective anti-smog plan. When the state announced a plan imposing no new controls on any sources of air pollution despite DFW being in continual violation of the Clean Air Act for the last quarter century, they feel they were proven right.
"It's as if the state is too embarrassed to do what EPA is asking for fear of finding facts that don't match its ideology," said Jim Schermbeck, Director of the local clean air group, Downwinders at Risk.
He noted among the most important missing items in the State’s final plan published November 20th was a "Reasonably Available Control Technology"(RACT) study for the Midlothian cement plants, as well as answers to the impact of controls on other sources like the East Texas coal plants and oil and gas facilities that EPA posed in its eleven pages of official comments on the first draft last February. Application of modern pollution controls to all major sources of air pollution in a smog-plagued region is a key component of the Clean Air Act.
In official comments last February, EPA specifically requested the state perform a new study of what kind of smog controls should be required of the three Midlothian cement plants immediately south of DFW. EPA warned lack of such a study would mean the plan would be disapproved:
"Failure to conduct a thorough RACT analysis for cement kilns which would include appropriate emission limits would prevent us from approving the RACT portion of the attainment plan submittal.”
By turning-in the same version of the technology review originally criticized by EPA, without any new additional analysis, the TCEQ began a bureaucratic game of "Chicken," daring the EPA to deny approval.
"If you're EPA, I don't see how you take this any other way than a big raised middle finger from Austin," said Schermbeck. "The question is: What's EPA gonna do about it now?"
Also missing in the final state version are any responses to other EPA's concerns and questions about the plan's chances of actually lowering smog levels and the possibilities of reducing smog with new controls on other sources, such as,
“How would a reduction in NOx emissions from utility electric generators in the counties closest to the eastern and southern boundaries of the DFW area impact the DFW area?”
EPA was already openly skeptical about the chances of the state’s plan succeeding without requiring any additional cuts in pollution. Stating “it would be difficult to see” how the plan meets its required 2017 deadline, the Agency concluded “we believe it is likely that additional reductions will need to be included to demonstrate attainment.”
TCEQ’s resubmitted plan doesn’t have any additional reductions. Failure of a state plan to show how it can reach the smog standard by 2017 would be cause for EPA to assume the job itself.
Evidence suggests the state is purposely overlooking the air quality benefits of controls on large industrial sources of air pollution affecting DFW.
In late October, Downwinders at Risk released a new study of its own. It paid for University of North Texas engineers to build a clone of the State’s DFW air computer model and run a series of control scenarios the state hasn’t performed in almost a decade. Using the TCEQ’s own numbers it showed new controls on the cement kilns, coal plants, and gas compressors in the Barnett Shale would lower smog levels enough to meet the current federal smog standard. DFW hasn’t met a federal standard for smog since once was created in 1991.
Dismissing the results as “limited,” TCEQ officials nevertheless agreed with them – since they were based on their own model. The State argues those new controls are not yet technically or economically feasible – despite their being commonplace around the world, in the US, and even in Texas.
This question is one of the keys to the standoff with EPA: are the proposed new controls for industry “Reasonably Available” or not? If they are, they must be included in the air plan. If not, they remain off the table. EPA makes the first call on a definition, and any aggrieved party can sue to expand or contract it.
Because it’s a national hot spot for smog, DFW is only one of a handful of US metro areas that even had to submit a clean air plan this last cycle. EPA computer modeling predicts the area will still be in violation of the Clean Air Act in 2015 unless significant reductions in pollution are made.
This summer saw the North Texas regional smog average rise twice in one hot August week, retreating from gains made during last year’s cooler, wetter summer. DFW once again has higher annual smog levels than Houston. Both cities remain well above the current standard.
According to the American Lung Association, the 10 county DFW “non-attainment” area for smog includes approximately 150,000 asthmatic children, 350,000 adults with asthma, and over 600,000 adults with cardiovascular disease or COPD – all of whom are at risk from the region’s bad air.
“The lungs and lives of seven million residents are being held hostage by a state government that doesn’t think smog is a problem and isn’t willing to require new pollution controls to reduce it, “ Schermbeck pleaded
“Expecting the State of Texas to enforce Environmental laws in 2015 is like expecting the State of Mississippi to enforce Civil Rights laws in 1965. Our only hope is federal intervention.”
A Barnett Shale Manifesto…From Austin
 Sometimes it takes a perspective above the grind of trench warfare to give you a better sense of what the entire battlefield looks like. That's what UT Law Professor Rachel Rawlins has done for Barnett Shale activists with the recent publication of her article "Planning for Fracking on the Barnett Shale: Urban Air Pollution, Improving Health Based Regulation, and the Role of Local Governments" in the new Virginia Environmental Law Review.
Sometimes it takes a perspective above the grind of trench warfare to give you a better sense of what the entire battlefield looks like. That's what UT Law Professor Rachel Rawlins has done for Barnett Shale activists with the recent publication of her article "Planning for Fracking on the Barnett Shale: Urban Air Pollution, Improving Health Based Regulation, and the Role of Local Governments" in the new Virginia Environmental Law Review.
Don't let the academic title fool you. This is a call for a radically new approach to how communities in Texas regulate the risks of fracking, and every other type of heavy industry. We put the link up for the piece on our Facebook page on Saturday based on a quick reading of its commentary on the Flower Mound cancer cluster, but it's more, so much more than that. Among other things, it's a comprehensive rebuttal of every claim of safety and well-being ever issued by the industry or state authorities about the health of residents living in the Barnett Shale, of which the Flower Mound case is only one example. Rawlins has produced a one-stop catalog of each major air pollution health controversy in the Barnett since concerns began to grow in the last decade, with an almost 30-page review of why no industry or government-sponsored study of fracking pollution and its health effects is a satisfactory response to those concerns. Want to convince your local officials that fracking isn't as safe as it's touted? Here's the staggering blow-by-blow commentary to do it.
But all of that documentation is presented in service to making the point that current state and federal regulation of fracking is failing to protect public health, both in design and in practice. Professor Rawlins' solution to this problem is not to give the state and federal government more power to regulate the gas industry. No, it's to turn the current regulatory framework upside down and give more power to local governments to do the things that the state and federal government should be doing.
In making this recommendation, she echoes the strategy that's been driving Downwinders since it was founded – that the best way to regulate pollution problems is at the local level where the most harm is being done, and it should be directed by the people being harmed. This is what drove our Green Cement campaign that closed the last obsolete wet cement kiln in Texas. This is what fueled our campaign to close down the trailer park-come-lead smelter in Frisco. And it's what was behind the recent Dallas fights over drilling. In each case, it wasn't Austin or Washington DC that was the instrument of change – it was local governments, pressed by their constituents, flexing their regulatory powers. The same thing is driving activists in Denton who are organizing the ban fracking petition drive and vote.
This strategy avoids battles where industry is strongest – in the halls of the state capitol and in DC, where citizens are outspent millions to one. Instead, it takes the fight to neighborhoods where the harm is being done or proposed, where people have the most to lose, where the heat that can be applied to elected officials is more intense. Citizens will still get outspent, but the money doesn't seem to buy corporations as much influence among those actually breathing the fumes of the drilling site, or smokestack.
Particularly now, with corporate-friendly faux-Tea Party types in control of state government and the House of Representatives in DC, there is little room for grassroots campaigns to make a difference by passing new legislation. Even if by some miracle a few bills did pass, their enforcement would be up to the same state or federal agencies that are currently failing citizens. Local is more direct, and more accountable. Professor Rawlins agrees, and spends most of the rest of her 81-page journal article citing the ways in which local control of fracking in the Barnett Shale is hampered by the out-dated top-down approach to regulation, and what should be done to fix that.
Included in her recommendations are two long-term Downwinders projects: Allowing local governments to close the "off-sets" loophole for the gas industry that exempts them from having to compensate for their smog-forming pollution in already smoggy areas like DFW, and creating California-like local air pollution control districts that could set their own health based exposure standards and pollution control measures without having to go through Austin or DC.
If there's a single major fault in Rawlins's analysis, it's that she believes more local control of pollution risks is itself dependent on action by an unwilling state government. But Downwinders and others have shown that isn't true. Our most significant and far-reaching victories – from the closing of the Midlothian wet kilns to the new Dallas drilling ordinance – have all taken place while Rick Perry was Governor and the state legislature was in the hands of our opponents. We did these things despite Austin, not because we had its permission. Local zoning laws, local permitting rules, local nuisance acts, and other local powers are under-utilized by both residents and their elected officials when it comes to pollution hazards.
The same is true now of Downwinders' off-sets campaign aimed at the gas industry. We think we've found a way to avoid the "preemption" argument that would keep local governments from acting on smog pollution from gas sources by aiming the off-sets at Greenhouse gases – an area of regulation Texas is loathe to enter. By targeting GHG reduction, we also reduce a lot of toxic and smog-forming air pollution. It's a back door way, but it accomplishes the same goal. It's going to be up to Texas activists to sew similar small threads of change through an otherwise hostile political environment.
Even given that flaw, Professor Rawlins' introduction to her article is the most concise summary of the air pollution problems caused by gas mining and production in the Barnett, as well as the most credible call to action for a new way of doing business there. Here it is reprinted in full for your consideration:
In the last decade hydraulic fracturing for natural gas has exploded on the Barnett Shale in Texas. The region is now home to the most intensive hydraulic fracking and gas production activities ever undertaken in densely urbanized areas. Faced with minimal state and federal regulation, Texas cities are on the front line in the effort to figure out how best to balance industry, land use, and environmental concerns. Local governments in Texas, however, do not currently have the regulatory authority, capacity, or the information required to closet he regulatory gap. Using the community experience on the Barnett Shale as a case study, this article focuses on the legal and regulatory framework governing air emissions and proposes changes to the current regulatory structure.
Under both the state and federal programs, the regulation of hazardous air emissions from gas operations is based largely on questions of cost and available technology. There is no comprehensive cumulative risk assessment to consider the potential impact to public health in urban areas. Drilling operations are being conducted in residential areas. Residents living in close proximity to gas operations on the Barnett Shale have voiced serious concerns for their health, which have yet to be comprehensively evaluated. Given the complexityof the science, and the dearth of clear, transparent, and enforceable standards, inadequate studies and limited statistical analysis have been allowed to provide potentially false assurances. The politically expedient bottom line dominates with little attention paid to the quality of the science or the adequacy of the standards.
Determining and applying comprehensive health-based standards for hazardous air pollutants has been largely abandoned at the federal level given uncertainties in the science, difficulties of determining and
measuring “safe” levels of toxic pollutants, and the potential for economic disruption. Neither the state nor the federal government has set enforceable ambient standards for hazardous air pollutants.Identifying cumulative air pollution problems that may occur in urban areas, the State of California has called upon local governments to identify “hot spots” and to consider air quality issues in their planning and zoning actions. In Texas, however, preemption discussions dominate the analysis. Any local government regulation that might provide protection from toxic air emissions otherwise regulated by the State must be justified by some other public purpose.
Texas should consider authorizing and encouraging local level air quality planning for industrial activities, similar to what California has done. Care should be taken to separate these facilities from sensitive receptors and “hot spots” that may already be burdened with excessive hazardous air emissions. Given the difficulty of the task, there is also an important role for the state and federal governments in working to establish ambient standards for hazardous air pollutants, as well as standards for health based assessment and public communication. The uncertainty inherent in any of these standards should be made clear and accessible to local governments so that it may be considered in making appropriate and protective land use decisions. Texas should consider allowing local governments to have the power to establish ambient air quality standards, emissions limitations, monitoring, reporting, and offsets for hazardous air pollutants, following the model applied to conventional air pollutants pursuant to the federal program.
Professor Rawlins' article provides Barnett Shale activists with a new map to guide them toward more effective action. We'd all do well to study it and pick local battles that promise to contribute toward its realization.
Can You Spot the Mistake in This Map?
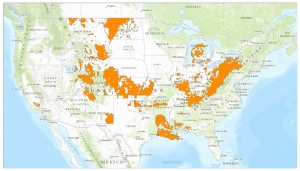 Here's why there's a missing big orange splotch….or two….or three, in Texas in this new national map of oil and gas well concentration.
Here's why there's a missing big orange splotch….or two….or three, in Texas in this new national map of oil and gas well concentration.
Sloshing Back and Forth Between Coal and Gas
 Around 2003 or so, the Dallas Morning News editorial board convened a roundtable of air pollution stakeholders and more or less facilitated a discussion of what could be done to clean up DFW's dirty air. You see, the area still hadn't complied with the 1997 national smog standard and more and more official air quality monitors were in violation of it. Pretty much, just like now.
Around 2003 or so, the Dallas Morning News editorial board convened a roundtable of air pollution stakeholders and more or less facilitated a discussion of what could be done to clean up DFW's dirty air. You see, the area still hadn't complied with the 1997 national smog standard and more and more official air quality monitors were in violation of it. Pretty much, just like now.
There was a memorable moment when one of the "environmentalists" at the table noted that for decades the Texas utility industry had been primarily reliant on natural gas for its power source, then switched almost entirely to coal during the 70's and 80's, exactly when the nation's first national air quality standards were being written and enforced. "Part of the problem is that there doesn't seem to have been any planning for the consequences of the industry switching over from one source to the other just like that. It's like a frenzied mob group of stockbrokers running back and forth between bidders."
"That's the marketplace," huffed a utility industry representative. And indeed it still is. One frenzied run after another back and forth between the two largest sources of fossil fuel.
You know the scene in Pirates of the Caribbean, At World's End where the crew runs back and forth, from each side of the ship, until it eventually turns upside down? It's like that, only with money doing the running. And it never ends.
That DMN discussion was only a decade ago. What happened next shows how quickly those runs can reverse themselves and the conventional wisdom. Fracking technology delivered new shale plays that flooded the market with new gas. So much new gas, that the price of it dropped to historic lows. That caused a huge switch in the utility industry. Gas was cheaper, so the coal-powered plants started to close and be replaced by gas-powered plants. At the same time the chemical industry, which uses voluminous amounts of gas in production of plastics and other products, announced a new wave of domestic construction because of cheaper gas supplies in the US. Finally, in order to prop-up the low gas prices that that are killing profits, the gas industry itself promoted the fuel for transportation use and export.
And students, what happens when all these elaborate plans to take advantage of cheap gas begin to blossom? Demand increases. Cheap gas turns into not-so-cheap gas. And then coal begins to look pretty good again. All of a sudden it's the negative image of 2003, and all that money is starting to run toward coal as gas prices rise.
And what that means is that the higher methane levels causing climate change are replaced by higher CO2 levels causing the same climate change. This is why we need to get out of the rut we're in where our choices are determined by short-term financial gain and not long-term survival.
Government puts its finger on the scales in the marketplace all the time to help this or that industry. Without government guarantees, whole sectors of the economy would not be able to function in a completely unfettered market. This is what the CO2 cap and trade system was designed to do – make the marketplace respond to pressures put there by government in order to achieve a goal of reducing the stuff that will make the place we live less habitable. But it was all a communist plot,or something like that. So in the meantime, we continue to slosh back and forth.
From the Houston Chronicle comes this summary of the latest trends:
After years of declining greenhouse gas emissions, Texas and other states reported sharply higher levels of carbon dioxide in 2012 as electric generating plants began to use more coal when natural gas prices began to rise, according to a study released Thursday.
Citing research done by the Environmental Integrity Project, Texas once again led the nation in CO2 from power plants in 2012, emitting 251 million tons. Florida was a distant second at 120 million tons. Just five states accounted for one-third of the nation's CO2 power plant emissions. Besides Texas and Florida, they include Pennsylvania, Indiana, and Ohio. Needless to say. the old TXU plants in East and Central Texas run by corporate off-spring Luminant are the largest contributors.
The price of gas will continue to go up and coal will be competitive. Or maybe it will go down and coal won't be attractive. Maybe we'll be downwind of lots more coal plant pollution. Or maybe we'll all have a rig or compressor station in our backyard. Who can say? That's the marketplace! The question is, do you want to bet our survival on it?
